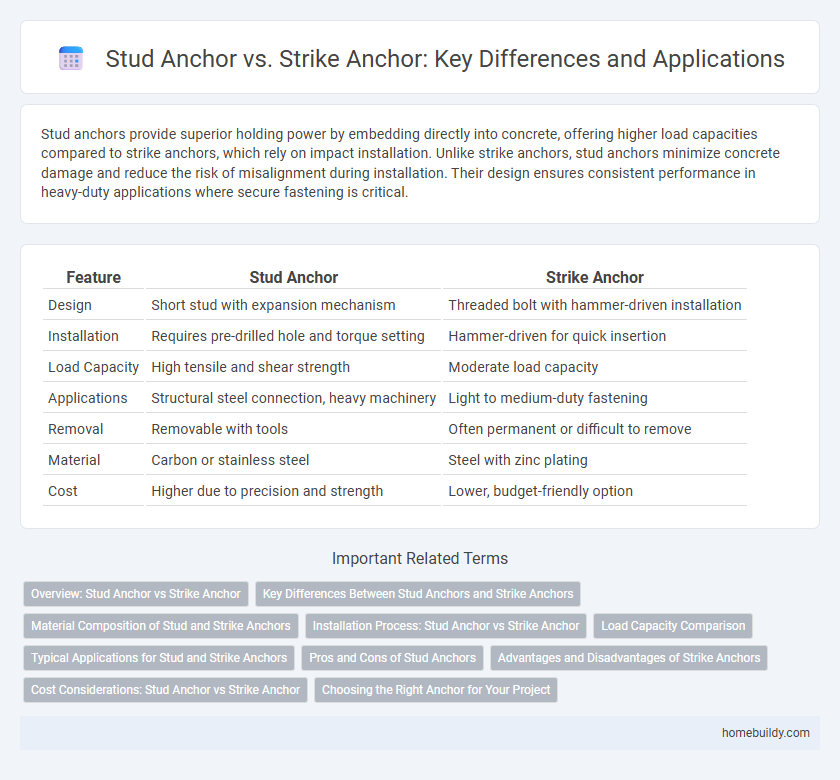
Stud anchors provide superior holding power by embedding directly into concrete, offering higher load capacities compared to strike anchors, which rely on impact installation. Unlike strike anchors, stud anchors minimize concrete damage and reduce the risk of misalignment during installation. Their design ensures consistent performance in heavy-duty applications where secure fastening is critical.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stud Anchor | Strike Anchor |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Short stud with expansion mechanism | Threaded bolt with hammer-driven installation |
| Installation | Requires pre-drilled hole and torque setting | Hammer-driven for quick insertion |
| Load Capacity | High tensile and shear strength | Moderate load capacity |
| Applications | Structural steel connection, heavy machinery | Light to medium-duty fastening |
| Removal | Removable with tools | Often permanent or difficult to remove |
| Material | Carbon or stainless steel | Steel with zinc plating |
| Cost | Higher due to precision and strength | Lower, budget-friendly option |
Overview: Stud Anchor vs Strike Anchor
Stud anchors provide superior holding power in concrete by expanding against the substrate upon installation, making them ideal for applications requiring high load capacity and durability. Strike anchors rely on impact-driven expansion, which can sometimes lead to less consistent engagement within the material, suitable for lighter or temporary fixtures. Selecting between stud and strike anchors depends on factors like substrate type, load requirements, and installation precision to ensure optimal performance in structural and fastening projects.
Key Differences Between Stud Anchors and Strike Anchors
Stud anchors are typically embedded into concrete through expansion, providing reliable resistance for static loads, whereas strike anchors rely on mechanical interlock and impact installation for quick fastening. Stud anchors offer superior load-bearing capacity and corrosion resistance compared to strike anchors, which are more suitable for temporary or light-duty applications. The selection between stud anchors and strike anchors depends on factors like load requirements, installation environment, and long-term durability needs.
Material Composition of Stud and Strike Anchors
Stud anchors are typically made from high-strength steel or stainless steel, providing superior corrosion resistance and load-bearing capacity, while strike anchors are often composed of zinc-plated or carbon steel, which offers moderate durability under standard conditions. The material composition of stud anchors allows them to perform better in harsh environments and heavy-duty applications, whereas strike anchors are suited for lighter loads and less demanding installations. Choosing the appropriate material depends on factors such as exposure to moisture, load requirements, and the specific structural demands of the project.
Installation Process: Stud Anchor vs Strike Anchor
The installation process of stud anchors involves drilling a hole, cleaning the debris, and inserting the anchor followed by tightening the nut to expand the anchor and secure it in place. Strike anchors require a pre-drilled hole and are installed by driving the anchor into the hole using a hammer, which sets the expansion mechanism for a secure fit. Stud anchors offer more controlled torque application, while strike anchors provide quick installation ideal for light-duty fastening.
Load Capacity Comparison
Stud anchors typically offer higher load capacity compared to strike anchors due to their mechanical expansion design, which provides stronger grip in concrete substrates. Strike anchors depend on impact-driven installation that can result in variable load performance, often lower than stud anchors in heavy-duty applications. Engineers prefer stud anchors for critical structural connections requiring maximum tensile and shear load resistance.
Typical Applications for Stud and Strike Anchors
Stud anchors are commonly used in concrete for securing fixtures like handrails, electrical boxes, and machinery where precision and pull-out strength are critical. Strike anchors excel in applications involving hollow or thin materials such as drywall or metal panels, providing reliable holding power with minimal surface damage. Both anchors serve distinct purposes; stud anchors are preferred for heavy-duty installations while strike anchors are ideal for lighter loads and easier installation in non-solid substrates.
Pros and Cons of Stud Anchors
Stud anchors offer superior load-bearing capacity and excellent resistance to vibration, making them ideal for high-stress construction applications. Their main disadvantage is the need for precise installation and specialized equipment, which can increase labor and setup costs. In contrast to strike anchors, stud anchors provide more consistent anchoring strength but lack the quick installation advantage that strike anchors offer.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Strike Anchors
Strike anchors provide quick installation and high load capacity for securing heavy fixtures in concrete or masonry, making them ideal for structural applications requiring strong, immediate hold. However, their disadvantages include potential difficulty in removal and risk of concrete cracking if not properly installed, which can limit their use in delicate materials or where frequent adjustments are needed. Compared to stud anchors, strike anchors may offer faster deployment but less versatility and precision, affecting project-specific performance and long-term durability.
Cost Considerations: Stud Anchor vs Strike Anchor
Stud anchors generally have a higher initial cost compared to strike anchors due to their specialized design and manufacturing requirements. However, stud anchors often provide greater load capacity and durability, potentially reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Strike anchors offer a more budget-friendly upfront option but may incur higher long-term costs due to lower performance in demanding applications.
Choosing the Right Anchor for Your Project
Stud anchors offer superior shear strength and are ideal for heavy-duty fastening in concrete, whereas strike anchors provide easier installation and cost efficiency for lighter applications. Selecting the right anchor depends on load requirements, material compatibility, and environmental conditions to ensure safety and durability. Understanding these factors enables optimal performance and project success.
Stud anchor vs strike anchor Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com