A sill plate is the horizontal wood component anchored directly to the foundation, providing a base for wall framing, while a rim joist caps the ends of the floor joists, enclosing the floor structure's perimeter. The sill plate acts as a crucial interface between the foundation and the framing, ensuring stability and load transfer. Rim joists contribute to lateral support and help enclose the floor cavity, improving insulation and structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
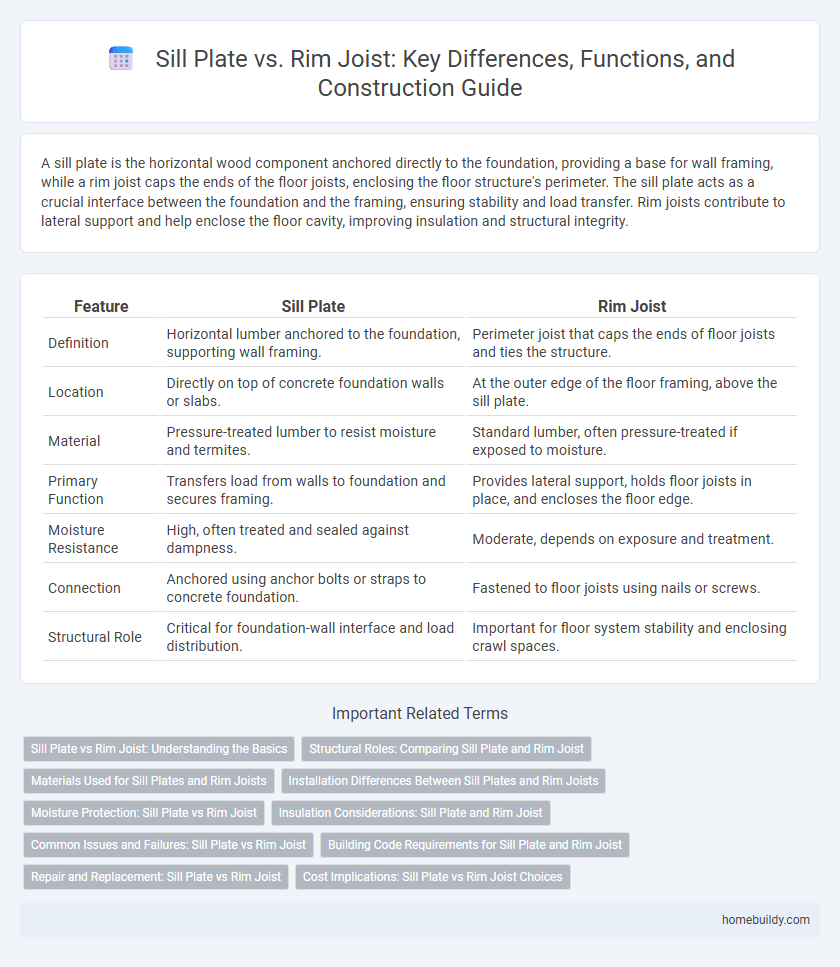
| Feature | Sill Plate | Rim Joist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Horizontal lumber anchored to the foundation, supporting wall framing. | Perimeter joist that caps the ends of floor joists and ties the structure. |
| Location | Directly on top of concrete foundation walls or slabs. | At the outer edge of the floor framing, above the sill plate. |
| Material | Pressure-treated lumber to resist moisture and termites. | Standard lumber, often pressure-treated if exposed to moisture. |
| Primary Function | Transfers load from walls to foundation and secures framing. | Provides lateral support, holds floor joists in place, and encloses the floor edge. |
| Moisture Resistance | High, often treated and sealed against dampness. | Moderate, depends on exposure and treatment. |
| Connection | Anchored using anchor bolts or straps to concrete foundation. | Fastened to floor joists using nails or screws. |
| Structural Role | Critical for foundation-wall interface and load distribution. | Important for floor system stability and enclosing crawl spaces. |
Sill Plate vs Rim Joist: Understanding the Basics
Sill plates are horizontal wood members anchored to the foundation, serving as the base for wall framing, while rim joists cap the ends of floor joists, providing structural support for floor edges. The sill plate transfers loads from the walls to the foundation, whereas the rim joist helps resist lateral forces and keeps floor joists aligned. Both components are critical in framing, with sill plates directly connected to the foundation and rim joists positioned above the floor system.
Structural Roles: Comparing Sill Plate and Rim Joist
The sill plate anchors the building to the foundation, providing a stable base that transfers loads from walls to the foundation, while the rim joist caps the ends of floor joists and forms the perimeter of the floor system, helping to maintain structural integrity and support lateral loads. The sill plate is typically treated lumber bolted to the foundation to resist moisture and termite damage, whereas the rim joist is connected to floor joists to tie the floor system together and resist racking forces. Both components play critical roles in load distribution, but the sill plate primarily interfaces with the foundation, and the rim joist serves to unify and support the floor framing above.
Materials Used for Sill Plates and Rim Joists
Sill plates are typically made from pressure-treated lumber to resist moisture and insect damage, ensuring durability at the foundation level, while rim joists are usually constructed from standard dimensional lumber like pine or fir due to their placement above the foundation. The pressure treatment in sill plates often involves chemicals such as alkaline copper quaternary (ACQ) or copper azole to enhance protection against rot and decay. Rim joists provide structural support for floor joists but do not require the same level of moisture resistance, influencing the choice of untreated or less-treated materials.
Installation Differences Between Sill Plates and Rim Joists
Sill plates are installed directly on the foundation wall and anchored with bolts to provide a secure base for framing, while rim joists are attached at the ends of floor joists to enclose and support the floor system. Sill plates require a moisture barrier like sill sealer to prevent rot, whereas rim joists often include insulation and air sealing to enhance energy efficiency. The precise anchoring of sill plates contrasts with the structural role of rim joists in distributing loads and framing edge support.
Moisture Protection: Sill Plate vs Rim Joist
Sill plates, typically treated wood placed directly on the foundation, provide a crucial moisture barrier to prevent water intrusion from the concrete slab. Rim joists, located at the perimeter of the floor framing, require proper sealing and insulation to protect against moisture and air leaks that can lead to mold growth. Effective moisture protection in construction relies on using pressure-treated sill plates combined with well-sealed rim joists to ensure structural durability and indoor air quality.
Insulation Considerations: Sill Plate and Rim Joist
Sill plates and rim joists both play crucial roles in a building's foundation framing but require different insulation approaches to prevent energy loss and moisture issues. Sill plates, positioned directly on the foundation, benefit from rigid foam insulation or spray foam to create an airtight seal against cold concrete, while rim joists, located at the perimeter of the floor framing, often require cavity spray foam or batt insulation with an air barrier to fill irregular gaps and reduce thermal bridging. Proper attention to insulating both components minimizes heat transfer, improves overall energy efficiency, and enhances moisture control within the building envelope.
Common Issues and Failures: Sill Plate vs Rim Joist
Sill plates often experience issues such as rot, termite damage, and improper anchoring, leading to structural instability and water infiltration. Rim joists commonly suffer from moisture retention, inadequate insulation, and warping, which can cause energy loss and compromised framing connections. Both elements require proper sealing and maintenance to prevent degradation that affects the building's foundation and framing integrity.
Building Code Requirements for Sill Plate and Rim Joist
Building code requirements for sill plates and rim joists focus on proper anchoring, material specifications, and moisture protection to ensure structural integrity and resistance to uplift forces. Sill plates must be anchored to the foundation with corrosion-resistant fasteners and often require a moisture barrier like sill sealer or foam to prevent rot, while rim joists, typically made from engineered wood or dimensional lumber, must comply with load requirements and be properly fastened to floor framing components. Both elements are critical in distributing loads and maintaining the overall stability of the building envelope according to codes such as the International Residential Code (IRC).
Repair and Replacement: Sill Plate vs Rim Joist
Repair and replacement of sill plates often address moisture damage and termite infestation, requiring careful removal and matching of treated wood to maintain structural integrity. Rim joist repairs focus on resolving rot and warping caused by water exposure, typically involving sistering new lumber alongside the damaged section for reinforcement. Proper assessment of both sill plates and rim joists is crucial, as timely intervention prevents compromised foundation connections and ensures long-lasting frame stability.
Cost Implications: Sill Plate vs Rim Joist Choices
Sill plates, typically made from treated lumber, tend to be more cost-effective than rim joists due to their simpler installation and smaller dimensions. Rim joists require additional labor and material for proper insulation and sealing, which can increase overall expenses. Choosing sill plates over rim joists can result in reduced upfront construction costs while maintaining structural integrity in foundation framing.
Sill plate vs Rim joist Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com