A sill plate is a horizontal piece of lumber anchored to the foundation of a building, providing a base for the wall framing, while a threshold is installed at the bottom of a doorway to seal and transition between interior and exterior spaces. The sill plate supports structural loads and resists moisture intrusion, whereas the threshold primarily enhances energy efficiency by preventing drafts and serves as a weather barrier. Understanding these differences ensures proper installation and improves the durability and comfort of a building.
Table of Comparison
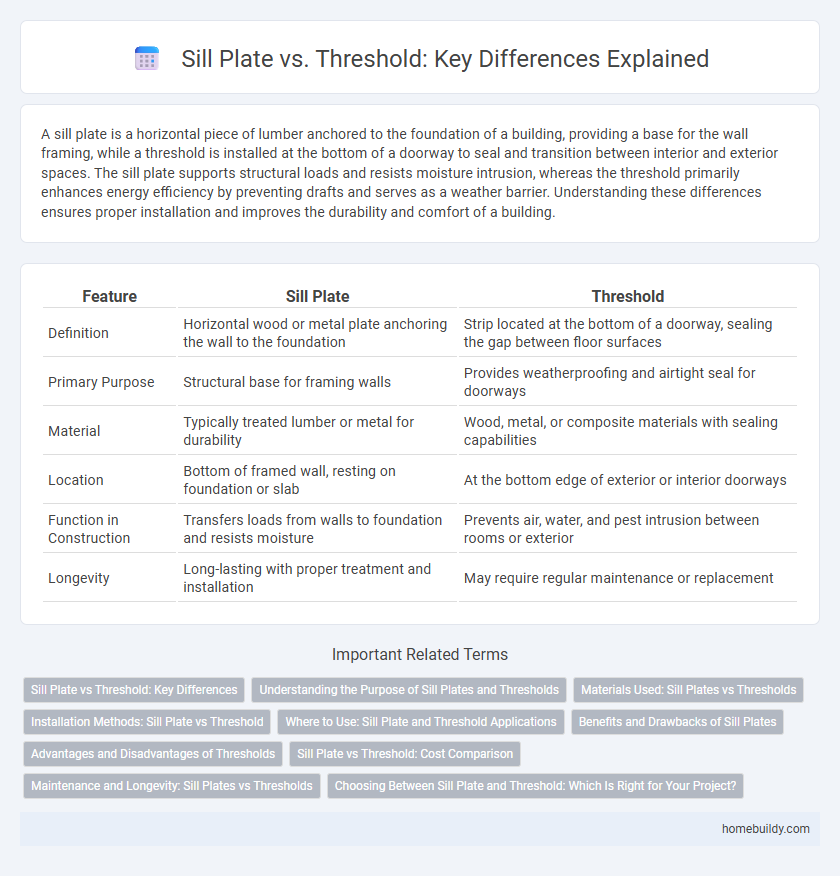
| Feature | Sill Plate | Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Horizontal wood or metal plate anchoring the wall to the foundation | Strip located at the bottom of a doorway, sealing the gap between floor surfaces |
| Primary Purpose | Structural base for framing walls | Provides weatherproofing and airtight seal for doorways |
| Material | Typically treated lumber or metal for durability | Wood, metal, or composite materials with sealing capabilities |
| Location | Bottom of framed wall, resting on foundation or slab | At the bottom edge of exterior or interior doorways |
| Function in Construction | Transfers loads from walls to foundation and resists moisture | Prevents air, water, and pest intrusion between rooms or exterior |
| Longevity | Long-lasting with proper treatment and installation | May require regular maintenance or replacement |
Sill Plate vs Threshold: Key Differences
Sill plates are horizontal wooden beams anchored to the foundation, serving as a structural base for wall framing, while thresholds are the flat strips installed at door bottoms to seal and provide a smooth transition between rooms. Unlike sill plates, which are critical for structural integrity and load distribution, thresholds primarily address weatherproofing, moisture protection, and aesthetic finishing. Understanding these distinctions highlights the sill plate's foundational role versus the threshold's function in enhancing door performance and energy efficiency.
Understanding the Purpose of Sill Plates and Thresholds
Sill plates serve as the horizontal framing member anchoring the structure to the foundation, providing stability and distributing loads evenly. Thresholds function as transition strips at doorways, sealing gaps and enhancing energy efficiency by preventing drafts and moisture intrusion. Understanding that sill plates form the building's structural base while thresholds create a weather-tight barrier clarifies their distinct roles in construction.
Materials Used: Sill Plates vs Thresholds
Sill plates are typically made from pressure-treated lumber to resist moisture and insect damage, ensuring a durable base for wall framing. Thresholds, on the other hand, often utilize hardwood, aluminum, or vinyl materials designed to withstand foot traffic and provide a weather-tight seal at doorways. The choice of materials reflects their distinct functions, with sill plates focusing on structural support and thresholds prioritizing durability and weather resistance.
Installation Methods: Sill Plate vs Threshold
Sill plates are installed directly on the foundation and secured with anchor bolts to create a stable base for wall framing, while thresholds are placed beneath doors to provide a weather-resistant transition between interior floors and exterior doorways. The installation of sill plates requires precise leveling and sealing to prevent moisture intrusion and ensure structural integrity, whereas threshold installation focuses on proper alignment and sealing to minimize drafts and water infiltration. Both components play essential roles in building envelope performance but demand different preparation and fastening techniques tailored to their functions.
Where to Use: Sill Plate and Threshold Applications
Sill plates are typically used at the bottom of exterior walls in residential construction, anchoring the framing to the foundation and providing a stable base for wall structures. Thresholds are installed at doorways, serving as a transition between different flooring types or between interior and exterior environments, enhancing weather resistance and sealing. Sill plates are critical for structural support and moisture protection, while thresholds focus on durability and energy efficiency at entry points.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Sill Plates
Sill plates provide a sturdy base for wall framing, improving structural stability and resistance to moisture by being anchored directly to the foundation, unlike thresholds which primarily serve as door transitions. The main benefit of sill plates is their ability to distribute loads evenly and prevent wood-to-concrete contact, reducing rot and extending the building's lifespan. However, sill plates can be prone to termite damage without proper treatment and may require a vapor barrier to minimize dampness issues.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thresholds
Thresholds provide a smooth transition between rooms and help seal doors against drafts, moisture, and dust, enhancing energy efficiency and indoor comfort. However, thresholds can create a tripping hazard and may wear out more quickly than sill plates, requiring more frequent maintenance or replacement. In contrast, sill plates serve as the foundational wood framing at the base of a wall, offering structural support but not directly contributing to door sealing or energy efficiency like thresholds.
Sill Plate vs Threshold: Cost Comparison
A sill plate, typically made of treated lumber, averages $10 to $20 per linear foot, including installation, while door thresholds generally cost between $30 and $100 depending on materials such as wood, aluminum, or stone. Sill plates serve as the structural base for walls and require precise fitting to ensure stability, often increasing labor costs compared to simpler threshold installation. Thresholds primarily provide a weather seal and aesthetic finish, making their overall cost more variable based on design choices but generally less intensive in structural labor than sill plates.
Maintenance and Longevity: Sill Plates vs Thresholds
Sill plates, made from treated lumber, require regular inspections to prevent rot and insect damage, ensuring structural stability and longevity of the building frame. Thresholds, typically constructed from metal, wood, or composite materials, demand maintenance to prevent warping and corrosion, enhancing entryway durability. Proper sealing and occasional refinishing of both sill plates and thresholds significantly extend their lifespan and maintain energy efficiency.
Choosing Between Sill Plate and Threshold: Which Is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between a sill plate and a threshold depends on the structural and weatherproofing needs of your project. Sill plates serve as the foundational wood base anchored to the concrete slab, providing structural support and a barrier against moisture, while thresholds act as transition strips between interior rooms or between exterior and interior spaces, focusing on sealing and aesthetic finish. Evaluating factors like load requirements, insulation, moisture control, and the building code will guide the appropriate choice for optimal durability and energy efficiency.
Sill plate vs Threshold Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com