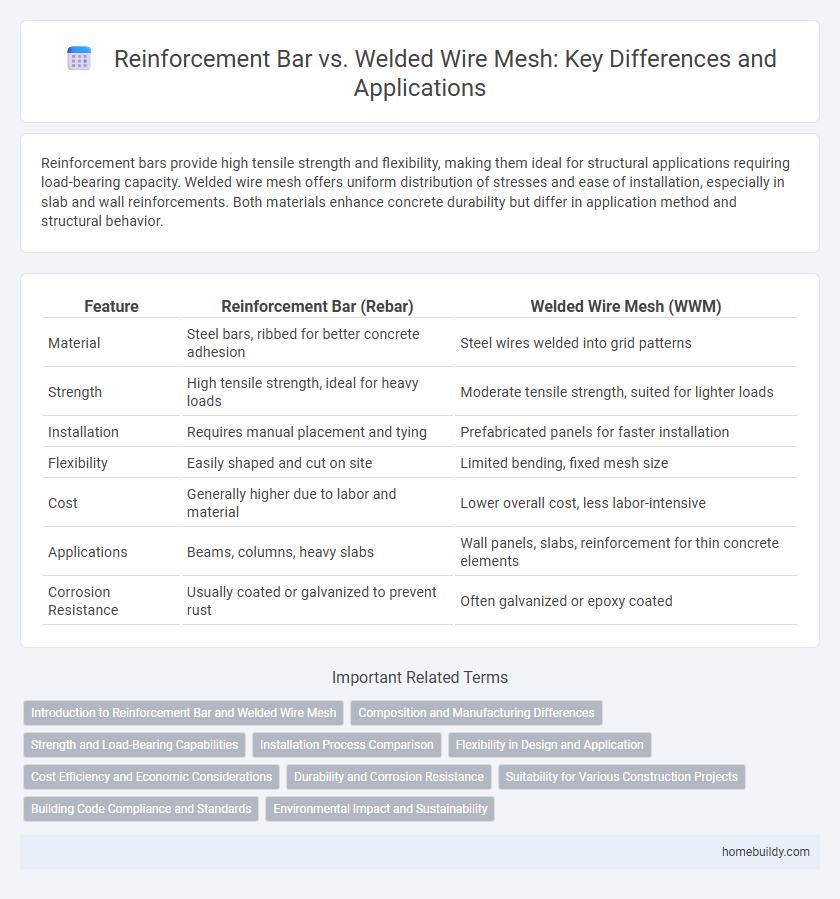
Reinforcement bars provide high tensile strength and flexibility, making them ideal for structural applications requiring load-bearing capacity. Welded wire mesh offers uniform distribution of stresses and ease of installation, especially in slab and wall reinforcements. Both materials enhance concrete durability but differ in application method and structural behavior.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reinforcement Bar (Rebar) | Welded Wire Mesh (WWM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel bars, ribbed for better concrete adhesion | Steel wires welded into grid patterns |
| Strength | High tensile strength, ideal for heavy loads | Moderate tensile strength, suited for lighter loads |
| Installation | Requires manual placement and tying | Prefabricated panels for faster installation |
| Flexibility | Easily shaped and cut on site | Limited bending, fixed mesh size |
| Cost | Generally higher due to labor and material | Lower overall cost, less labor-intensive |
| Applications | Beams, columns, heavy slabs | Wall panels, slabs, reinforcement for thin concrete elements |
| Corrosion Resistance | Usually coated or galvanized to prevent rust | Often galvanized or epoxy coated |
Introduction to Reinforcement Bar and Welded Wire Mesh
Reinforcement bars, commonly known as rebars, are steel bars used to strengthen concrete structures by providing tensile strength and improving overall durability. Welded wire mesh consists of intersecting steel wires welded together to form a grid, offering uniform load distribution and reducing cracking in concrete slabs. Both materials serve crucial roles in reinforced concrete construction but differ in application methods, with rebars typically used in beams and columns, while welded wire mesh is preferred for slabs and pavements.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Reinforcement bars are made from carbon steel, typically featuring ribbed surfaces to enhance concrete bonding, and are produced through hot rolling processes that shape and strengthen the bars. Welded wire mesh consists of cold-drawn or hot-rolled steel wires welded at intersections to form a grid pattern, providing uniform tensile strength and easier handling. The primary manufacturing difference lies in reinforcement bars being singular, ribbed rods formed by rolling, while welded wire mesh is an assembly of steel wires joined by electric resistance welding.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capabilities
Reinforcement bars (rebar) offer superior tensile strength compared to welded wire mesh, making them ideal for supporting heavy loads in concrete structures. Their ribbed surface enhances bonding with concrete, improving overall load-bearing capacity and minimizing slippage under stress. Welded wire mesh provides uniform distribution of load but lacks the high tensile strength and flexibility that rebar delivers for structural reinforcement.
Installation Process Comparison
Reinforcement bars require precise bending and placement, often involving labor-intensive tying with wire to secure the bars in position before concrete pouring. Welded wire mesh offers faster installation due to prefabricated grid panels that can be quickly laid out and fixed in place, reducing labor time and complexity. Both methods demand careful alignment and support, but welded wire mesh streamlines the reinforcement process in large-scale concrete applications.
Flexibility in Design and Application
Reinforcement bars offer greater flexibility in design and application compared to welded wire mesh, allowing for customized shapes and sizes to meet specific structural requirements. Their adaptability enables engineers to tailor reinforcement configurations for complex geometries and varied load conditions. Welded wire mesh, while easier to install, provides limited design versatility due to fixed grid patterns and standardized dimensions.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Reinforcement bars typically offer greater cost efficiency compared to welded wire mesh due to their availability, ease of customization, and lower installation labor costs. While welded wire mesh provides uniform strength and faster placement, its higher material and fabrication expenses often increase overall project budgets. Economic considerations favor reinforcement bars in large-scale construction where adaptability and budget constraints are critical.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Reinforcement bars (rebar) typically exhibit superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to welded wire mesh due to their thicker cross-section and ability to be coated with anti-corrosive materials such as epoxy or galvanized layers. High-quality rebar made from stainless steel or treated carbon steel offers enhanced structural integrity in aggressive environments, reducing the risk of cracking and spalling. In contrast, welded wire mesh is more susceptible to rust and deterioration over time without proper surface treatment, making rebar a preferred choice for long-term construction projects in corrosive settings.
Suitability for Various Construction Projects
Reinforcement bars offer superior adaptability for structural elements requiring high tensile strength, making them ideal for beams, columns, and heavy load-bearing foundations. Welded wire mesh excels in uniform load distribution and crack resistance, fitting well for slabs, flooring, and precast concrete panels. Project demands for flexibility, load specifications, and structural integrity determine the optimal choice between reinforcement bars and welded wire mesh.
Building Code Compliance and Standards
Reinforcement bars (rebar) and welded wire mesh must both comply with building codes such as the ACI (American Concrete Institute) standards and ASTM specifications to ensure structural integrity and safety. Rebar typically adheres to ASTM A615 or A706 standards, providing proven tensile strength and ductility, while welded wire mesh is manufactured according to ASTM A185, designed for uniform stress distribution in concrete slabs. Choosing between rebar and welded wire mesh depends on project-specific structural requirements and compliance with local building regulations governing reinforcement materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reinforcement bars, typically made from steel, have a higher embodied energy compared to welded wire mesh but offer superior recyclability, contributing to lower long-term environmental impact. Welded wire mesh involves less material waste during production, yet its lower durability often results in more frequent replacements, increasing resource consumption over time. Evaluating sustainability, reinforcement bars provide enhanced structural integrity and lifespan, reducing overall ecological footprint through decreased maintenance and extended service life.
Reinforcement bar vs Welded wire mesh Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com