Rebar cover blocks are used to maintain the required distance between the reinforcement bars and the formwork, ensuring proper concrete cover for corrosion protection. Concrete spacers also serve a similar purpose but are typically designed to hold multiple reinforcement bars in position, providing uniform spacing and improving structural integrity. Both components are essential for achieving durability, strength, and compliance with construction standards in reinforced concrete structures.
Table of Comparison
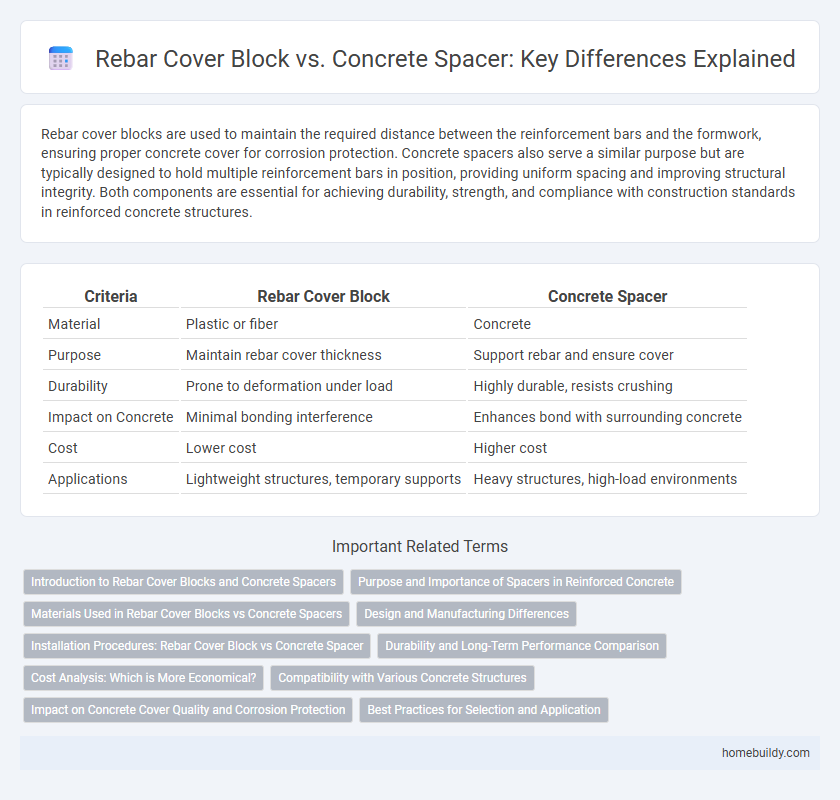
| Criteria | Rebar Cover Block | Concrete Spacer |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic or fiber | Concrete |
| Purpose | Maintain rebar cover thickness | Support rebar and ensure cover |
| Durability | Prone to deformation under load | Highly durable, resists crushing |
| Impact on Concrete | Minimal bonding interference | Enhances bond with surrounding concrete |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Lightweight structures, temporary supports | Heavy structures, high-load environments |
Introduction to Rebar Cover Blocks and Concrete Spacers
Rebar cover blocks and concrete spacers serve the critical function of maintaining proper concrete cover to protect reinforcement bars from corrosion and ensure structural integrity. Rebar cover blocks, typically made from concrete or plastic, provide direct support beneath the rebar to maintain the specified cover height during concrete pouring. Concrete spacers, often plastic or metal, are designed to securely hold rebar in position within the formwork, ensuring uniform concrete cover throughout the structure.
Purpose and Importance of Spacers in Reinforced Concrete
Rebar cover blocks and concrete spacers ensure precise concrete cover, protecting reinforcement bars from corrosion and fire damage while maintaining structural integrity. These spacers provide consistent positioning of rebar during concrete pouring, preventing displacement that could weaken the load-bearing capacity of reinforced concrete structures. Proper use of cover blocks and spacers enhances durability, extends service life, and complies with construction standards such as ACI and ASTM guidelines.
Materials Used in Rebar Cover Blocks vs Concrete Spacers
Rebar cover blocks are typically made from high-strength concrete or plastic resin designed to maintain the specified cover thickness and protect steel reinforcement from corrosion. Concrete spacers are usually fabricated from concrete but can also incorporate rubber or plastic components to enhance durability and adhesion to the reinforcing bars. The choice of materials affects the structural integrity, durability, and ease of installation in reinforced concrete constructions.
Design and Manufacturing Differences
Rebar cover blocks are typically manufactured from concrete and designed to provide a consistent cover thickness between the reinforcement steel and the formwork, ensuring optimal protection against corrosion. Concrete spacers, often molded from polymer or plastic materials, offer enhanced precision in positioning reinforcement and are engineered for lighter weight and higher durability in construction environments. The design of cover blocks emphasizes compressive strength to withstand concrete pouring, while spacers prioritize dimensional accuracy and ease of installation.
Installation Procedures: Rebar Cover Block vs Concrete Spacer
Rebar cover blocks are installed by directly placing them underneath or alongside reinforcement bars before pouring concrete, ensuring consistent concrete cover and positioning. Concrete spacers, typically pre-shaped and fixed to rebar, are clipped or tied at specific intervals to maintain accurate cover and alignment during construction. Both installation methods require careful placement to prevent displacement of reinforcement, but concrete spacers often provide more precise and secure positioning compared to manual placement of cover blocks.
Durability and Long-Term Performance Comparison
Rebar cover blocks provide consistent concrete cover thickness, ensuring optimal protection against corrosion and enhancing the durability of reinforced structures. Concrete spacers, while effective, may shift during placement, potentially compromising cover uniformity and long-term performance. Selecting high-quality cover blocks improves structural integrity by maintaining precise rebar positioning and reducing the risk of concrete degradation over time.
Cost Analysis: Which is More Economical?
Rebar cover blocks typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to concrete spacers due to cheaper materials like plastic or mortar-based compositions. Concrete spacers, while more expensive initially, provide enhanced durability and reduced risk of displacement during concrete pouring, potentially lowering long-term repair costs. Overall, rebar cover blocks remain more economical for budget-sensitive projects, whereas concrete spacers deliver better value in high-quality, longevity-focused constructions.
Compatibility with Various Concrete Structures
Rebar cover blocks and concrete spacers both ensure proper concrete cover but differ in compatibility with concrete structures. Cover blocks are typically rigid and suited for flat surfaces or slabs, maintaining consistent cover in standard construction. Concrete spacers are more adaptable, conforming to irregular or complex geometries like beams and columns, enhancing stability and ensuring optimal protection against corrosion.
Impact on Concrete Cover Quality and Corrosion Protection
Rebar cover blocks provide consistent concrete cover thickness, ensuring uniform protection against corrosion by preventing rebar exposure to moisture and chlorides. Concrete spacers, while simpler to install, may shift during pouring, risking uneven cover and compromising the concrete's durability and corrosion resistance. Proper selection and placement of cover blocks significantly enhance the longevity and structural integrity of reinforced concrete by maintaining optimal cover quality.
Best Practices for Selection and Application
Rebar cover block and concrete spacer are essential for ensuring proper concrete cover and reinforcement placement in construction projects. Selecting the right option depends on factors such as load conditions, concrete consistency, and environmental exposure, with cover blocks typically preferred for horizontal reinforcement and concrete spacers ideal for complex or vertical applications. Best practices emphasize using high-quality, non-corrosive materials like plastic or fiber-reinforced composites to maintain durability and structural integrity throughout the concrete curing process.
Rebar cover block vs Concrete spacer Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com