Rebar chairs provide stable support for rebar during concrete pouring, ensuring proper positioning and structural integrity. Concrete spacers maintain consistent cover thickness by separating rebar from formwork, preventing corrosion and enhancing durability. Both components are essential for achieving accurate rebar placement and long-lasting concrete structures.
Table of Comparison
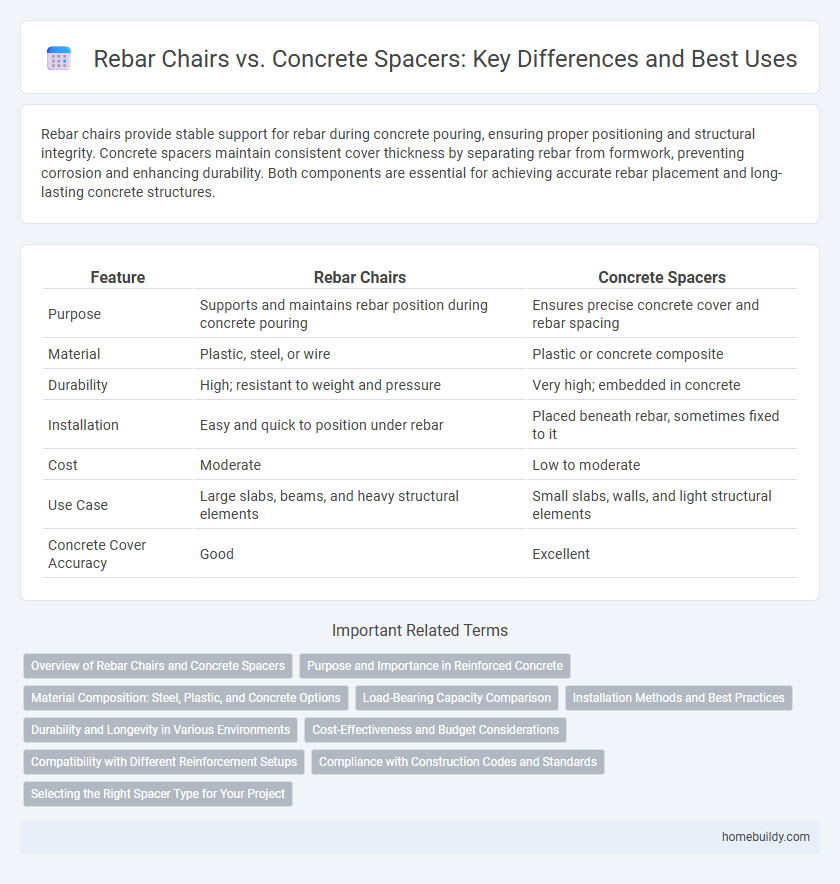
| Feature | Rebar Chairs | Concrete Spacers |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Supports and maintains rebar position during concrete pouring | Ensures precise concrete cover and rebar spacing |
| Material | Plastic, steel, or wire | Plastic or concrete composite |
| Durability | High; resistant to weight and pressure | Very high; embedded in concrete |
| Installation | Easy and quick to position under rebar | Placed beneath rebar, sometimes fixed to it |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Use Case | Large slabs, beams, and heavy structural elements | Small slabs, walls, and light structural elements |
| Concrete Cover Accuracy | Good | Excellent |
Overview of Rebar Chairs and Concrete Spacers
Rebar chairs are durable supports designed to hold reinforcement bars at precise heights, ensuring consistent concrete cover and structural integrity in construction projects. Concrete spacers, typically molded from concrete, maintain the rebar's position by directly embedding into the slab, offering enhanced corrosion resistance and compatibility with the concrete matrix. Both components are essential for maintaining proper rebar alignment, but rebar chairs provide adjustable support while concrete spacers integrate seamlessly into the concrete surface.
Purpose and Importance in Reinforced Concrete
Rebar chairs provide critical support to reinforcement bars, ensuring precise positioning and maintaining proper concrete cover during the pouring process, which enhances structural integrity. Concrete spacers, often made from the same material as the concrete mix, prevent direct contact between steel and soil or water, reducing corrosion risk and improving durability. Both components are essential for achieving accurate reinforcement placement and long-lasting performance in reinforced concrete structures.
Material Composition: Steel, Plastic, and Concrete Options
Rebar chairs are commonly made from steel or plastic, offering high durability and corrosion resistance, while concrete spacers are composed of the same material as the surrounding concrete, ensuring compatibility and thermal expansion alignment. Steel rebar chairs provide superior load-bearing capacity, plastic variants resist chemical exposure and reduce concrete contamination risk, whereas concrete spacers integrate seamlessly, improving structural bonding. The choice between these materials depends on specific project requirements, environmental conditions, and the desired performance of the reinforcement system.
Load-Bearing Capacity Comparison
Rebar chairs provide superior load-bearing capacity by evenly distributing the weight of reinforcement bars during concrete pouring, ensuring structural integrity and reducing deformation under stress. Concrete spacers, while effective in maintaining rebar positioning, typically bear less load and are more prone to crushing or displacement under heavy reinforcement clusters. Selecting rebar chairs enhances overall durability and load management in reinforced concrete construction.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
Rebar chairs and concrete spacers serve critical roles in maintaining proper reinforcement bar positioning within concrete structures to ensure structural integrity. Rebar chairs, typically made from plastic or metal, are installed by placing them directly under the rebar to elevate and support the bars at a specific height, allowing concrete to flow underneath for optimal coverage. Concrete spacers are precast blocks set between rebar and formwork, providing consistent concrete cover and easy installation by simply aligning them along the reinforcement grid, with both methods requiring adherence to project specifications and careful placement to avoid misalignment or insufficient cover.
Durability and Longevity in Various Environments
Rebar chairs, constructed from corrosion-resistant materials like polymer or stainless steel, provide superior durability and maintain structural integrity in harsh environments compared to traditional concrete spacers. Their design prevents concrete contamination and resists chemical degradation, extending service life in marine or industrial settings. Concrete spacers, while cost-effective, often suffer from cracking and spalling under freeze-thaw cycles, reducing overall longevity in varied climates.
Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Considerations
Rebar chairs generally offer greater cost-effectiveness compared to concrete spacers due to their reusability and durability on multiple projects, reducing overall material expenses. Concrete spacers can increase budget costs as they are typically single-use and may require more frequent replacement, impacting long-term project profitability. Considering factors such as labor time, material waste, and project scale can significantly influence budget decisions when selecting between rebar chairs and concrete spacers.
Compatibility with Different Reinforcement Setups
Rebar chairs provide adjustable support specifically designed to hold reinforcement bars at precise heights, making them highly compatible with complex reinforcement setups involving varying bar sizes and configurations. Concrete spacers, typically molded from hardened concrete, offer fixed positioning but are less adaptable for intricate or densely packed rebar arrangements. Choosing between rebar chairs and concrete spacers depends on the reinforcement layout complexity, with rebar chairs offering superior flexibility for multi-tiered or irregular reinforcement assemblies.
Compliance with Construction Codes and Standards
Rebar chairs and concrete spacers both serve to maintain proper rebar positioning but differ in compliance aspects with construction codes and standards. Rebar chairs, often made from plastic or metal, typically meet ASTM A951 and ACI 318 requirements for strength and stability, ensuring adherence to industry regulations. Concrete spacers, molded from grout or concrete, provide excellent compressive strength compliant with specific project specifications and often align with local building codes emphasizing durability and load-bearing capacity.
Selecting the Right Spacer Type for Your Project
Selecting the right spacer type for your project is crucial to ensure proper concrete coverage and structural integrity in reinforcement bar installation. Rebar chairs provide stable support for vertical and horizontal bars, maintaining precise positioning during concrete pouring, while concrete spacers are molded to fit specific rebar sizes, offering enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion. Choosing between rebar chairs and concrete spacers depends on factors such as load conditions, environmental exposure, and project specifications to optimize reinforcement performance.
Rebar Chairs vs Concrete Spacers Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com