Dry-packed column bases provide superior load-bearing capacity by allowing concrete to be compacted in a controlled, dry state, minimizing voids and improving structural integrity. Wet-packed column bases involve pouring fluid concrete directly into the formwork, which can lead to honeycombing and weaker bonding if not properly vibrated. Selecting between dry-packed and wet-packed bases depends on site conditions, required strength, and ease of application.
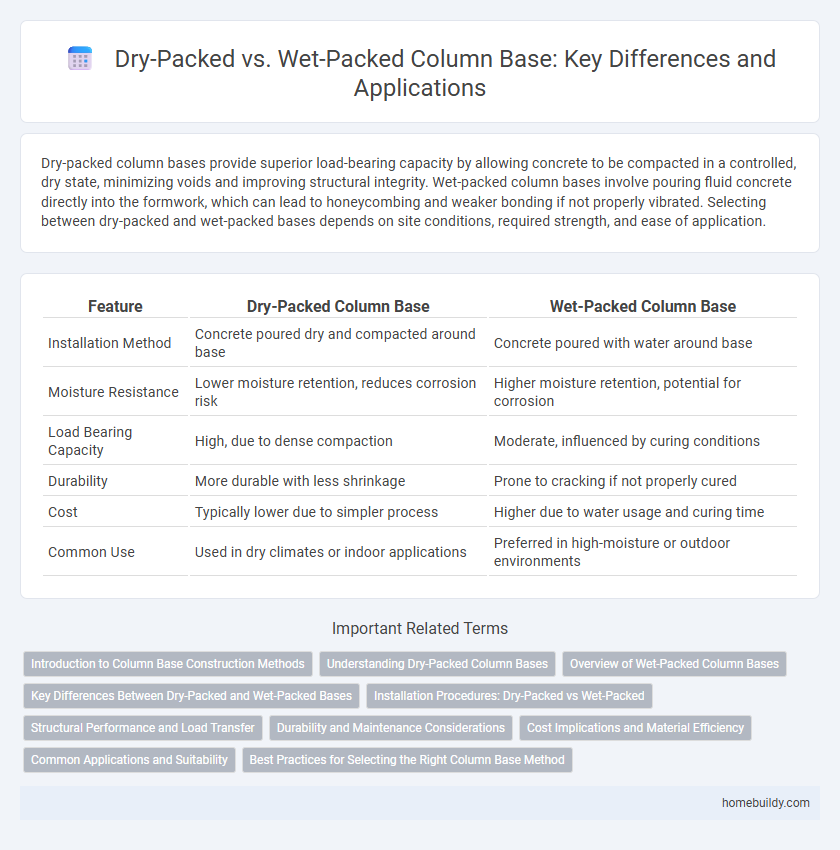
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dry-Packed Column Base | Wet-Packed Column Base |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Method | Concrete poured dry and compacted around base | Concrete poured with water around base |
| Moisture Resistance | Lower moisture retention, reduces corrosion risk | Higher moisture retention, potential for corrosion |
| Load Bearing Capacity | High, due to dense compaction | Moderate, influenced by curing conditions |
| Durability | More durable with less shrinkage | Prone to cracking if not properly cured |
| Cost | Typically lower due to simpler process | Higher due to water usage and curing time |
| Common Use | Used in dry climates or indoor applications | Preferred in high-moisture or outdoor environments |
Introduction to Column Base Construction Methods
Dry-packed column bases rely on compacted granular material without water, providing rapid setting and drainage benefits suitable for lightweight structures. Wet-packed column bases use a fluid concrete mix poured into forms, ensuring uniform bonding and enhanced strength for heavy-load applications. Selection between dry-packed and wet-packed methods depends on soil conditions, load requirements, and environmental factors influencing structural stability.
Understanding Dry-Packed Column Bases
Dry-packed column bases utilize densely compacted granular materials, such as gravel or crushed stone, to provide a stable and well-drained foundation, significantly reducing settlement risks. Unlike wet-packed column bases, which involve the use of fluid concrete or grout that can lead to inconsistent compaction and potential voids, dry-packed bases ensure uniform load distribution and enhanced bearing capacity. This method optimizes soil-cement interaction and improves durability, making dry-packed column bases a preferred choice in geotechnical engineering for supporting heavy structural loads.
Overview of Wet-Packed Column Bases
Wet-packed column bases involve casting concrete around the column base while it remains wet, ensuring thorough compaction and strong bonding between the foundation and the column. This method enhances load transfer capacity and minimizes voids, leading to improved structural stability in high-load applications. Wet-packing is preferred in conditions requiring superior strength and durability compared to dry-packed alternatives.
Key Differences Between Dry-Packed and Wet-Packed Bases
Dry-packed column bases use dry concrete compacted into forms, offering faster construction and higher early strength, while wet-packed bases employ fluid concrete poured and consolidated with vibration for uniformity and reduced voids. Dry-packed bases are ideal for repair work or confined spaces due to minimal slump and quick setting, whereas wet-packed bases provide better bonding and load distribution in new construction. Key differences include consistency, placement method, curing time, structural integrity, and suitability for specific project conditions.
Installation Procedures: Dry-Packed vs Wet-Packed
Dry-packed column bases require the precise placement of dry grout or mortar beneath the column to achieve a rigid and uniform bearing surface, ensuring proper load transfer without voids. Wet-packed column bases involve pouring a fluid grout mixture that self-levels and fills all gaps, providing superior adhesion and consolidation around the column base. Accurate surface preparation and controlled curing times are critical in both methods to optimize structural stability and prevent settlement or misalignment.
Structural Performance and Load Transfer
Dry-packed column bases exhibit superior structural performance due to their ability to maintain consistent concrete density and minimize voids, which enhances load transfer efficiency from the column to the foundation. Wet-packed column bases may experience segregation and shrinkage during curing, potentially reducing load transfer capacity and increasing the risk of differential settlement. Optimized dry-packing techniques improve the interface bond strength, resulting in a more reliable and durable column base under various load conditions.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Dry-packed column bases offer superior durability by minimizing moisture retention, which reduces the risk of corrosion and concrete degradation. Maintenance is simplified since dry-packed bases allow for easier inspection and repair without the need for water removal or drying time. Wet-packed column bases may experience increased wear due to trapped moisture, leading to higher maintenance demands over time.
Cost Implications and Material Efficiency
Dry-packed column bases reduce initial material costs by using minimal grout and allowing faster installation, whereas wet-packed bases require more grout leading to higher material expenses and longer curing times. Material efficiency in dry-packed methods results from precise grout application, minimizing waste and improving load transfer, while wet-packed projects often experience excess grout usage and potential voids that can compromise durability. Choosing dry-packed column bases optimizes budget and resource allocation, enhancing overall construction cost-effectiveness.
Common Applications and Suitability
Dry-packed column bases are commonly used in environments where long-term stability and minimal settlement are crucial, such as in bridges, industrial buildings, and heavy machinery supports. Wet-packed column bases are suitable for applications requiring faster installation and where slight settlement is acceptable, often found in residential construction and temporary structures. The choice between dry-packed and wet-packed methods depends on load-bearing requirements, soil conditions, and project timelines.
Best Practices for Selecting the Right Column Base Method
Dry-packed column bases provide superior load transfer and durability by ensuring a well-compacted, granular material beneath the footing, minimizing settlement risk compared to wet-packed methods. Wet-packed column bases may introduce excess moisture, potentially leading to weaker bearing capacity and increased long-term deformation. Selecting dry-packed bases is best practice in high-load or variable soil conditions, while wet-packed may be suitable in low-load scenarios with stable soil and controlled moisture content.
dry-packed column base vs wet-packed column base Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com