Flitch plate connectors provide superior load distribution by sandwiching steel plates between timber beams, enhancing structural strength and reducing deflection. Beam bracket connectors offer easier installation with visible metal brackets that secure beams externally, ideal for retrofit projects or visible design elements. Choosing between the two depends on the desired strength requirements, aesthetic preferences, and installation complexity.
Table of Comparison
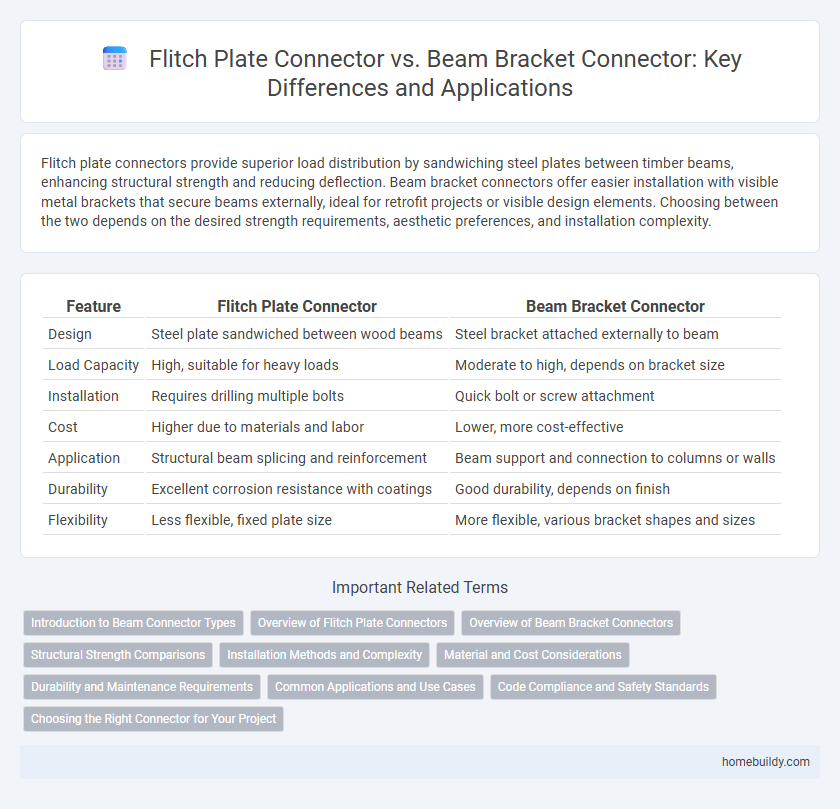
| Feature | Flitch Plate Connector | Beam Bracket Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Steel plate sandwiched between wood beams | Steel bracket attached externally to beam |
| Load Capacity | High, suitable for heavy loads | Moderate to high, depends on bracket size |
| Installation | Requires drilling multiple bolts | Quick bolt or screw attachment |
| Cost | Higher due to materials and labor | Lower, more cost-effective |
| Application | Structural beam splicing and reinforcement | Beam support and connection to columns or walls |
| Durability | Excellent corrosion resistance with coatings | Good durability, depends on finish |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed plate size | More flexible, various bracket shapes and sizes |
Introduction to Beam Connector Types
Flitch plate connectors consist of steel plates bolted between timber beams, providing enhanced load bearing and stiffness in composite beam construction. Beam bracket connectors are prefabricated metal brackets attached to the side or end of beams, enabling quick installation and strong connections in framing applications. Both connectors serve to improve structural integrity, with flitch plates favored for heavy loads and beam brackets for ease of assembly.
Overview of Flitch Plate Connectors
Flitch plate connectors are steel plates bolted between two wooden beams to increase load-bearing capacity and reduce deflection in structural applications. These connectors provide a cost-effective solution for strengthening beams without significantly increasing their depth or weight. In comparison to beam bracket connectors, flitch plates offer enhanced stiffness and improved resistance to bending moments, making them ideal for supporting heavy loads in residential and commercial construction.
Overview of Beam Bracket Connectors
Beam bracket connectors provide a robust and versatile solution for joining beams in structural applications, offering enhanced load-bearing capacity compared to flitch plate connectors. These connectors are typically fabricated from high-strength steel and designed to distribute loads evenly, reducing stress concentrations and improving overall joint stability. Their ease of installation and capacity to accommodate various beam sizes make them ideal for both commercial and residential construction projects.
Structural Strength Comparisons
Flitch plate connectors provide enhanced structural strength by combining steel plates with wood beams, significantly increasing load-bearing capacity and resistance to bending moments. Beam bracket connectors rely solely on metal brackets, offering easier installation but generally lower load capacity and reduced stiffness compared to flitch plates. Structural engineers often prefer flitch plate connectors for projects requiring superior strength and long-span support due to their superior composite action.
Installation Methods and Complexity
Flitch plate connectors require precise alignment and bolting of steel plates between wooden beams, involving more complex installation steps and tools for drilling and fastening. Beam bracket connectors are typically easier to install, using pre-fabricated metal brackets secured with screws or bolts directly to the beam, reducing installation time and complexity. The choice impacts labor costs and suitability for projects where installation speed or structural requirements are prioritized.
Material and Cost Considerations
Flitch plate connectors are typically made from steel plates, offering high strength and durability but often at a higher material cost due to the thickness and quality of the steel. Beam bracket connectors are usually fabricated from lighter gauge steel or aluminum, reducing material costs while providing sufficient support for moderate loads. Cost considerations favor beam bracket connectors in budget-sensitive projects, whereas flitch plate connectors suit applications requiring enhanced structural integrity despite higher expenses.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Flitch plate connectors offer superior durability due to their robust steel plates that provide strong load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation, making them ideal for heavy structural applications. Beam bracket connectors, typically made from galvanized steel or aluminum, require more frequent inspection and maintenance to prevent corrosion and ensure long-term performance. Regular maintenance of beam bracket connectors includes tightening fasteners and treating rust-prone areas, whereas flitch plate connectors generally demand less upkeep over time.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Flitch plate connectors are commonly used in load-bearing timber beam splices and reinforcement applications where high shear strength is required, such as in floor joists and bridge construction. Beam bracket connectors serve as versatile support elements for attaching beams to columns or walls, frequently found in residential decking, pergola frameworks, and general structural framing. Both connectors ensure stability and load distribution but differ in installation methods and specific structural roles.
Code Compliance and Safety Standards
Flitch plate connectors and beam bracket connectors must both meet stringent code compliance and safety standards, including ASTM and ICC approvals, to ensure structural integrity in load-bearing applications. Flitch plate connectors offer enhanced lateral stability and are often preferred in commercial construction for their ability to distribute loads uniformly, complying with building codes focused on seismic resistance. Beam bracket connectors, while easier to install and inspect, require rigorous adherence to manufacturer specifications and local codes to prevent potential failure under dynamic loading conditions.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your Project
Flitch plate connectors offer superior load distribution by combining steel plates with timber beams, ideal for projects requiring enhanced structural support and rigidity. Beam bracket connectors provide easier installation and flexibility for various beam-to-column connections, making them suitable for lighter loads or retrofit applications. Selecting the right connector hinges on factors like load capacity, installation complexity, and the specific structural requirements of your construction project.
Flitch plate connector vs Beam bracket connector Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com