A beam connector is specifically designed to join two structural beams, ensuring stability and load transfer in construction frameworks. A splice plate, on the other hand, is a flat piece of metal used to connect two sections of the same beam or structural member, reinforcing the joint to maintain strength. Both components are essential for structural integrity but serve different purposes depending on the connection type and load requirements.
Table of Comparison
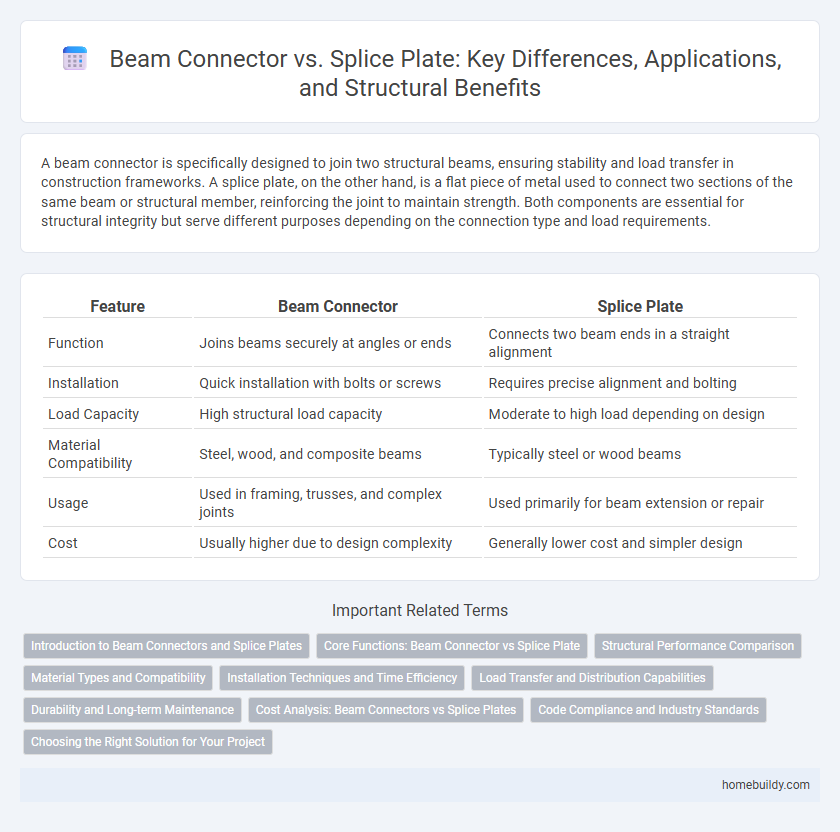
| Feature | Beam Connector | Splice Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Joins beams securely at angles or ends | Connects two beam ends in a straight alignment |
| Installation | Quick installation with bolts or screws | Requires precise alignment and bolting |
| Load Capacity | High structural load capacity | Moderate to high load depending on design |
| Material Compatibility | Steel, wood, and composite beams | Typically steel or wood beams |
| Usage | Used in framing, trusses, and complex joints | Used primarily for beam extension or repair |
| Cost | Usually higher due to design complexity | Generally lower cost and simpler design |
Introduction to Beam Connectors and Splice Plates
Beam connectors are engineered to join structural beams securely, providing superior load distribution and enhanced stability in construction projects. Splice plates, typically flat steel plates bolted or welded to beam ends, offer a straightforward method for connecting beams but may limit flexibility in load transfer compared to specialized beam connectors. Selecting between beam connectors and splice plates depends on factors such as load requirements, structural design complexity, and installation efficiency.
Core Functions: Beam Connector vs Splice Plate
Beam connectors primarily provide rigid and secure connections between beams and columns, ensuring structural stability and load transfer in construction frameworks. In contrast, splice plates function to join two beam sections end-to-end, effectively extending the beam length while maintaining alignment and strength. Both components are critical for maintaining integrity in steel or wooden framing systems, but beam connectors focus on angular or perpendicular connections, whereas splice plates emphasize longitudinal continuity.
Structural Performance Comparison
Beam connectors provide superior structural performance compared to splice plates by enhancing load transfer and reducing stress concentrations at joint interfaces. Unlike splice plates, beam connectors distribute forces more evenly across the connection, improving overall rigidity and resistance to bending moments. This results in increased durability and safety in structural applications, particularly in steel frame construction.
Material Types and Compatibility
Beam connectors typically utilize high-strength steel alloys, ensuring superior load-bearing capacity and corrosion resistance compared to splice plates, which often use standard mild steel. Compatibility-wise, beam connectors are designed for precise joint integration with various steel beam profiles, including I-beams and H-beams, offering enhanced structural stability. Splice plates may require additional welding or bolting adjustments due to their more generalized material composition and less tailored fit.
Installation Techniques and Time Efficiency
Beam connectors offer faster installation compared to splice plates due to their simplified attachment methods, often requiring fewer bolts or welds. Their design allows for quicker alignment and secure fastening, reducing labor time and minimizing the need for heavy equipment during assembly. In contrast, splice plates typically demand precise positioning and multiple fasteners, increasing both installation complexity and duration.
Load Transfer and Distribution Capabilities
Beam connectors provide superior load transfer by ensuring direct, continuous connection between structural elements, allowing for efficient distribution of shear and bending forces. Unlike splice plates, which rely on bolted or welded joints that may introduce stress concentrations, beam connectors enhance structural integrity by maintaining alignment and minimizing deformation under load. Their design optimizes load distribution across the connected beams, improving overall performance in dynamic and heavy-load applications.
Durability and Long-term Maintenance
Beam connectors offer superior durability compared to splice plates due to their ability to distribute loads more evenly and reduce stress concentrations. The use of robust materials like galvanized steel in beam connectors enhances resistance to corrosion and wear, minimizing long-term maintenance requirements. This results in extended structural integrity and reduced frequency of inspections or repairs in construction applications.
Cost Analysis: Beam Connectors vs Splice Plates
Beam connectors generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to splice plates due to reduced labor time and simplified installation processes, which lower overall project expenses. Splice plates often require precise alignment and additional fastening components, increasing material and labor costs. Selecting beam connectors can optimize budget allocation while maintaining structural integrity in construction projects.
Code Compliance and Industry Standards
Beam connectors and splice plates must comply with strict industry standards such as the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) and International Building Code (IBC) for structural safety. Beam connectors often provide enhanced performance in load transfer and ease of installation, meeting or exceeding ASTM testing requirements. Splice plates require precise installation to maintain code compliance, ensuring proper alignment and bolt grading as specified by standards like AWS D1.1 for steel welding.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Beam connectors provide superior load transfer and ease of installation compared to splice plates, making them ideal for projects requiring precise alignment and enhanced structural integrity. Splice plates, while cost-effective and simple to use, may not offer the same level of rigidity and are better suited for less demanding applications. Selecting the right solution depends on factors such as load requirements, installation speed, and long-term performance needs.
beam connector vs splice plate Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com