Beam connectors and joist hangers serve different structural purposes in construction; beam connectors attach beams securely to columns or other beams, providing critical support for heavy loads. Joist hangers are designed specifically to support joists, ensuring they remain flush and stable within a framework, preventing sagging or displacement. Choosing the appropriate fastener improves overall stability and load distribution in wood framing systems.
Table of Comparison
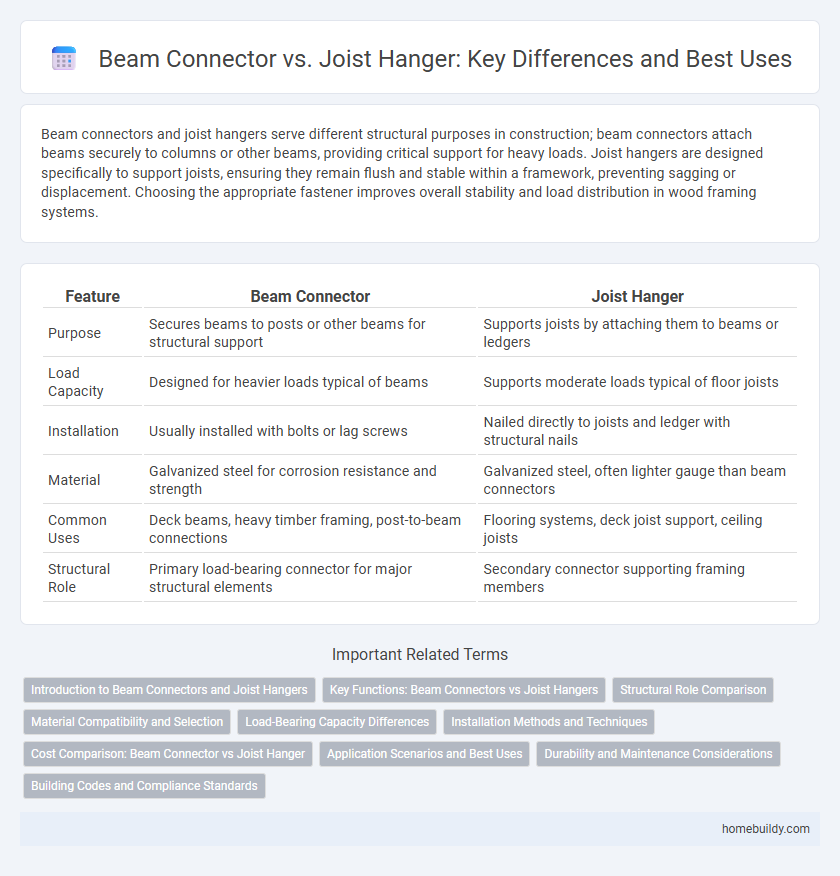
| Feature | Beam Connector | Joist Hanger |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Secures beams to posts or other beams for structural support | Supports joists by attaching them to beams or ledgers |
| Load Capacity | Designed for heavier loads typical of beams | Supports moderate loads typical of floor joists |
| Installation | Usually installed with bolts or lag screws | Nailed directly to joists and ledger with structural nails |
| Material | Galvanized steel for corrosion resistance and strength | Galvanized steel, often lighter gauge than beam connectors |
| Common Uses | Deck beams, heavy timber framing, post-to-beam connections | Flooring systems, deck joist support, ceiling joists |
| Structural Role | Primary load-bearing connector for major structural elements | Secondary connector supporting framing members |
Introduction to Beam Connectors and Joist Hangers
Beam connectors provide robust support by securely fastening beams to posts or other structural elements, ensuring stability in heavy load applications. Joist hangers are specifically designed to hold the ends of joists, offering precise alignment and enhanced load distribution in floor and ceiling framing. Both hardware components are essential in construction, with beam connectors optimized for larger structural loads and joist hangers tailored to framing requirements.
Key Functions: Beam Connectors vs Joist Hangers
Beam connectors provide robust lateral and vertical support by securely fastening beams to posts or other structural elements, enabling load transfer and stability in framing systems. Joist hangers primarily support horizontal members such as joists by anchoring them to ledger boards or beams, ensuring proper load distribution and preventing sagging. Both play critical roles in structural integrity, but beam connectors handle larger, multidirectional loads while joist hangers focus on precise alignment and support of joist spans.
Structural Role Comparison
Beam connectors provide critical support by securing beams to posts or other structural elements, distributing loads vertically and maintaining stability in heavy framing applications. Joist hangers primarily support horizontal joists within floor or ceiling systems, transferring concentrated loads to beams or walls while preventing lateral movement. The structural role of beam connectors is more versatile in load-bearing and framing connections, whereas joist hangers specialize in uniform load distribution for decking and flooring assemblies.
Material Compatibility and Selection
Beam connectors and joist hangers differ significantly in material compatibility and selection, with beam connectors often designed for heavier loads requiring steel or galvanized options for enhanced corrosion resistance. Joist hangers typically prioritize compatibility with wood structures, available in different steel grades and coatings to prevent rust and ensure structural integrity. Choosing between them depends on the specific application, load requirements, and environmental conditions to ensure proper connection and durability.
Load-Bearing Capacity Differences
Beam connectors typically offer higher load-bearing capacity compared to joist hangers due to their robust design and ability to support heavier structural beams. Joist hangers are primarily designed for lighter loads, securely fastening joists to beams or ledgers but with lower weight tolerance. Understanding load specifications in building codes is crucial when choosing between beam connectors and joist hangers for structural integrity.
Installation Methods and Techniques
Beam connectors typically require precise alignment and secure fastening using structural screws or bolts, allowing for strong load transfer between beams and columns. Joist hangers are installed by nailing directly to the supporting beam's face, providing a quicker, more straightforward attachment for securing joists but with less load capacity than beam connectors. Proper installation technique for beam connectors demands accurate positioning and torque control on fasteners to ensure maximum structural integrity and compliance with building codes.
Cost Comparison: Beam Connector vs Joist Hanger
Beam connectors typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to joist hangers, making them a cost-effective solution for supporting wooden beams in construction projects. While joist hangers provide greater load distribution and durability, their price is generally higher due to the use of heavier gauge steel and more complex manufacturing processes. Budget-conscious builders often select beam connectors for simpler applications where cost savings outweigh the enhanced structural benefits of joist hangers.
Application Scenarios and Best Uses
Beam connectors provide robust support for heavy, load-bearing beams in large structural frameworks, making them ideal for applications requiring high horizontal stability, such as decks and bridge construction. Joist hangers are best suited for securing lighter joists perpendicular to beams or ledgers, commonly used in flooring, ceiling, and roof framing where distributing vertical loads efficiently is critical. Selecting between beam connectors and joist hangers depends on the structural demands, load types, and installation angles specific to residential or commercial construction projects.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Beam connectors offer superior durability compared to joist hangers due to their robust steel construction and enhanced load-bearing capacity, reducing the risk of deformation over time. Maintenance requirements for beam connectors are minimal since their corrosion-resistant coatings prevent rust and degradation in harsh environmental conditions. Joist hangers, by contrast, may require more frequent inspections and upkeep to ensure structural integrity, especially in outdoor or moisture-prone applications.
Building Codes and Compliance Standards
Beam connectors and joist hangers must meet rigorous building codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) and American Wood Council's standards to ensure structural integrity. Compliance with ASTM specifications, including ASTM A653 for steel connectors, is critical for both products to guarantee load capacity and corrosion resistance. Understanding the differences in code requirements helps builders select the appropriate hardware for safe, code-compliant installation in wood framing systems.
beam connector vs joist hanger Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com