Slotted beam connectors offer flexibility by allowing slight adjustments during installation, improving alignment and reducing stress on structural components. Solid beam connectors provide superior strength and rigidity, ensuring stable and secure joints in heavy-load applications. Choosing between them depends on project requirements such as load capacity, ease of installation, and flexibility needed in the structural framework.
Table of Comparison
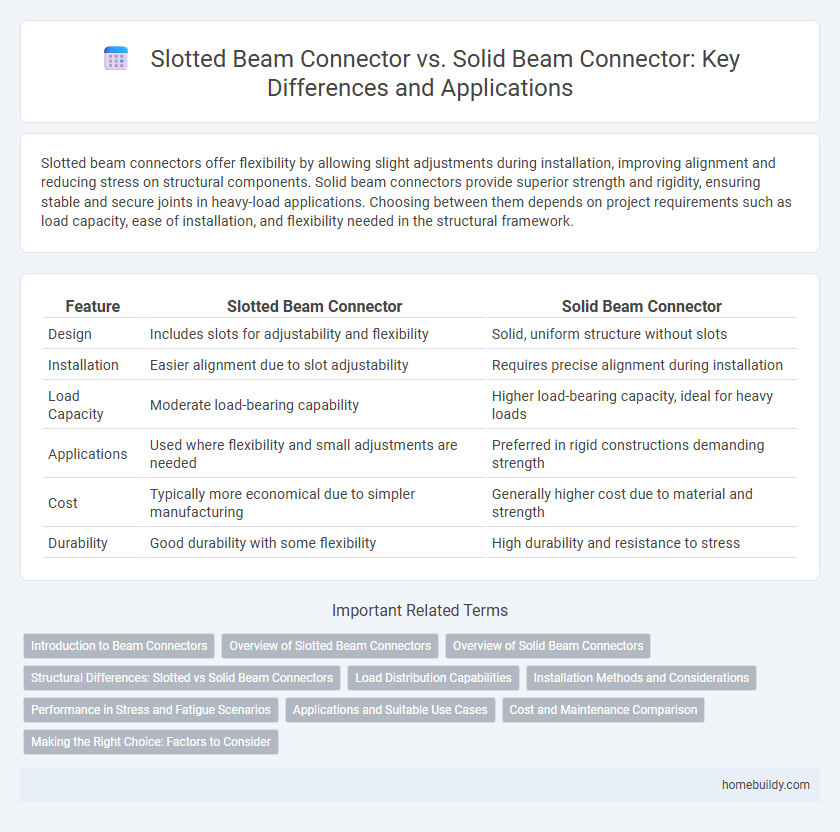
| Feature | Slotted Beam Connector | Solid Beam Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Includes slots for adjustability and flexibility | Solid, uniform structure without slots |
| Installation | Easier alignment due to slot adjustability | Requires precise alignment during installation |
| Load Capacity | Moderate load-bearing capability | Higher load-bearing capacity, ideal for heavy loads |
| Applications | Used where flexibility and small adjustments are needed | Preferred in rigid constructions demanding strength |
| Cost | Typically more economical due to simpler manufacturing | Generally higher cost due to material and strength |
| Durability | Good durability with some flexibility | High durability and resistance to stress |
Introduction to Beam Connectors
Slotted beam connectors feature a slot or groove that allows for adjustable positioning and easier alignment during assembly, making them ideal for applications requiring flexibility and precision. Solid beam connectors provide a fixed, robust connection with higher structural integrity and load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy-duty construction and permanent installations. Choosing between slotted and solid beam connectors depends on the specific project requirements, including adjustability, strength, and installation complexity.
Overview of Slotted Beam Connectors
Slotted beam connectors feature precisely engineered slots that allow for easy adjustment and alignment during installation, improving structural flexibility and load distribution. These connectors enable quicker assembly and enhanced adaptability in connecting beams, making them ideal for complex frameworks requiring precise positioning. Compared to solid beam connectors, slotted versions offer superior versatility and reduce installation errors in construction projects.
Overview of Solid Beam Connectors
Solid beam connectors provide robust structural support by ensuring a continuous, rigid connection between beams and columns, enhancing load transfer and stability in framing systems. Constructed from solid metal or composite materials, these connectors resist deformation and offer superior strength compared to slotted beam connectors, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Their fixed design minimizes movement and vibration, contributing to overall building integrity and longevity.
Structural Differences: Slotted vs Solid Beam Connectors
Slotted beam connectors feature precise slots allowing for flexible alignment and easier installation, whereas solid beam connectors provide rigid, continuous contact ensuring maximum load-bearing capacity and structural integrity. The slotted design accommodates slight adjustments and movement, reducing stress concentrations, while solid connectors excel in applications requiring high stiffness and minimal deflection. Material use varies accordingly, with slotted connectors often incorporating reinforcement around slots to maintain strength compared to uniformly solid connectors.
Load Distribution Capabilities
Slotted beam connectors offer enhanced load distribution capabilities by allowing slight movements within the slot, which reduces stress concentrations and improves structural flexibility. In contrast, solid beam connectors provide rigid connections that concentrate loads at specific points, potentially leading to higher stress and reduced overall load dispersal. Engineers favor slotted connectors in designs requiring dynamic load accommodation and improved durability under variable forces.
Installation Methods and Considerations
Slotted beam connectors simplify installation by allowing slight adjustments during assembly, making alignment easier on uneven surfaces, while solid beam connectors require precise pre-measurement and positioning for secure attachment. The slotted design accommodates minor structural movement and thermal expansion without compromising joint integrity, whereas solid connectors provide rigid, fixed connections best suited for stable, load-bearing applications. Choosing between these connectors depends on the project's tolerance for flexibility, load requirements, and installation environment constraints.
Performance in Stress and Fatigue Scenarios
Slotted beam connectors offer improved flexibility and stress distribution, reducing localized stress concentrations and enhancing fatigue resistance under cyclic loading. Solid beam connectors provide higher initial stiffness and load-bearing capacity but are more prone to stress accumulation and fatigue cracks due to reduced deformation capacity. In stress and fatigue scenarios, slotted connectors outperform solid ones by maintaining structural integrity and extending service life through better energy dissipation.
Applications and Suitable Use Cases
Slotted beam connectors are ideal for applications requiring flexibility and easy adjustments, commonly used in modular furniture and shelving systems where alignment and repositioning are critical. Solid beam connectors provide superior strength and rigidity, making them suitable for heavy-duty construction, permanent installations, and structural frameworks that demand high load-bearing capacity. Selecting between slotted and solid beam connectors depends on whether the project prioritizes adaptability or maximum structural integrity.
Cost and Maintenance Comparison
Slotted beam connectors typically offer lower initial costs due to simpler manufacturing processes and reduced material usage compared to solid beam connectors. Maintenance expenses for slotted connectors tend to be higher over time because the slots can accumulate debris and require more frequent inspections to prevent structural weaknesses. Solid beam connectors, while more expensive upfront, usually demand less maintenance and provide longer-lasting durability in high-stress environments.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Choosing between slotted beam connectors and solid beam connectors depends on load-bearing requirements, installation flexibility, and material strength. Slotted connectors offer adjustable positioning for complex assembly, enhancing structural alignment, while solid connectors provide superior rigidity and strength for heavy-duty applications. Evaluate project-specific factors such as load capacity, ease of customization, and environmental conditions to make an informed decision.
Slotted beam connector vs Solid beam connector Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com