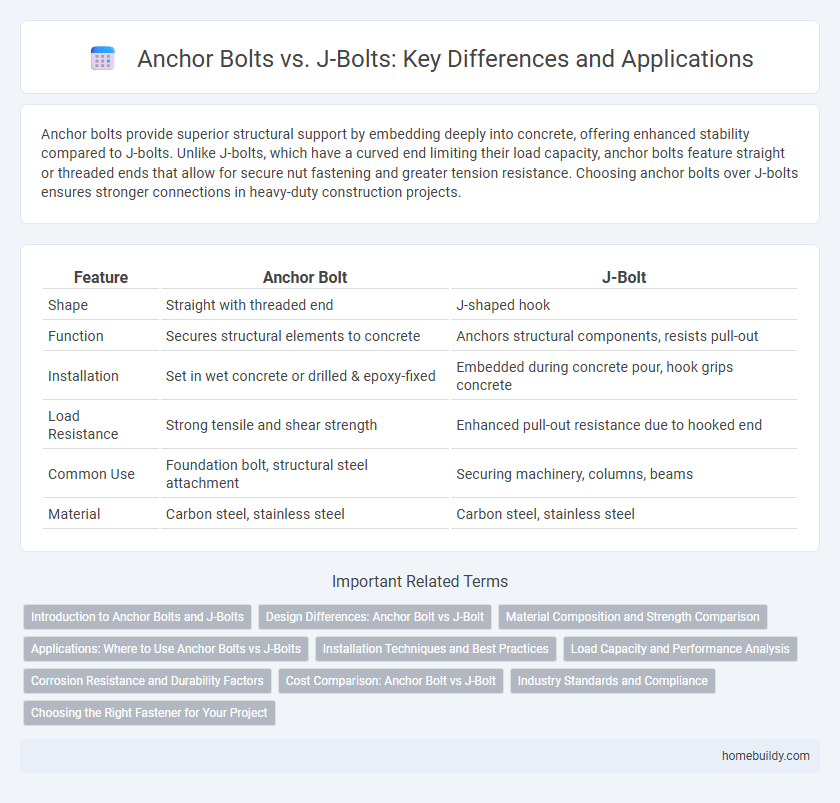
Anchor bolts provide superior structural support by embedding deeply into concrete, offering enhanced stability compared to J-bolts. Unlike J-bolts, which have a curved end limiting their load capacity, anchor bolts feature straight or threaded ends that allow for secure nut fastening and greater tension resistance. Choosing anchor bolts over J-bolts ensures stronger connections in heavy-duty construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anchor Bolt | J-Bolt |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Straight with threaded end | J-shaped hook |
| Function | Secures structural elements to concrete | Anchors structural components, resists pull-out |
| Installation | Set in wet concrete or drilled & epoxy-fixed | Embedded during concrete pour, hook grips concrete |
| Load Resistance | Strong tensile and shear strength | Enhanced pull-out resistance due to hooked end |
| Common Use | Foundation bolt, structural steel attachment | Securing machinery, columns, beams |
| Material | Carbon steel, stainless steel | Carbon steel, stainless steel |
Introduction to Anchor Bolts and J-Bolts
Anchor bolts are critical fasteners embedded in concrete to secure structural elements and withstand heavy loads, while J-bolts feature a distinctive curved end shaped like the letter "J" to enhance grip within concrete. Anchor bolts typically come straight or with varying hooked ends, designed for specific load requirements, whereas J-bolts provide superior resistance to pull-out forces due to their bent configuration. Both types ensure stability in construction, but the choice depends on the specific application, load conditions, and installation preferences.
Design Differences: Anchor Bolt vs J-Bolt
Anchor bolts feature a straight, often threaded shaft designed for embedment in concrete to provide secure structural connections, whereas J-bolts have a distinctive hooked end shaped like the letter "J" to prevent pull-out by anchoring deeper within the concrete. The design of anchor bolts typically supports vertical load resistance through friction and embedment depth, while J-bolts offer enhanced mechanical interlock due to their bent shape, improving resistance to tensile forces. These design differences influence their applications, with anchor bolts favored for adjustable connections and J-bolts preferred where higher pull-out strength is critical.
Material Composition and Strength Comparison
Anchor bolts are typically made from high-strength carbon steel or stainless steel, providing superior corrosion resistance and load-bearing capacity compared to J-bolts, which are often manufactured from mild steel. The material composition of anchor bolts enhances their tensile strength and durability under heavy structural loads, making them ideal for anchoring applications in concrete and masonry. In contrast, J-bolts have lower tensile strength due to their simpler steel grades and design, limiting their use in high-stress environments.
Applications: Where to Use Anchor Bolts vs J-Bolts
Anchor bolts excel in securing heavy machinery and structural components to concrete foundations, providing high load capacity and stability in industrial and commercial construction. J-bolts are commonly used for attaching base plates, columns, and light structural elements where embedded fastening is required, especially in wood framing and light steel structures. Choosing between anchor bolts and J-bolts depends on load requirements, environmental conditions, and the specific type of connection needed in foundation and structural applications.
Installation Techniques and Best Practices
Anchor bolts are typically installed by embedding them into concrete with precise positioning before the concrete sets, ensuring optimal structural support and load distribution. J-bolts, shaped like a "J," are often cast into concrete foundations, providing resistance to pull-out forces, but require careful alignment and secure fastening to prevent movement. Best practices for both include verifying bolt placement with templates, using corrosion-resistant materials, and ensuring proper torque specifications during installation to maximize durability and performance.
Load Capacity and Performance Analysis
Anchor bolts and J-bolts differ significantly in load capacity and performance analysis, with anchor bolts generally providing higher tensile and shear strength due to their straight shank and effective embedment depth. Performance tests show that anchor bolts offer superior resistance to dynamic loads and vibrations, making them ideal for heavy structural applications, whereas J-bolts tend to have a lower load capacity owing to their hook shape, which concentrates stress at the bend. Engineers often select anchor bolts for critical infrastructure requiring reliable load transfer and enhanced durability under fluctuating conditions.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability Factors
Anchor bolts offer superior corrosion resistance compared to J-bolts due to their typical use of galvanized or stainless steel materials, enhancing longevity in harsh environments. The threaded design of anchor bolts facilitates secure fastening and reduces the risk of loosening over time, improving durability under dynamic loads. In contrast, J-bolts, with their hooked shape, may be more susceptible to corrosion at bend points, which can compromise structural integrity in moisture-heavy or corrosive conditions.
Cost Comparison: Anchor Bolt vs J-Bolt
Anchor bolts generally have a higher upfront cost compared to J-bolts due to their robust design and enhanced load-bearing capacity, which makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications. J-bolts are typically less expensive and easier to install, offering a cost-effective solution for lighter structural requirements. When comparing long-term value, anchor bolts often provide better durability and reduced maintenance costs, offsetting their initial price difference in many construction projects.
Industry Standards and Compliance
Anchor bolts and J-bolts are both critical in construction for securing structural components, but they differ significantly in industry standards and compliance requirements. Anchor bolts must conform to ASTM F1554 or A307 standards, ensuring tensile strength and corrosion resistance for structural integrity, whereas J-bolts are typically designed to meet ASTM A307 specifications, focusing on bend radius and load capacity. Compliance with these standards impacts safety, performance, and regulatory approval in building projects, making the correct bolt selection essential for engineering reliability.
Choosing the Right Fastener for Your Project
Anchor bolts provide superior load-bearing capacity and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for structural applications requiring high strength and durability. J-bolts, with their easy installation and cost-effectiveness, are suitable for lightweight projects and temporary fixtures. Selecting the right fastener depends on project requirements such as load demands, environmental conditions, and long-term stability.
Anchor bolt vs J-bolt Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com