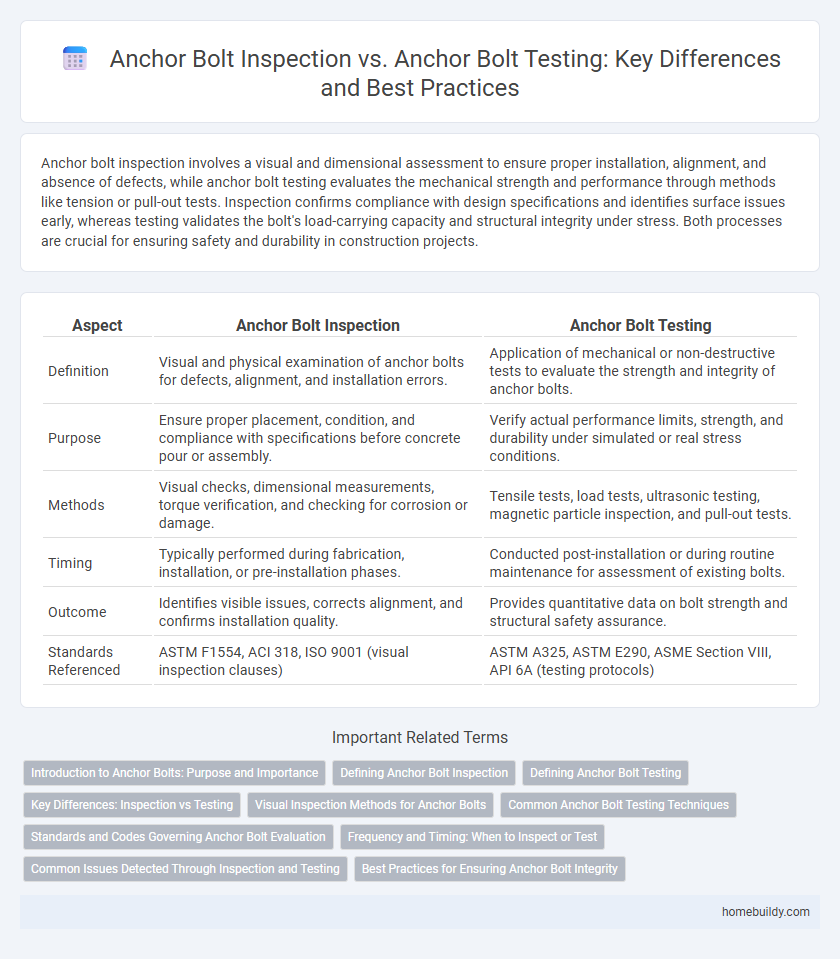
Anchor bolt inspection involves a visual and dimensional assessment to ensure proper installation, alignment, and absence of defects, while anchor bolt testing evaluates the mechanical strength and performance through methods like tension or pull-out tests. Inspection confirms compliance with design specifications and identifies surface issues early, whereas testing validates the bolt's load-carrying capacity and structural integrity under stress. Both processes are crucial for ensuring safety and durability in construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Anchor Bolt Inspection | Anchor Bolt Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visual and physical examination of anchor bolts for defects, alignment, and installation errors. | Application of mechanical or non-destructive tests to evaluate the strength and integrity of anchor bolts. |
| Purpose | Ensure proper placement, condition, and compliance with specifications before concrete pour or assembly. | Verify actual performance limits, strength, and durability under simulated or real stress conditions. |
| Methods | Visual checks, dimensional measurements, torque verification, and checking for corrosion or damage. | Tensile tests, load tests, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and pull-out tests. |
| Timing | Typically performed during fabrication, installation, or pre-installation phases. | Conducted post-installation or during routine maintenance for assessment of existing bolts. |
| Outcome | Identifies visible issues, corrects alignment, and confirms installation quality. | Provides quantitative data on bolt strength and structural safety assurance. |
| Standards Referenced | ASTM F1554, ACI 318, ISO 9001 (visual inspection clauses) | ASTM A325, ASTM E290, ASME Section VIII, API 6A (testing protocols) |
Introduction to Anchor Bolts: Purpose and Importance
Anchor bolt inspection involves visual assessment and verification of proper installation, ensuring bolts are free from defects, corrosion, and alignment issues critical for structural stability. Anchor bolt testing evaluates mechanical properties such as tensile strength and embedment integrity to confirm performance under load conditions. Both inspection and testing are essential to guarantee anchor bolts fulfill their role in securing structural elements and maintaining overall safety.
Defining Anchor Bolt Inspection
Anchor bolt inspection involves a thorough visual and physical assessment to verify correct installation, alignment, and condition before concrete pouring or structural assembly. It ensures fastener placement meets engineering specifications, identifies defects such as corrosion, bending, or improper embedment, and confirms compliance with design drawings. This process is critical for structural integrity, distinguishing it from anchor bolt testing, which typically evaluates mechanical properties under load.
Defining Anchor Bolt Testing
Anchor bolt testing involves a series of procedures to evaluate the strength, durability, and installation quality of anchor bolts, ensuring they meet engineering standards and safety requirements. Unlike inspection, which visually assesses the condition and placement, testing uses methods such as torque testing, load testing, and non-destructive evaluation to verify the bolt's performance under operational stresses. Effective anchor bolt testing is critical to preventing structural failures and guaranteeing long-term stability in construction projects.
Key Differences: Inspection vs Testing
Anchor bolt inspection involves a visual and physical examination to identify surface defects, alignment, and proper installation according to project specifications. Anchor bolt testing assesses material properties and structural integrity through methods such as tensile, pull-out, or ultrasonic tests to ensure performance under load. The key difference lies in inspection focusing on observable conditions, while testing evaluates mechanical strength and durability.
Visual Inspection Methods for Anchor Bolts
Visual inspection methods for anchor bolts primarily involve checking for surface defects such as corrosion, cracks, and deformation that compromise structural integrity. These inspections use tools like magnifying glasses, borescopes, and digital cameras to detect visible irregularities without causing damage. Unlike destructive testing, visual inspections provide a non-invasive, quick assessment to ensure anchor bolts meet safety and performance standards.
Common Anchor Bolt Testing Techniques
Anchor bolt inspection primarily involves visual assessment for corrosion, alignment, and damage, ensuring compliance with installation standards. Anchor bolt testing techniques commonly include tension testing, ultrasonic testing, and magnetic particle inspection, which detect internal defects and verify material strength. These testing methods provide quantitative data that supplements inspection findings, ensuring anchor bolt reliability in structural applications.
Standards and Codes Governing Anchor Bolt Evaluation
Anchor bolt inspection involves visual and dimensional checks to ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM F1554 and ACI 318, which specify material properties and installation criteria. Anchor bolt testing includes mechanical evaluations like tension and pull-out strength tests conducted according to ASTM E488 and ASCE 7 guidelines to verify performance under load. Both inspection and testing are governed by codes emphasizing safety, durability, and structural integrity in construction applications.
Frequency and Timing: When to Inspect or Test
Anchor bolt inspection should be performed regularly during installation and post-installation phases to ensure proper placement, alignment, and integrity before concrete curing. Anchor bolt testing, including load and pull-out tests, is typically conducted after installation to verify functional performance and compliance with design specifications. Inspection frequency is often higher and more visual, while testing is performed less frequently but involves precise measurement under controlled conditions.
Common Issues Detected Through Inspection and Testing
Anchor bolt inspection identifies visible defects such as corrosion, misalignment, and damaged threads, which can compromise structural integrity. Anchor bolt testing evaluates the mechanical properties and load-bearing capacity, detecting issues like insufficient embedment depth and inadequate tensile strength. Both inspection and testing are critical for ensuring anchor bolts meet safety standards and performance requirements in construction projects.
Best Practices for Ensuring Anchor Bolt Integrity
Anchor bolt inspection involves a thorough visual assessment to identify surface defects, corrosion, and proper installation alignment, ensuring foundational stability and structural safety. Anchor bolt testing includes non-destructive methods such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and torque verification to detect internal flaws and confirm mechanical performance. Combining regular inspections with precise testing protocols adheres to best practices for maintaining anchor bolt integrity and preventing structural failures.
Anchor bolt inspection vs Anchor bolt testing Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com