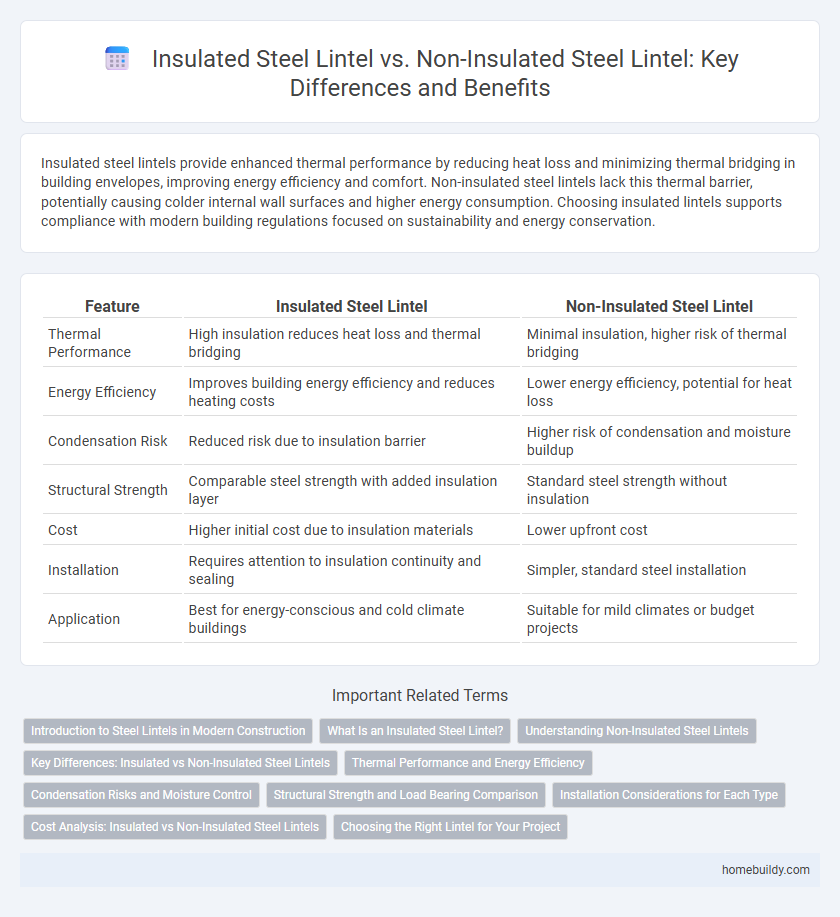
Insulated steel lintels provide enhanced thermal performance by reducing heat loss and minimizing thermal bridging in building envelopes, improving energy efficiency and comfort. Non-insulated steel lintels lack this thermal barrier, potentially causing colder internal wall surfaces and higher energy consumption. Choosing insulated lintels supports compliance with modern building regulations focused on sustainability and energy conservation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Insulated Steel Lintel | Non-Insulated Steel Lintel |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Performance | High insulation reduces heat loss and thermal bridging | Minimal insulation, higher risk of thermal bridging |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves building energy efficiency and reduces heating costs | Lower energy efficiency, potential for heat loss |
| Condensation Risk | Reduced risk due to insulation barrier | Higher risk of condensation and moisture buildup |
| Structural Strength | Comparable steel strength with added insulation layer | Standard steel strength without insulation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to insulation materials | Lower upfront cost |
| Installation | Requires attention to insulation continuity and sealing | Simpler, standard steel installation |
| Application | Best for energy-conscious and cold climate buildings | Suitable for mild climates or budget projects |
Introduction to Steel Lintels in Modern Construction
Steel lintels serve as critical structural elements in modern construction, supporting loads above openings such as windows and doors. Insulated steel lintels incorporate thermal breaks or insulation materials that reduce heat transfer, improving energy efficiency compared to non-insulated steel lintels. Choosing insulated steel lintels helps meet building regulations for thermal performance while maintaining the strength and durability required for structural stability.
What Is an Insulated Steel Lintel?
An insulated steel lintel is a structural component designed to support loads above openings like windows and doors while incorporating a thermal break to reduce heat transfer. Unlike non-insulated steel lintels, insulated lintels contain a layer of insulation material between steel sections, enhancing energy efficiency and minimizing thermal bridging in building envelopes. These features help maintain interior temperature stability and contribute to achieving better thermal performance standards in construction.
Understanding Non-Insulated Steel Lintels
Non-insulated steel lintels consist of a solid steel section without any thermal break or insulation material, resulting in higher thermal conductivity and potential cold bridging in building envelopes. These lintels are typically chosen for interior applications or areas where thermal performance is not a critical factor. Understanding the heat transfer properties and structural capabilities of non-insulated steel lintels is essential when assessing their suitability for specific construction projects.
Key Differences: Insulated vs Non-Insulated Steel Lintels
Insulated steel lintels feature built-in thermal breaks or insulation materials, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency in building envelopes. Non-insulated steel lintels lack these thermal barriers, resulting in higher thermal bridging and potential condensation issues. The choice between insulated and non-insulated lintels significantly impacts thermal performance, moisture control, and compliance with energy codes in construction projects.
Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
Insulated steel lintels significantly improve thermal performance by reducing heat transfer through the lintel, helping to maintain consistent indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption. Non-insulated steel lintels often create thermal bridging, leading to heat loss and increased heating or cooling demands. Using insulated steel lintels enhances overall energy efficiency in buildings, contributing to lower utility bills and improved compliance with energy codes.
Condensation Risks and Moisture Control
Insulated steel lintels effectively reduce condensation risks by providing a thermal break that minimizes cold bridging, preventing moisture buildup on interior surfaces. Non-insulated steel lintels often lead to temperature differentials that cause condensation, increasing the potential for mold growth and structural deterioration. Proper moisture control is enhanced with insulated steel lintels, promoting durability and indoor air quality by maintaining consistent thermal performance across the window opening.
Structural Strength and Load Bearing Comparison
Insulated steel lintels feature a thermal break that reduces heat transfer while maintaining comparable structural strength to non-insulated steel lintels. Non-insulated steel lintels often exhibit higher thermal conductivity but provide robust load-bearing capacity suitable for heavy masonry loads. Both types are engineered to meet building codes, yet insulated steel lintels offer enhanced energy efficiency without compromising essential structural performance.
Installation Considerations for Each Type
Insulated steel lintels require careful handling to maintain the integrity of the insulation layer during installation, necessitating precise alignment and sealing to prevent thermal bridging and energy loss. Non-insulated steel lintels are simpler to install but demand additional measures such as the application of separate insulating materials to meet energy efficiency standards. Both types require secure anchoring into masonry structures, but insulated lintels often involve more complex detailing to integrate moisture barriers and thermal breaks effectively.
Cost Analysis: Insulated vs Non-Insulated Steel Lintels
Insulated steel lintels typically have higher initial costs due to the added thermal break materials and manufacturing processes, but they provide significant energy savings by reducing thermal bridging and enhancing building insulation efficiency. Non-insulated steel lintels are less expensive upfront but may lead to increased heating and cooling expenses over time due to heat loss. Long-term cost analysis favors insulated steel lintels in energy-efficient building designs, especially in climates with extreme temperature variations.
Choosing the Right Lintel for Your Project
Insulated steel lintels provide superior thermal performance by reducing heat transfer and preventing cold bridging, making them ideal for energy-efficient building projects. Non-insulated steel lintels offer cost-effective structural support but may lead to higher thermal conductivity and potential condensation issues in colder climates. Selecting the right lintel depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for improved insulation and compliance with local building codes.
insulated steel lintel vs non-insulated steel lintel Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com