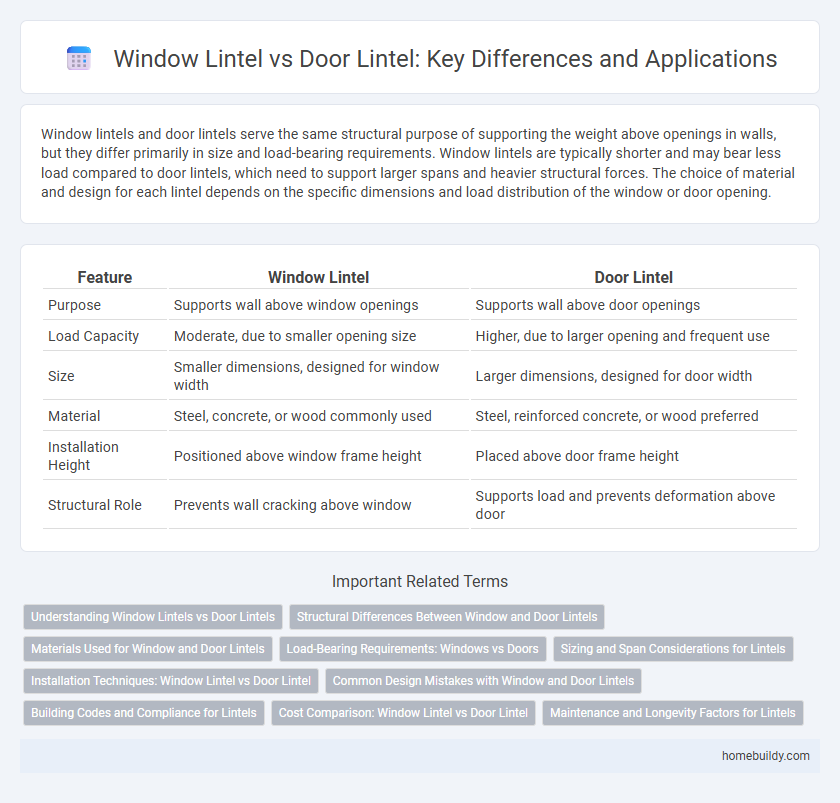
Window lintels and door lintels serve the same structural purpose of supporting the weight above openings in walls, but they differ primarily in size and load-bearing requirements. Window lintels are typically shorter and may bear less load compared to door lintels, which need to support larger spans and heavier structural forces. The choice of material and design for each lintel depends on the specific dimensions and load distribution of the window or door opening.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Window Lintel | Door Lintel |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Supports wall above window openings | Supports wall above door openings |
| Load Capacity | Moderate, due to smaller opening size | Higher, due to larger opening and frequent use |
| Size | Smaller dimensions, designed for window width | Larger dimensions, designed for door width |
| Material | Steel, concrete, or wood commonly used | Steel, reinforced concrete, or wood preferred |
| Installation Height | Positioned above window frame height | Placed above door frame height |
| Structural Role | Prevents wall cracking above window | Supports load and prevents deformation above door |
Understanding Window Lintels vs Door Lintels
Window lintels and door lintels differ primarily in size and load-bearing requirements, with window lintels typically being shorter and supporting lighter loads due to smaller spans. Door lintels must withstand greater structural stresses since doors generally have larger openings and increased traffic loads. Material choices for both lintels often overlap, but design considerations prioritize strength and durability based on the specific opening dimensions and usage.
Structural Differences Between Window and Door Lintels
Window lintels are generally lighter and shorter than door lintels due to the smaller span and load they support, primarily holding up the masonry above window openings. Door lintels require greater strength and depth to bear the increased weight and stress from larger openings and higher traffic impact. The structural differences include variations in material thickness, reinforcement, and support design tailored to the distinct load demands of windows versus doors.
Materials Used for Window and Door Lintels
Window lintels are commonly constructed from reinforced concrete, steel, or timber, chosen for their ability to bear moderate loads and fit within narrower wall openings. Door lintels typically require stronger materials such as steel beams or reinforced concrete with higher reinforcement, designed to support heavier structural loads due to larger span widths. Both window and door lintels utilize materials based on load-bearing requirements, but door lintels often incorporate more robust reinforcement to accommodate greater stress.
Load-Bearing Requirements: Windows vs Doors
Window lintels typically bear less load compared to door lintels due to smaller openings and reduced weight above. Door lintels require higher strength and rigidity to support heavier structural loads and dynamic forces from foot traffic. Material selection and cross-sectional size are critical in meeting these load-bearing requirements for both window and door lintels.
Sizing and Span Considerations for Lintels
Window lintels typically have smaller sizing and shorter span requirements compared to door lintels due to the reduced opening width and load distribution. Door lintels must accommodate wider spans and heavier structural loads, often necessitating stronger materials and larger cross-sections. Accurate span calculation and sizing ensure structural integrity and prevent deformation above both window and door openings.
Installation Techniques: Window Lintel vs Door Lintel
Window lintels are installed with precise sizing to accommodate smaller spans and often support lighter loads compared to door lintels, which require robust construction due to wider openings and heavier load-bearing needs. Installation techniques for window lintels emphasize tight fitting within the masonry to prevent air leaks and ensure thermal efficiency, whereas door lintels involve deeper embedment and stronger reinforcement to manage structural stresses. Both lintel types use materials like reinforced concrete or steel, but door lintels often necessitate additional anchoring and sealing practices to maintain durability and security.
Common Design Mistakes with Window and Door Lintels
Common design mistakes with window and door lintels include improper sizing that fails to support the load, leading to structural weaknesses. Using the same lintel specifications for both windows and doors disregards differing load requirements and span widths, causing potential defects. Insufficient reinforcement and neglecting thermal insulation around lintels can result in cracks and energy inefficiency in the building envelope.
Building Codes and Compliance for Lintels
Window lintels and door lintels must both comply with local building codes, which specify load-bearing capacities, materials, and installation methods to ensure structural integrity. Building codes often require window lintels to accommodate lighter loads compared to door lintels, reflecting different span widths and expected stress levels. Compliance with these standards is critical for safety, preventing structural failures and ensuring legal approval during construction inspections.
Cost Comparison: Window Lintel vs Door Lintel
Window lintels generally cost less than door lintels due to their smaller size and lighter load-bearing requirements. Door lintels must support larger openings and more structural weight, which increases material and installation expenses. The cost difference between window and door lintels can range from 20% to 50%, depending on dimensions and material choices like steel, concrete, or wood.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors for Lintels
Window lintels generally require less maintenance than door lintels due to their smaller size and reduced load-bearing demands. The longevity of both lintels depends on the material, with reinforced concrete and steel offering superior durability compared to stone or wood. Proper sealing and regular inspection to prevent moisture ingress significantly enhance the lifespan of lintels in both window and door applications.
window lintel vs door lintel Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com