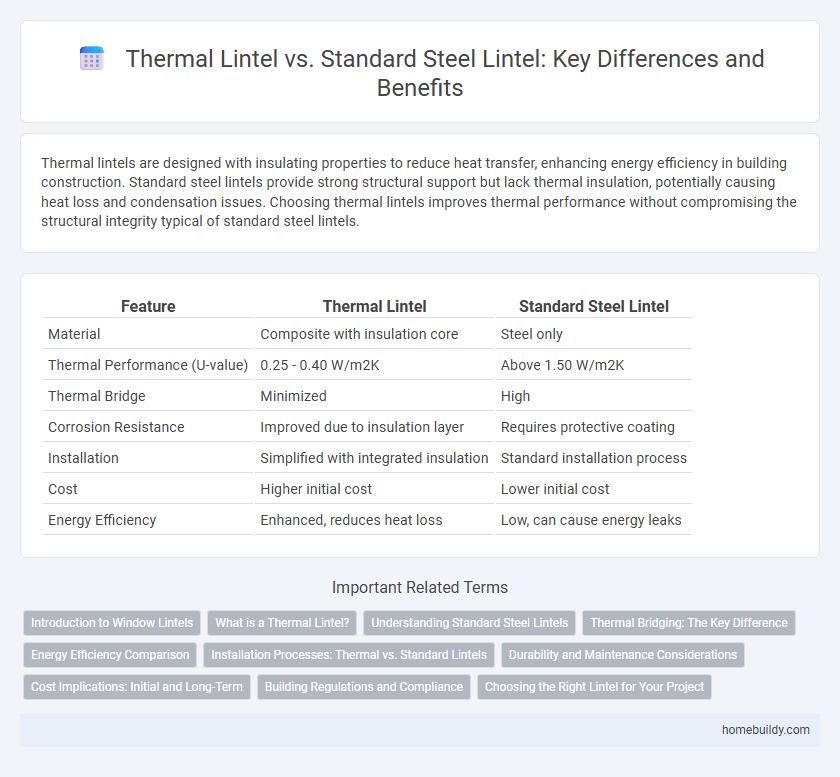
Thermal lintels are designed with insulating properties to reduce heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency in building construction. Standard steel lintels provide strong structural support but lack thermal insulation, potentially causing heat loss and condensation issues. Choosing thermal lintels improves thermal performance without compromising the structural integrity typical of standard steel lintels.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Thermal Lintel | Standard Steel Lintel |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Composite with insulation core | Steel only |
| Thermal Performance (U-value) | 0.25 - 0.40 W/m2K | Above 1.50 W/m2K |
| Thermal Bridge | Minimized | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Improved due to insulation layer | Requires protective coating |
| Installation | Simplified with integrated insulation | Standard installation process |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Energy Efficiency | Enhanced, reduces heat loss | Low, can cause energy leaks |
Introduction to Window Lintels
Window lintels serve as critical structural supports above openings, bearing loads from the wall above. Thermal lintels incorporate insulating materials to reduce thermal bridging and improve energy efficiency, unlike standard steel lintels that conduct heat and can cause heat loss. Choosing thermal lintels enhances building performance by minimizing cold spots and moisture buildup around window frames.
What is a Thermal Lintel?
A thermal lintel is an insulated steel lintel designed to reduce heat transfer across window and door openings, improving the building's energy efficiency. Unlike standard steel lintels, which lack thermal breaks and can create cold bridges, thermal lintels feature a polyurethane or polystyrene core that minimizes thermal conductivity. This innovation helps prevent condensation and enhances overall thermal performance in modern construction.
Understanding Standard Steel Lintels
Standard steel lintels are structural supports commonly used above window openings to bear the load of the wall above. They consist of galvanized steel angles or channels designed to provide strength and durability while resisting corrosion. Unlike thermal lintels, standard steel lintels lack insulation properties, which can result in thermal bridging and reduced energy efficiency in building envelopes.
Thermal Bridging: The Key Difference
Thermal lintels significantly reduce thermal bridging compared to standard steel lintels by incorporating insulated materials that prevent heat transfer through the window opening. This insulation enhances energy efficiency and minimizes condensation risks, contributing to improved building performance. Standard steel lintels, lacking this thermal break, create cold spots that increase heat loss and compromise thermal comfort.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Thermal lintels offer superior energy efficiency compared to standard steel lintels by reducing thermal bridging and minimizing heat loss around window openings. These lintels incorporate insulating materials or thermal breaks that enhance the overall building envelope performance and help maintain consistent indoor temperatures. Choosing thermal lintels can significantly lower heating and cooling costs while improving comfort and reducing carbon emissions.
Installation Processes: Thermal vs. Standard Lintels
Thermal lintels simplify installation by integrating insulation directly within the steel frame, reducing the need for additional thermal barriers and minimizing on-site adjustments. Standard steel lintels demand supplementary insulation materials and meticulous sealing during installation to prevent thermal bridging and energy loss. Installing thermal lintels typically shortens labor time and enhances building envelope performance compared to standard steel lintels.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Thermal lintels are designed with insulated cores, significantly reducing thermal bridging and condensation risks compared to standard steel lintels, which often require additional insulation to prevent heat loss. Durability of thermal lintels is enhanced by corrosion-resistant coatings, decreasing long-term maintenance needs, whereas standard steel lintels are prone to rust and require regular painting or treatment. Maintenance considerations favor thermal lintels due to their integrated insulation and protective layers, reducing repair frequency and extending lifespan in both residential and commercial construction.
Cost Implications: Initial and Long-Term
Thermal lintels typically incur higher initial costs than standard steel lintels due to their insulated design and materials that reduce thermal bridging. Over the long term, thermal lintels contribute to lower energy bills and increased building efficiency by enhancing insulation and minimizing heat loss. Standard steel lintels may save on upfront expenses but can lead to higher heating and cooling costs, affecting overall building cost efficiency.
Building Regulations and Compliance
Thermal lintels are specifically designed to meet stringent Building Regulations by providing enhanced insulation properties that reduce thermal bridging around window openings. Standard steel lintels often lack adequate thermal breaks, potentially resulting in heat loss and non-compliance with regulations such as Approved Document L. Incorporating thermal lintels ensures compliance with energy efficiency standards and helps achieve targets for fabric energy performance in modern construction.
Choosing the Right Lintel for Your Project
Thermal lintels provide enhanced insulation properties by incorporating a polyurethane core that reduces thermal bridging compared to standard steel lintels. Selecting the right lintel depends on the building's energy efficiency requirements, with thermal lintels ideal for meeting stringent thermal performance standards in modern construction. Standard steel lintels remain suitable for non-insulated or renovation projects where thermal performance is less critical.
thermal lintel vs standard steel lintel Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com