A thermal break lintel significantly improves energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer through the building envelope, unlike a standard lintel that allows more thermal bridging. This innovation helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures, lowering heating and cooling costs. Installing thermal break lintels is crucial for meeting modern building regulations focused on sustainability and energy performance.
Table of Comparison
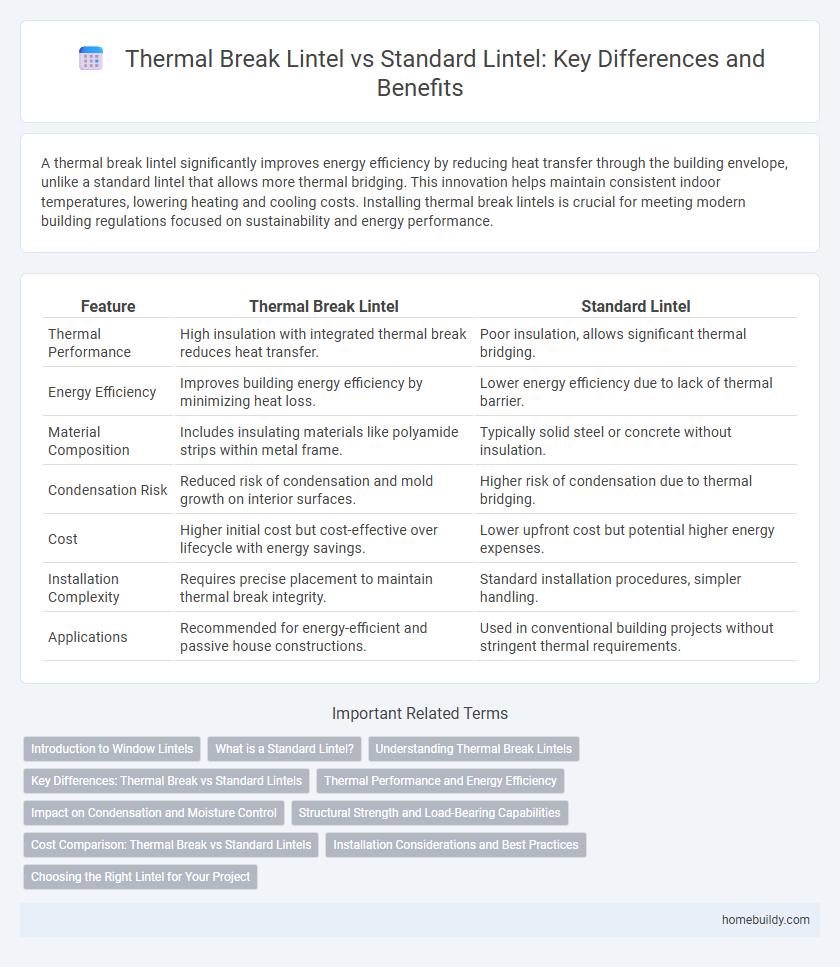
| Feature | Thermal Break Lintel | Standard Lintel |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Performance | High insulation with integrated thermal break reduces heat transfer. | Poor insulation, allows significant thermal bridging. |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves building energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss. | Lower energy efficiency due to lack of thermal barrier. |
| Material Composition | Includes insulating materials like polyamide strips within metal frame. | Typically solid steel or concrete without insulation. |
| Condensation Risk | Reduced risk of condensation and mold growth on interior surfaces. | Higher risk of condensation due to thermal bridging. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but cost-effective over lifecycle with energy savings. | Lower upfront cost but potential higher energy expenses. |
| Installation Complexity | Requires precise placement to maintain thermal break integrity. | Standard installation procedures, simpler handling. |
| Applications | Recommended for energy-efficient and passive house constructions. | Used in conventional building projects without stringent thermal requirements. |
Introduction to Window Lintels
Window lintels provide critical structural support above openings, distributing loads from above to prevent stress on window frames. Thermal break lintels incorporate insulating materials to reduce thermal bridging, significantly enhancing energy efficiency compared to standard lintels made solely from steel or concrete. This thermal separation minimizes heat loss and condensation risks, contributing to improved building performance and occupant comfort.
What is a Standard Lintel?
A standard lintel is a structural horizontal support typically made from steel, concrete, or timber, spanning the opening above windows or doors to bear loads from the wall above. Unlike thermal break lintels, standard lintels do not incorporate insulating materials, leading to potential thermal bridging and heat loss. This lack of thermal separation can reduce energy efficiency and increase condensation risks around window openings in building envelopes.
Understanding Thermal Break Lintels
Thermal break lintels incorporate insulating materials such as polyurethane or expanded polystyrene to significantly reduce thermal bridging compared to standard steel or concrete lintels. This enhancement improves energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss and condensation risk around window openings in walls. Choosing thermal break lintels supports compliance with energy regulations and contributes to improved building envelope performance.
Key Differences: Thermal Break vs Standard Lintels
Thermal break lintels feature insulating materials that reduce heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency and minimizing condensation risks in buildings, whereas standard lintels are typically made of steel or concrete without thermal insulation, leading to potential thermal bridging. The design of thermal break lintels incorporates a thermal barrier that interrupts the conductivity of heat, which is absent in standard lintels, affecting overall building thermal performance. Choosing thermal break lintels contributes to lower heating and cooling costs and improved indoor comfort compared to standard lintels.
Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
Thermal break lintels significantly improve thermal performance by minimizing heat transfer through the window opening, reducing thermal bridging compared to standard steel or concrete lintels. Enhanced energy efficiency results from their insulated core materials, which maintain consistent indoor temperatures and lower heating and cooling costs. Using thermal break lintels supports building compliance with energy codes and promotes sustainability in construction projects.
Impact on Condensation and Moisture Control
Thermal break lintels significantly reduce thermal bridging compared to standard lintels, minimizing condensation risks around window openings by maintaining warmer internal surface temperatures. This improved insulation barrier prevents moisture accumulation and mold growth, enhancing the building's overall moisture control. Standard lintels, lacking thermal breaks, often cause cold spots where condensation can form, potentially compromising structural integrity and indoor air quality.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capabilities
Thermal break lintels incorporate insulating materials that reduce thermal bridging while maintaining robust structural strength comparable to standard lintels. Standard lintels, typically made from steel or reinforced concrete, excel in load-bearing capabilities but lack the thermal efficiency provided by thermal breaks. Choosing a thermal break lintel ensures effective support for openings with enhanced energy performance without compromising load-bearing capacity.
Cost Comparison: Thermal Break vs Standard Lintels
Thermal break lintels typically cost 20-30% more than standard lintels due to added insulation materials like foam or plastic inserts that reduce thermal bridging. However, the higher upfront cost can be offset by improved energy efficiency, leading to lower heating and cooling expenses over the building's lifecycle. Standard lintels have lower initial costs but may contribute to increased energy loss and potential condensation issues, resulting in higher maintenance and utility costs long-term.
Installation Considerations and Best Practices
Thermal break lintels require careful alignment with insulation layers to prevent thermal bridging and ensure energy efficiency, making precision during installation crucial. Standard lintels typically offer simpler installation without the need for additional thermal insulation integration, reducing labor time but compromising on energy performance. Best practices for thermal break lintel installation include using compatible insulation materials, maintaining continuous thermal barriers, and verifying airtight seals to enhance building envelope performance.
Choosing the Right Lintel for Your Project
Choosing the right lintel for your project involves understanding the thermal performance of thermal break lintels compared to standard lintels. Thermal break lintels incorporate insulating materials that reduce heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency and minimizing thermal bridging in window installations. Standard lintels, typically made of steel or concrete without insulation, may lead to increased heat loss and condensation issues, making thermal break lintels the preferred choice for sustainable building projects.
thermal break lintel vs standard lintel Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com