A tie rod connects the steering rack to the steering arm, directly controlling wheel direction and alignment. A link bar, or sway bar link, connects the sway bar to the suspension, stabilizing the vehicle during turns by reducing body roll. Both components are essential for safe handling but serve distinct functions in the steering and suspension systems.
Table of Comparison
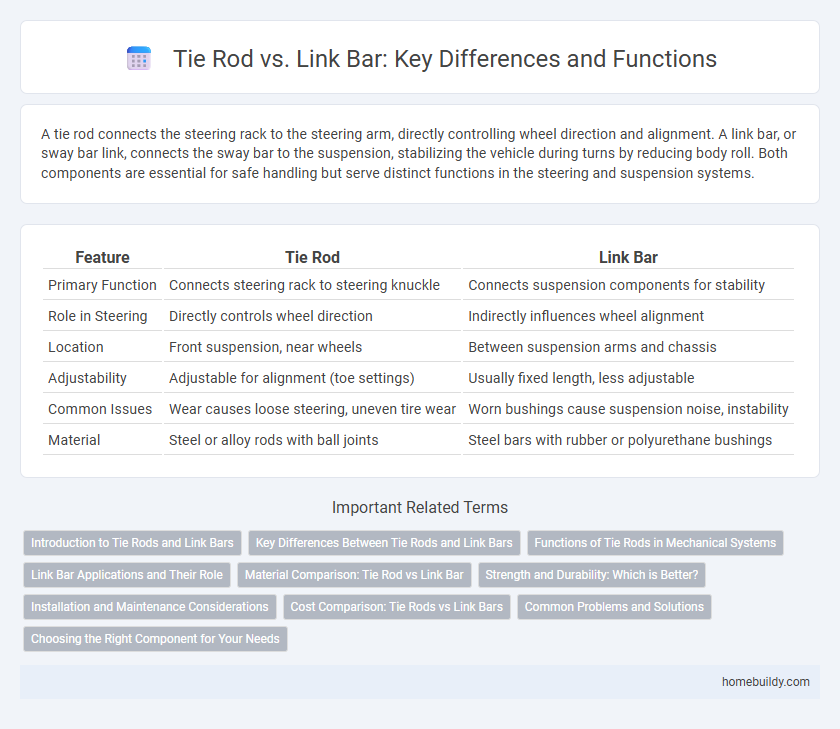
| Feature | Tie Rod | Link Bar |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Connects steering rack to steering knuckle | Connects suspension components for stability |
| Role in Steering | Directly controls wheel direction | Indirectly influences wheel alignment |
| Location | Front suspension, near wheels | Between suspension arms and chassis |
| Adjustability | Adjustable for alignment (toe settings) | Usually fixed length, less adjustable |
| Common Issues | Wear causes loose steering, uneven tire wear | Worn bushings cause suspension noise, instability |
| Material | Steel or alloy rods with ball joints | Steel bars with rubber or polyurethane bushings |
Introduction to Tie Rods and Link Bars
Tie rods are crucial suspension components that connect the steering rack to the steering knuckle, enabling precise wheel control and alignment. Link bars, often used interchangeably in casual conversation, typically refer to various suspension links that serve distinct roles such as stabilizing or controlling suspension movement. Understanding the differences between tie rods and link bars is essential for diagnosing steering issues and ensuring optimal vehicle handling performance.
Key Differences Between Tie Rods and Link Bars
Tie rods primarily serve to steer the vehicle by transmitting force from the steering center link or rack gear to the steering knuckle, allowing precise wheel angle control. Link bars, on the other hand, connect suspension components for stability and alignment, typically absorbing lateral forces rather than steering inputs. The key differences lie in their functions--tie rods are integral to steering mechanics, while link bars support suspension geometry and vehicle handling.
Functions of Tie Rods in Mechanical Systems
Tie rods in mechanical systems primarily provide essential structural support by transmitting tensile forces, ensuring stability and alignment in assemblies such as steering mechanisms and suspension systems. Unlike link bars, which often transfer compressive and compressive-tensile loads and facilitate motion control, tie rods are designed specifically to resist tension and prevent components from separating under load. Their function is critical in maintaining precise positioning and reducing mechanical wear, thereby enhancing overall system durability and performance.
Link Bar Applications and Their Role
Link bars play a crucial role in automotive and mechanical systems by providing precise control and stability in suspension and steering mechanisms. Unlike tie rods, link bars are often used to connect different suspension components, such as control arms and sway bars, enhancing vehicle handling and reducing unwanted movement. Their applications extend to off-road vehicles, heavy machinery, and performance cars where robust and adjustable connections are necessary for optimal alignment and responsiveness.
Material Comparison: Tie Rod vs Link Bar
Tie rods are typically manufactured from high-strength steel alloys, offering superior tensile strength and durability under dynamic loads compared to link bars, which are often made from lighter metals such as aluminum or composite materials to prioritize weight reduction. The enhanced material composition of tie rods ensures better resistance to bending and torsional stresses, crucial for maintaining precise steering and suspension alignment in automotive and heavy machinery applications. Conversely, link bars benefit from corrosion resistance and ease of manufacturing but may exhibit reduced lifespan and load-bearing capacity due to their comparatively lower material strength.
Strength and Durability: Which is Better?
Tie rods typically offer greater strength and durability compared to link bars due to their solid construction and ability to withstand higher tensile forces, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Link bars, while more flexible and easier to install, generally lack the robustness required for long-term exposure to high-stress environments. In terms of longevity and resistance to wear, tie rods outperform link bars, providing improved reliability in steering and suspension systems.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Tie rods offer straightforward installation with fewer adjustment points compared to link bars, reducing complexity during alignment. Maintenance of tie rods typically involves inspecting for wear or damage at the ball joints and ensuring secure attachments, which tends to be less frequent than the more complex link bar systems. Properly maintained tie rods enhance steering precision and vehicle safety, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
Cost Comparison: Tie Rods vs Link Bars
Tie rods generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to link bars due to their simpler design and lower manufacturing expenses. Link bars, often engineered for enhanced durability and performance in heavy-duty applications, tend to have higher material and production costs. When budget constraints are critical, choosing tie rods can lead to significant savings without compromising essential steering and suspension functions.
Common Problems and Solutions
Tie rods often suffer from wear and tear, leading to issues like uneven tire wear, steering instability, and vibrations. Link bars, while similar, typically transmit torque and may develop problems such as looseness or bending under stress, affecting alignment and handling. Regular inspections, proper lubrication, and timely replacement of damaged tie rods or link bars are essential solutions to maintain vehicle safety and steering performance.
Choosing the Right Component for Your Needs
Choosing the right component between a tie rod and a link bar depends on the specific application and load requirements. Tie rods are ideal for applications needing tension control and precise alignment, especially in steering and suspension systems, while link bars typically provide added structural support and stability under compression loads. Understanding the mechanical demands and the environment of use ensures optimal performance and longevity of the chosen part.
tie rod vs link bar Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com