Tie rods provide rigid support by resisting axial forces in structures, ensuring stability and alignment under compression or tension. Tension cables, made from flexible materials like steel wire, primarily handle tensile loads by stretching to absorb forces, often used in suspension and cable-stayed systems. Both elements optimize structural performance, but tie rods offer stiffness while tension cables allow flexibility and dynamic load distribution.
Table of Comparison
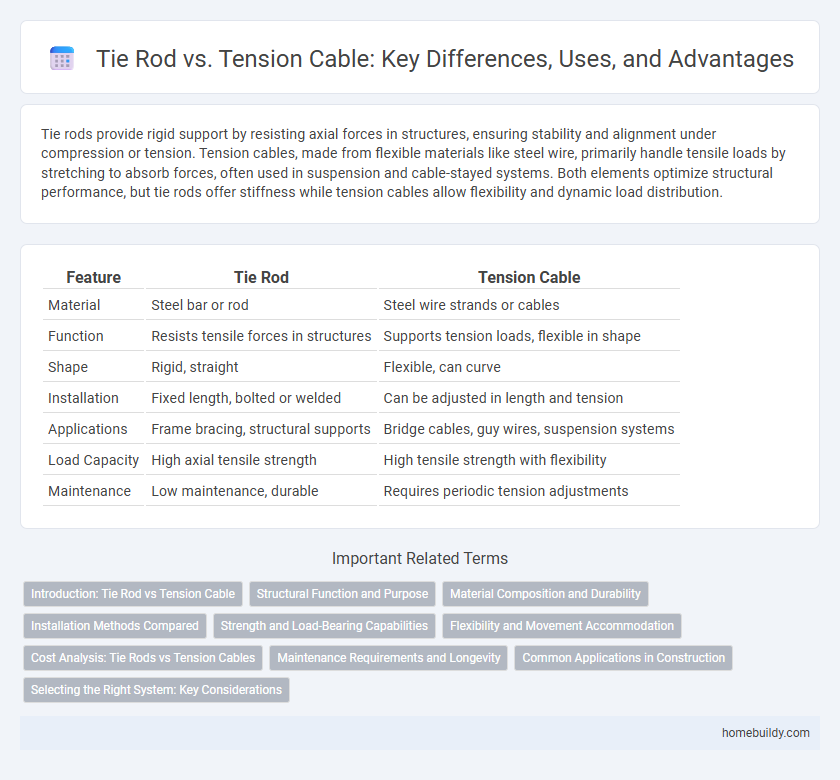
| Feature | Tie Rod | Tension Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel bar or rod | Steel wire strands or cables |
| Function | Resists tensile forces in structures | Supports tension loads, flexible in shape |
| Shape | Rigid, straight | Flexible, can curve |
| Installation | Fixed length, bolted or welded | Can be adjusted in length and tension |
| Applications | Frame bracing, structural supports | Bridge cables, guy wires, suspension systems |
| Load Capacity | High axial tensile strength | High tensile strength with flexibility |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable | Requires periodic tension adjustments |
Introduction: Tie Rod vs Tension Cable
Tie rods are rigid structural elements designed to withstand tensile forces, providing stability in frameworks by resisting elongation. Tension cables, typically made of flexible steel cables, are used to carry tensile loads but can accommodate slight bending and movement in structures. The choice between tie rods and tension cables depends on factors like load type, structural design requirements, and desired flexibility.
Structural Function and Purpose
Tie rods and tension cables both serve to resist tensile forces in structural applications, but tie rods typically provide higher stiffness and are used in frameworks requiring precise alignment and rigidity. Tie rods are often made of steel with threaded ends for adjustable tensioning, ensuring structural elements maintain their intended positions. Tension cables, commonly flexible and less rigid, are better suited for applications where dynamic loads or movement occur, such as suspension bridges or tensioned fabric structures.
Material Composition and Durability
Tie rods are typically made from high-strength steel alloys, providing excellent tensile strength and rigidity, which ensure long-lasting performance under heavy loads. In contrast, tension cables often use galvanized or stainless steel wire strands, offering flexibility but potentially reduced durability in harsh environmental conditions due to corrosion susceptibility. The solid construction of tie rods generally results in superior durability and resistance to deformation compared to the more flexible, yet less durable, tension cables.
Installation Methods Compared
Tie rods typically require precise alignment and are installed using threaded ends with nuts or clevis pins, allowing for adjustable tension and rigidity. In contrast, tension cables are usually installed by crimping or swaging end fittings, enabling easier adjustments and flexibility in structural applications. The installation of tie rods demands careful calibration to maintain structural integrity, while tension cables offer quicker setup suited for dynamic load environments.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capabilities
Tie rods exhibit superior strength and load-bearing capabilities compared to tension cables due to their rigid steel construction, which can withstand higher tensile forces without stretching or deforming. They provide consistent structural support in frameworks by maintaining precise alignment under heavy loads, whereas tension cables, made from flexible steel strands, allow some elongation that may reduce overall rigidity. Engineering applications requiring minimal deformation and maximum load transfer often prefer tie rods for their enhanced durability and strength.
Flexibility and Movement Accommodation
Tie rods offer superior stiffness and structural support compared to tension cables, making them ideal for applications requiring minimal flex and precise alignment. Unlike tension cables, which allow more elasticity and dynamic movement, tie rods restrict displacement, ensuring rigid connections in frameworks and machinery. The reduced flexibility in tie rods limits long-term deformation, enhancing durability in load-bearing scenarios.
Cost Analysis: Tie Rods vs Tension Cables
Tie rods generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to tension cables due to simpler manufacturing processes and materials like steel or aluminum. Maintenance expenses for tie rods are typically less frequent and less costly, as their rigid structure reduces wear over time, whereas tension cables may require regular tension adjustments and corrosion protection. Overall, tie rods provide a more economical solution in applications prioritizing durability and minimal maintenance over flexible load distribution.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Tie rods generally require less maintenance compared to tension cables due to their rigid construction and fewer moving parts, which lowers the risk of wear and corrosion over time. Tension cables, composed of multiple strands, need regular inspections and lubrication to prevent fraying and rust, increasing maintenance demands. The longevity of tie rods typically surpasses tension cables in structural applications, as their solid design provides greater durability and resistance to environmental stressors.
Common Applications in Construction
Tie rods are widely used in construction for stabilizing frameworks, supporting walls, and reinforcing concrete structures due to their high load-bearing capacity and rigidity. Tension cables, often found in suspension bridges and large-span roofs, provide flexibility and tensile strength, allowing for dynamic load distribution and adaptability to structural movements. Choosing between tie rods and tension cables depends on factors like required stiffness, load type, and environmental conditions in specific construction projects.
Selecting the Right System: Key Considerations
Selecting the right system between tie rods and tension cables depends on load capacity, installation environment, and structural requirements. Tie rods offer rigid support ideal for precise alignment and high load resistance, while tension cables provide flexibility and ease of adjustment in dynamic or curved structures. Understanding application-specific factors such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and maintenance needs ensures optimal performance and longevity of the chosen system.
tie rod vs tension cable Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com