A tie rod is a tension member designed to resist tensile forces, commonly used to stabilize structures by preventing components from pulling apart. A column rod functions primarily as a compression member, supporting compressive loads and transferring weight vertically through structural frameworks. Both elements serve distinct purposes in construction, with tie rods enhancing lateral stability and column rods bearing vertical loads.
Table of Comparison
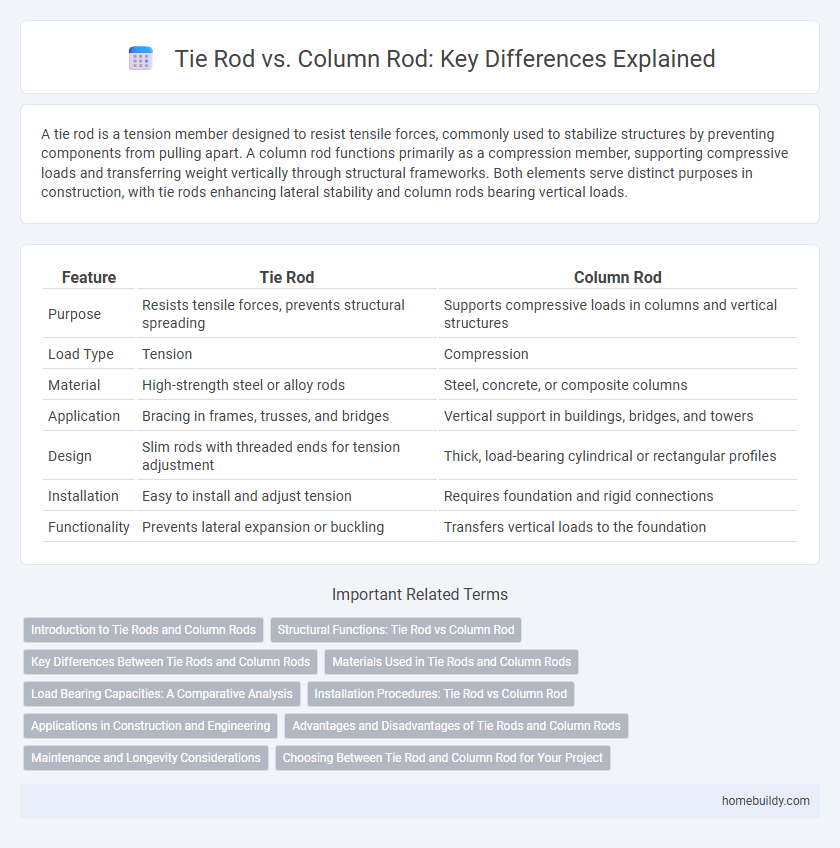
| Feature | Tie Rod | Column Rod |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Resists tensile forces, prevents structural spreading | Supports compressive loads in columns and vertical structures |
| Load Type | Tension | Compression |
| Material | High-strength steel or alloy rods | Steel, concrete, or composite columns |
| Application | Bracing in frames, trusses, and bridges | Vertical support in buildings, bridges, and towers |
| Design | Slim rods with threaded ends for tension adjustment | Thick, load-bearing cylindrical or rectangular profiles |
| Installation | Easy to install and adjust tension | Requires foundation and rigid connections |
| Functionality | Prevents lateral expansion or buckling | Transfers vertical loads to the foundation |
Introduction to Tie Rods and Column Rods
Tie rods are structural components designed primarily to resist tensile forces, commonly used in frameworks to maintain stability and prevent separation. Column rods, in contrast, often serve as vertical supports that bear compressive loads, providing structural integrity by transferring weight directly to the foundation. Understanding the distinct roles of tie rods and column rods is essential for optimizing load distribution and ensuring the durability of construction frameworks.
Structural Functions: Tie Rod vs Column Rod
Tie rods primarily provide tensile strength by resisting pulling forces in structural frameworks, ensuring stability and preventing deformation under load. Column rods, in contrast, mainly bear compressive loads, supporting vertical weight and maintaining the structure's upright integrity. Understanding these distinct structural functions is essential for optimal load distribution and preventing failure in engineering designs.
Key Differences Between Tie Rods and Column Rods
Tie rods are tension members designed to resist pulling forces, primarily used to stabilize structures by holding components together, whereas column rods function as compression members supporting vertical loads. Tie rods are typically slender, designed to bear tensile stresses only, while column rods are often thicker and engineered to withstand compressive forces without buckling. The key difference lies in their load-bearing nature: tie rods pull, whereas column rods push.
Materials Used in Tie Rods and Column Rods
Tie rods are typically constructed from high-strength steel alloys or stainless steel to ensure durability and resistance to tensile forces, while column rods often utilize carbon steel or structural steel for enhanced compressive strength and load-bearing capacity. The choice of materials for tie rods prioritizes tensile strength and corrosion resistance, whereas column rods are designed with materials that provide stability and rigidity in vertical applications. Material specifications directly influence the performance characteristics and suitability of tie rods and column rods in structural engineering projects.
Load Bearing Capacities: A Comparative Analysis
Tie rods exhibit higher tensile strength compared to column rods, making them ideal for applications requiring resistance to stretching forces. Column rods primarily bear compressive loads and are prone to buckling under excessive axial stress. Engineers select tie rods for structures where tension dominates, while column rods suit frameworks designed to withstand compressive forces.
Installation Procedures: Tie Rod vs Column Rod
Tie rod installation involves securing threaded rods with nuts and washers to provide lateral support in concrete formwork systems, ensuring precise tension adjustment for structural stability. Column rod installation requires embedding steel rods vertically within concrete columns, often using couplers or hooks, to enhance axial load-bearing capacity and resist buckling. Proper alignment, anchorage, and corrosion protection are critical in both procedures to maintain long-term structural integrity.
Applications in Construction and Engineering
Tie rods offer superior tensile strength and flexibility, making them ideal for stabilizing frameworks in bridges, roofs, and steel structures, whereas column rods primarily support compressive loads in vertical columns and pillars. In construction and engineering, tie rods prevent lateral movement and resist tension forces, enhancing structural integrity during seismic or wind loads. Their application is critical in suspension systems and truss designs, contrasting with the load-bearing function of column rods that maintain vertical alignment and support weight.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tie Rods and Column Rods
Tie rods offer high tensile strength and flexibility, making them ideal for structural applications requiring tension support, while column rods provide superior compressive strength and stability for vertical load-bearing components. Tie rods are advantageous due to their lightweight design and ease of installation but may require periodic tension adjustments and are less effective under compression compared to column rods. Conversely, column rods excel in compressive load resistance but tend to be heavier and less adaptable to dynamic stress conditions.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Tie rods require regular inspection for corrosion and tension adjustments to maintain structural integrity, whereas column rods generally demand less frequent maintenance due to their compression-based role. Proper lubrication and timely replacement of worn tie rod ends significantly extend the lifespan of mechanical linkages in automotive and industrial applications. In contrast, column rods benefit from routine checks for alignment and surface wear but typically exhibit longer service intervals due to their design and load distribution.
Choosing Between Tie Rod and Column Rod for Your Project
Choosing between a tie rod and a column rod depends on the specific structural requirements of your project. Tie rods provide tension support, ideal for resisting lateral forces and preventing separation in frameworks, whereas column rods primarily offer compressive strength to support vertical loads. Evaluating load direction, material properties, and design constraints ensures optimal selection for durability and stability.
tie rod vs column rod Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com