A tie rod is a crucial component in a steering system that connects the steering gear to the wheel, allowing for precise control and directional stability. A sag rod, commonly used in structures like poles or masts, provides support by counteracting sagging or bending under load through tension. While tie rods focus on steering mechanics, sag rods primarily maintain structural integrity by preventing deformation.
Table of Comparison
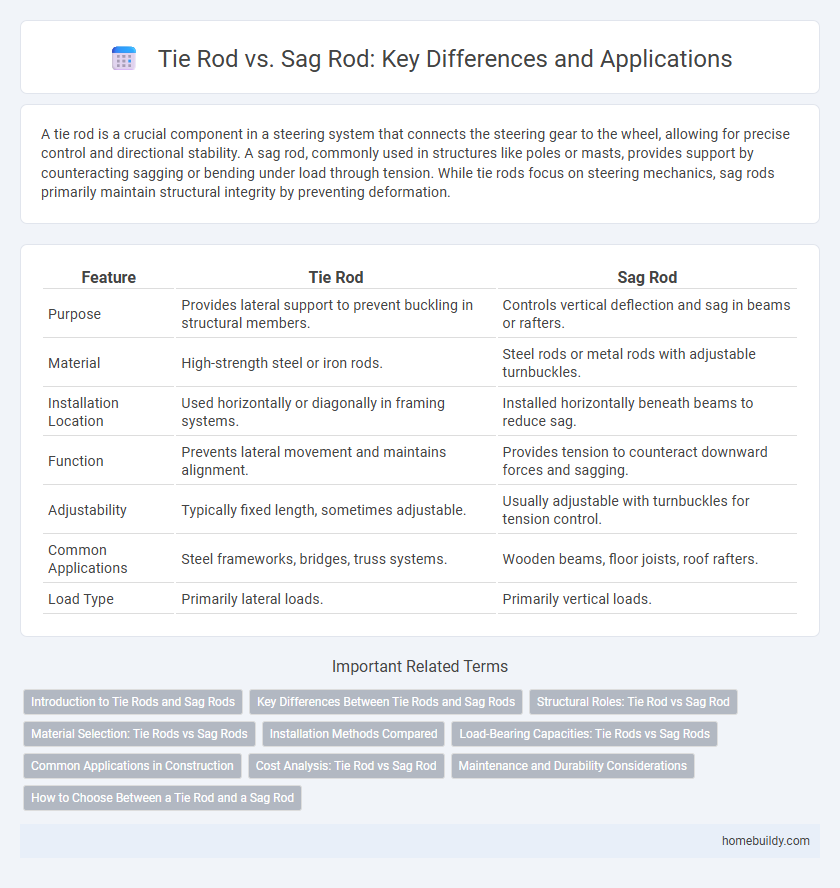
| Feature | Tie Rod | Sag Rod |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides lateral support to prevent buckling in structural members. | Controls vertical deflection and sag in beams or rafters. |
| Material | High-strength steel or iron rods. | Steel rods or metal rods with adjustable turnbuckles. |
| Installation Location | Used horizontally or diagonally in framing systems. | Installed horizontally beneath beams to reduce sag. |
| Function | Prevents lateral movement and maintains alignment. | Provides tension to counteract downward forces and sagging. |
| Adjustability | Typically fixed length, sometimes adjustable. | Usually adjustable with turnbuckles for tension control. |
| Common Applications | Steel frameworks, bridges, truss systems. | Wooden beams, floor joists, roof rafters. |
| Load Type | Primarily lateral loads. | Primarily vertical loads. |
Introduction to Tie Rods and Sag Rods
Tie rods are crucial structural elements designed to resist tension forces and maintain the stability of frameworks by preventing components from spreading apart. Sag rods, in contrast, provide vertical support primarily to counteract sagging in horizontal members like beams or ceiling joists, ensuring alignment and reducing deflection. Understanding the distinct roles of tie rods and sag rods is essential for effective structural reinforcement in construction and engineering applications.
Key Differences Between Tie Rods and Sag Rods
Tie rods primarily provide lateral support to resist wind and seismic forces in structural frameworks, connecting different parts of a frame to ensure stability. Sag rods serve to prevent vertical sagging in horizontal members like beams or joists, maintaining level alignment under load. The key differences lie in their function--tie rods counteract tensile forces horizontally, while sag rods support vertical loads to prevent deflection.
Structural Roles: Tie Rod vs Sag Rod
Tie rods function primarily to resist tension forces, maintaining structural integrity by preventing components from pulling apart, while sag rods are designed to counteract sagging or downward bending by providing vertical support. In steel frameworks and bridges, tie rods stabilize compressive loads through tensile strength, whereas sag rods support beams or joists to maintain alignment and reduce deflection under load. Understanding these distinct roles is critical in structural engineering for optimizing load distribution and ensuring durability.
Material Selection: Tie Rods vs Sag Rods
Tie rods are typically made from high-strength steel alloys to withstand tensile forces in structural applications, providing robust load-bearing capacity and durability. Sag rods, often fabricated from galvanized steel or aluminum, prioritize corrosion resistance and flexibility to counteract cable sag due to temperature fluctuations or load changes. Material selection for tie rods focuses on tensile strength and rigidity, whereas sag rods emphasize lightweight construction and environmental resilience.
Installation Methods Compared
Tie rod installation involves securing threaded rods with nuts and washers at each end to provide tension, ensuring structural alignment and stability. Sag rod installation typically requires fastening a rod or cable to support horizontal members and reduce deflection by counteracting gravitational forces. The key difference in installation methods lies in the tie rod's focus on tension adjustment for alignment, while sag rods primarily prevent sagging through vertical support.
Load-Bearing Capacities: Tie Rods vs Sag Rods
Tie rods offer higher load-bearing capacities compared to sag rods due to their design flexibility and use of tension forces, making them ideal for supporting heavy structural elements. Sag rods primarily counteract deflection by providing vertical support, but their load-bearing capability is limited compared to the tensile strength utilized by tie rods. Engineers often select tie rods when maximum load resistance and structural stability are critical factors in construction projects.
Common Applications in Construction
Tie rods and sag rods serve different purposes in construction, with tie rods primarily used to resist tension and provide lateral stability in frameworks such as bridges, trusses, and roof structures. Sag rods are often employed to support horizontal members and prevent deflection or sagging in beams and joists. Both components are critical in ensuring structural integrity, especially in large-scale projects requiring precise load management and alignment.
Cost Analysis: Tie Rod vs Sag Rod
Tie rods generally incur higher initial costs due to their robust materials and precision manufacturing, whereas sag rods are more affordable and easier to install. Maintenance expenses for tie rods tend to be lower over time because of their enhanced durability and resistance to deformation. When analyzing cost-effectiveness, tie rods offer long-term savings despite higher upfront investment, while sag rods remain a budget-friendly option with potentially increased upkeep.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Tie rods require regular inspection for signs of wear, corrosion, and bending to ensure optimal performance and safety in structural applications. Sag rods, designed primarily to prevent vertical sagging in beams, demand fewer maintenance interventions but must be checked periodically for tension loss and hardware integrity. Durability considerations highlight tie rods' susceptibility to environmental stressors, whereas sag rods benefit from simpler designs that often extend their service life with minimal upkeep.
How to Choose Between a Tie Rod and a Sag Rod
When choosing between a tie rod and a sag rod, consider the specific structural requirements and load distribution needs of your project. Tie rods are ideal for providing tensile strength and preventing lateral movement in frameworks, especially in steel or timber construction. Sag rods are better suited for supporting and stabilizing overhead components to prevent sagging under weight, particularly in roofing systems or suspended structures.
tie rod vs sag rod Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com