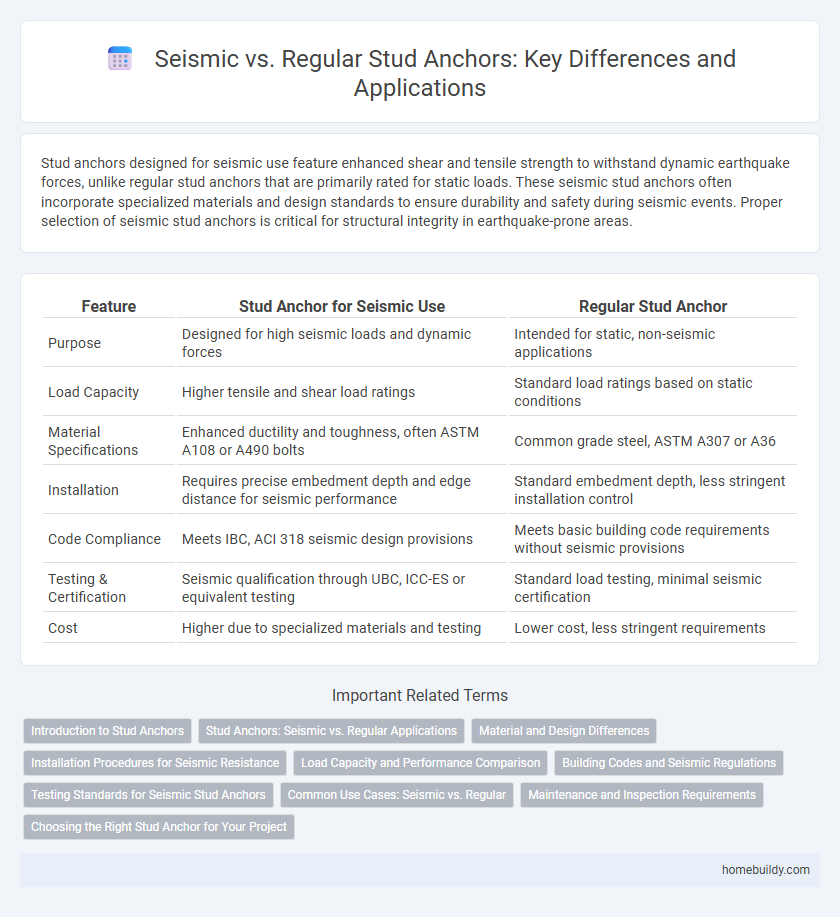
Stud anchors designed for seismic use feature enhanced shear and tensile strength to withstand dynamic earthquake forces, unlike regular stud anchors that are primarily rated for static loads. These seismic stud anchors often incorporate specialized materials and design standards to ensure durability and safety during seismic events. Proper selection of seismic stud anchors is critical for structural integrity in earthquake-prone areas.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stud Anchor for Seismic Use | Regular Stud Anchor |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed for high seismic loads and dynamic forces | Intended for static, non-seismic applications |
| Load Capacity | Higher tensile and shear load ratings | Standard load ratings based on static conditions |
| Material Specifications | Enhanced ductility and toughness, often ASTM A108 or A490 bolts | Common grade steel, ASTM A307 or A36 |
| Installation | Requires precise embedment depth and edge distance for seismic performance | Standard embedment depth, less stringent installation control |
| Code Compliance | Meets IBC, ACI 318 seismic design provisions | Meets basic building code requirements without seismic provisions |
| Testing & Certification | Seismic qualification through UBC, ICC-ES or equivalent testing | Standard load testing, minimal seismic certification |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials and testing | Lower cost, less stringent requirements |
Introduction to Stud Anchors
Stud anchors designed for seismic use feature enhanced ductility and superior load capacity compared to regular anchors, ensuring stability during dynamic seismic events. These anchors incorporate high-strength steel and are tested to rigorous seismic standards like ACI 318 and ICC-ES AC232 to resist cyclic loading and prevent structural failure. Their specialized geometry and installation methods improve energy dissipation and reduce the risk of anchor pullout or concrete breakout under earthquake forces.
Stud Anchors: Seismic vs. Regular Applications
Stud anchors designed for seismic applications feature enhanced ductility and load-bearing capacity to withstand dynamic forces during earthquakes, unlike regular stud anchors that primarily support static loads. Seismic stud anchors incorporate specialized materials and installation techniques to ensure structural integrity under cyclic loading conditions. These adaptations make seismic stud anchors critical for building safety in earthquake-prone regions, whereas regular stud anchors are suitable for non-seismic environments with minimal dynamic stresses.
Material and Design Differences
Stud anchors designed for seismic use feature enhanced materials such as high-strength steel alloys with superior ductility to withstand cyclic loading and dynamic forces. Their design incorporates increased safety factors, larger diameters, and deeper embedment to resist seismic shear and tensile stresses, unlike regular stud anchors optimized mainly for static loads. Seismic stud anchors often include specialized corrosion-resistant coatings and fatigue-resistant features to maintain integrity during earthquake events.
Installation Procedures for Seismic Resistance
Stud anchors designed for seismic use require specialized installation procedures, including deeper embedment and enhanced epoxy bonding to withstand dynamic loads and prevent pullout during an earthquake. Unlike regular stud anchors, seismic anchors must be installed with precise torque settings and verified through rigorous quality control measures such as ultrasonic testing or impact hammer tests to ensure optimal seismic resistance. The use of seismic-specific materials and adherence to strict building codes, such as ACI 318 or ASCE 7, are critical for maintaining structural integrity under seismic stress.
Load Capacity and Performance Comparison
Stud anchors designed for seismic use exhibit higher load capacity and enhanced performance compared to regular stud anchors, due to specialized materials and installation techniques that improve their resistance to dynamic forces. Seismic stud anchors maintain structural integrity under cyclic loading and vibrations, offering superior reliability in earthquake-prone environments. Regular stud anchors, while adequate for static loads, typically lack the ductility and energy dissipation features critical for seismic applications, resulting in lower overall performance during seismic events.
Building Codes and Seismic Regulations
Stud anchors for seismic use are specifically designed and tested to meet stringent building codes such as ASCE 7 and IBC, ensuring enhanced performance under dynamic seismic loads compared to regular studs. Seismic regulations require anchors to have higher load capacities, ductility, and strict installation standards to prevent failure during earthquakes. Compliance with these codes is critical for structural safety, as regular anchors may not provide the necessary resilience against seismic forces.
Testing Standards for Seismic Stud Anchors
Testing standards for seismic stud anchors prioritize higher performance criteria than those for regular use, ensuring enhanced load capacity and ductility under dynamic seismic forces. Seismic stud anchors must comply with rigorous protocols such as ICC-ES AC398 and ACI 355.2, which evaluate cyclic load resistance and anchorage reliability during earthquakes. These standards mandate comprehensive testing, including tension, shear, and moment evaluations, to certify seismic suitability beyond conventional anchor requirements.
Common Use Cases: Seismic vs. Regular
Stud anchors designed for seismic use provide enhanced vibration resistance and load-bearing capacity compared to regular stud anchors, making them ideal for critical structural applications in earthquake-prone regions. Common use cases for seismic stud anchors include securing heavy machinery, structural steel connections, and safety barriers, where dynamic loads and lateral forces prevail. In contrast, regular stud anchors are typically employed in static load scenarios such as attaching fixtures, signage, and light structural elements in non-seismic environments.
Maintenance and Inspection Requirements
Stud anchors designed for seismic use require more frequent and rigorous maintenance and inspections compared to regular applications due to the critical safety demands during earthquakes. Seismic-rated stud anchors must be checked for signs of deformation, corrosion, and grout integrity to ensure their load-bearing capacity remains uncompromised under dynamic seismic forces. Regular stud anchors undergo standard inspections that focus mainly on physical wear and installation integrity, but do not typically account for cyclic loading or ductility demands present in seismic conditions.
Choosing the Right Stud Anchor for Your Project
Selecting the right stud anchor for seismic applications involves prioritizing anchors with high load capacity and superior ductility to withstand dynamic forces during earthquakes. Seismic stud anchors are designed to meet stringent building codes and standards such as ACI 318 and ASCE 7, ensuring reliable performance under cyclic loading conditions. Regular stud anchors may suffice for static loads but lack the specialized properties required for seismic resilience, making them unsuitable for projects in earthquake-prone areas.
Stud anchor for seismic use vs regular use Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com