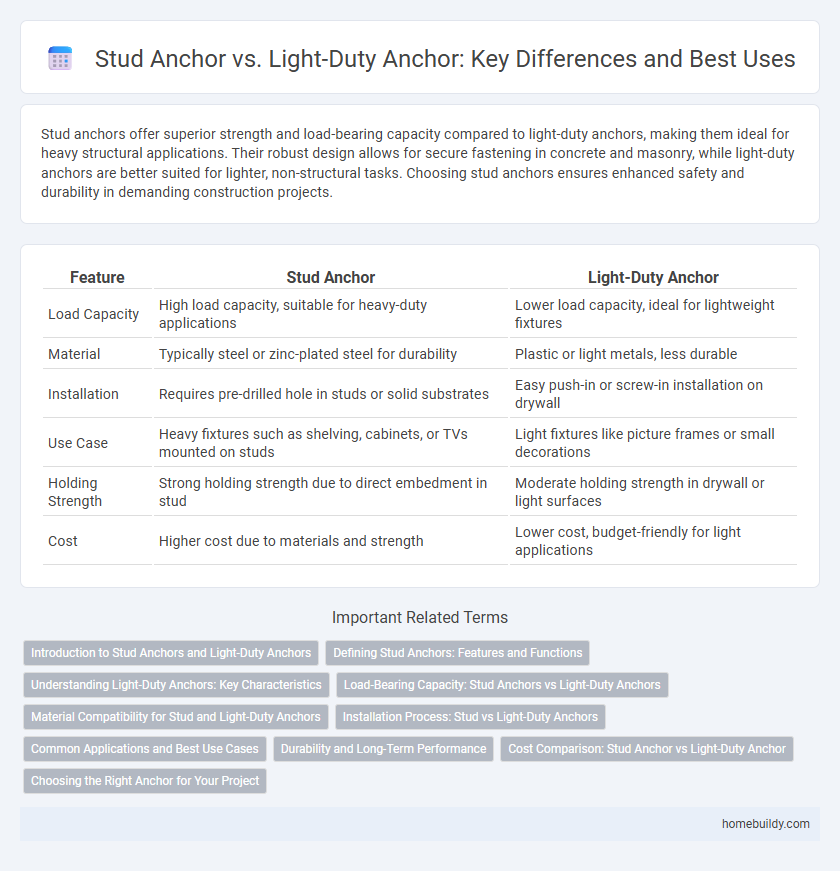
Stud anchors offer superior strength and load-bearing capacity compared to light-duty anchors, making them ideal for heavy structural applications. Their robust design allows for secure fastening in concrete and masonry, while light-duty anchors are better suited for lighter, non-structural tasks. Choosing stud anchors ensures enhanced safety and durability in demanding construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stud Anchor | Light-Duty Anchor |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | High load capacity, suitable for heavy-duty applications | Lower load capacity, ideal for lightweight fixtures |
| Material | Typically steel or zinc-plated steel for durability | Plastic or light metals, less durable |
| Installation | Requires pre-drilled hole in studs or solid substrates | Easy push-in or screw-in installation on drywall |
| Use Case | Heavy fixtures such as shelving, cabinets, or TVs mounted on studs | Light fixtures like picture frames or small decorations |
| Holding Strength | Strong holding strength due to direct embedment in stud | Moderate holding strength in drywall or light surfaces |
| Cost | Higher cost due to materials and strength | Lower cost, budget-friendly for light applications |
Introduction to Stud Anchors and Light-Duty Anchors
Stud anchors are heavy-duty fasteners designed for securing structural elements in concrete and masonry, offering superior load-bearing capacity and durability. Light-duty anchors, typically smaller and less robust, are intended for temporary or low-stress applications such as hanging fixtures or light shelves. The choice between stud anchors and light-duty anchors depends on the required strength, with stud anchors preferred in construction and industrial settings for their resilience and load performance.
Defining Stud Anchors: Features and Functions
Stud anchors are heavy-duty fasteners designed for securing structural components to concrete, offering superior load-bearing capacity compared to light-duty anchors. They feature a threaded stud with a welded or mechanically attached expansion sleeve that provides strong, reliable hold in various base materials. Their primary function is to support high-stress applications such as steel columns, machinery, and heavy equipment installations where enhanced durability and performance are essential.
Understanding Light-Duty Anchors: Key Characteristics
Light-duty anchors are designed primarily for low-load applications and are typically smaller, making them ideal for fastening lightweight materials to drywall or masonry. These anchors offer easy installation with minimal tools, providing moderate holding strength that suits hanging picture frames, small shelves, or decorative fixtures. In contrast to stud anchors, light-duty anchors lack the robust support and load-bearing capacity needed for structural or heavy-duty demands.
Load-Bearing Capacity: Stud Anchors vs Light-Duty Anchors
Stud anchors exhibit significantly higher load-bearing capacity compared to light-duty anchors, making them ideal for heavy structural applications. Engineered to withstand tensile loads often exceeding several thousand pounds, stud anchors provide robust performance in concrete and masonry substrates. Light-duty anchors, by contrast, are designed for applications with minimal load requirements, typically supporting lighter fixtures and non-structural elements.
Material Compatibility for Stud and Light-Duty Anchors
Stud anchors are typically made from stainless steel or carbon steel with corrosion-resistant coatings, offering superior compatibility with high-strength concrete and metal fixtures. Light-duty anchors often utilize zinc-plated steel, which may corrode faster when exposed to moisture or incompatible materials such as certain metals or chemicals. Selecting the appropriate material for stud anchors ensures durability and prevents galvanic corrosion, critical when anchoring in harsh environments or with metal assemblies.
Installation Process: Stud vs Light-Duty Anchors
Stud anchors feature a straightforward installation process involving drilling a hole, inserting the anchor, and tightening the nut to secure heavy loads, making them ideal for structural applications. Light-duty anchors require a simpler installation with less drilling depth and torque, suitable for lighter fixtures and non-structural attachments. The choice between stud and light-duty anchors depends on load requirements and substrate material, affecting installation complexity and performance.
Common Applications and Best Use Cases
Stud anchors provide superior strength and load-bearing capacity ideal for heavy-duty industrial and structural applications such as securing machinery, steel columns, and large-scale construction components. Light-duty anchors are best suited for less demanding tasks like mounting fixtures, securing light shelving, or attaching non-structural elements to drywall or masonry. Choosing between stud anchors and light-duty anchors depends on load requirements, substrate type, and safety factors in complex engineering projects.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Stud anchors offer superior durability and long-term performance compared to light-duty anchors due to their robust steel construction and deep embedment capabilities. Engineered for heavy-load applications, stud anchors resist corrosion and mechanical wear, maintaining structural integrity over extended periods. In contrast, light-duty anchors are typically designed for temporary or low-stress situations and may degrade faster under sustained loads or harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Comparison: Stud Anchor vs Light-Duty Anchor
Stud anchors generally incur higher upfront costs compared to light-duty anchors due to their robust construction and superior load-bearing capacity. Light-duty anchors offer a more economical solution suitable for less demanding applications, reducing material and installation expenses. Evaluating project requirements against budget constraints is essential to determine the most cost-effective anchor type.
Choosing the Right Anchor for Your Project
Stud anchors provide superior load capacity and stability for heavy-duty applications, making them ideal for structural or high-stress projects. Light-duty anchors are better suited for simpler tasks involving lighter materials and lower loads, ensuring cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Selecting the right anchor depends on the project's load requirements, substrate type, and environmental conditions to ensure long-term performance and safety.
Stud anchor vs light-duty anchor Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com