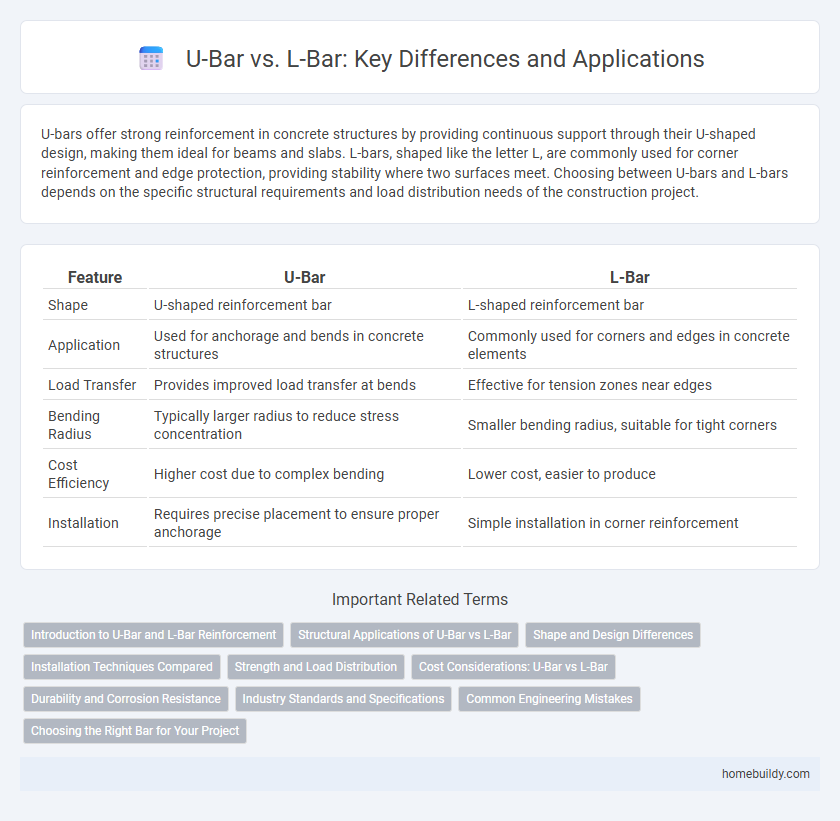
U-bars offer strong reinforcement in concrete structures by providing continuous support through their U-shaped design, making them ideal for beams and slabs. L-bars, shaped like the letter L, are commonly used for corner reinforcement and edge protection, providing stability where two surfaces meet. Choosing between U-bars and L-bars depends on the specific structural requirements and load distribution needs of the construction project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | U-Bar | L-Bar |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | U-shaped reinforcement bar | L-shaped reinforcement bar |
| Application | Used for anchorage and bends in concrete structures | Commonly used for corners and edges in concrete elements |
| Load Transfer | Provides improved load transfer at bends | Effective for tension zones near edges |
| Bending Radius | Typically larger radius to reduce stress concentration | Smaller bending radius, suitable for tight corners |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost due to complex bending | Lower cost, easier to produce |
| Installation | Requires precise placement to ensure proper anchorage | Simple installation in corner reinforcement |
Introduction to U-Bar and L-Bar Reinforcement
U-bar and L-bar reinforcement are critical components in concrete construction, designed to enhance structural strength and durability. U-bars, shaped like the letter "U," provide effective anchorage and shear resistance by wrapping around rebar cages or at the edges of slabs and walls. L-bars, shaped like the letter "L," serve as corner reinforcements, offering superior anchorage in confined spaces and improving load transfer in beams and columns.
Structural Applications of U-Bar vs L-Bar
U-bars provide superior tensile strength and load distribution in reinforced concrete beams, making them ideal for structural beams and slabs subject to bending stresses. L-bars are primarily used for anchorage and corner reinforcement, offering enhanced resistance against shear forces and improving joint stability in concrete columns and wall intersections. Choosing between U-bars and L-bars depends on the specific load requirements and structural design criteria of the project.
Shape and Design Differences
U-bars feature a curved shape resembling the letter "U," designed to provide continuous support and improve load distribution in reinforced concrete structures. L-bars have an angular design with a sharp bend, forming an "L" shape, which is ideal for corner reinforcement and anchorage in concrete elements. The distinct geometric shapes of U-bars and L-bars cater to specific structural requirements, enhancing stability and bonding within concrete frameworks.
Installation Techniques Compared
U-bars offer straightforward installation with their pre-bent shape, enabling easy placement around column corners and reducing manual bending on-site. L-bars require precise angle measurements and manual bending, demanding skilled labor to maintain structural integrity and alignment within the concrete framework. The choice between U-bar and L-bar installation techniques impacts labor time, accuracy, and the overall reinforcement quality in construction projects.
Strength and Load Distribution
U-bar reinforcement provides superior strength due to its closed-loop design, which enhances load distribution by effectively resisting bending and shear forces in concrete structures. L-bar, with its open-ended shape, offers localized reinforcement primarily at corners but lacks the comprehensive load transfer capabilities of U-bars. Choosing U-bars improves overall structural integrity by evenly distributing stresses and minimizing crack propagation under heavy loads.
Cost Considerations: U-Bar vs L-Bar
U-bars generally offer lower material costs due to their simpler manufacturing process and reduced waste compared to L-bars, which require bending at precise angles. Installation expenses for U-bars tend to be less since their shape facilitates easier placement and alignment within concrete structures. However, L-bars may incur higher costs arising from specialized fabrication and handling requirements, impacting overall project budgets.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
U-bars exhibit superior durability compared to L-bars due to their continuous shape, which evenly distributes stress and reduces the risk of cracking under load. The closed curve of U-bars limits the exposure of reinforcement to corrosive elements, enhancing corrosion resistance in aggressive environments. L-bars, with their open angles, are more susceptible to corrosion and mechanical damage, making them less effective in structures requiring high longevity and resistance to environmental degradation.
Industry Standards and Specifications
U-bars and L-bars used in construction differ primarily in shape and application, influencing their compliance with industry standards set by organizations such as ASTM and ACI. U-bars, typically used for anchorage and structural detailing, must meet specific tensile strength and bend radius requirements outlined in ASTM A615, ensuring durability and performance in reinforced concrete structures. L-bars, commonly employed for corner reinforcement and seismic design, follow strict dimensional tolerances and bend practices specified in ACI 318 to maintain structural integrity and prevent cracking under load.
Common Engineering Mistakes
Common engineering mistakes with U-bars and L-bars often involve improper bending angles and incorrect embedment depths, compromising structural integrity. Misalignment during installation leads to uneven load distribution, increasing the risk of concrete cracking and rebar corrosion. Accurate measurement and adherence to design specifications are critical to avoid these costly errors in reinforced concrete structures.
Choosing the Right Bar for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate reinforcement bar depends on the specific structural requirements and load distribution of your project. U-bars provide superior anchorage and are ideal for corner reinforcement and tensile stress zones, while L-bars offer excellent stability in edge and beam applications with simpler bending needs. Evaluating the project's design load and reinforcement layout ensures optimal use of U-bars or L-bars for enhanced concrete strength and durability.
U-bar vs L-bar Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com