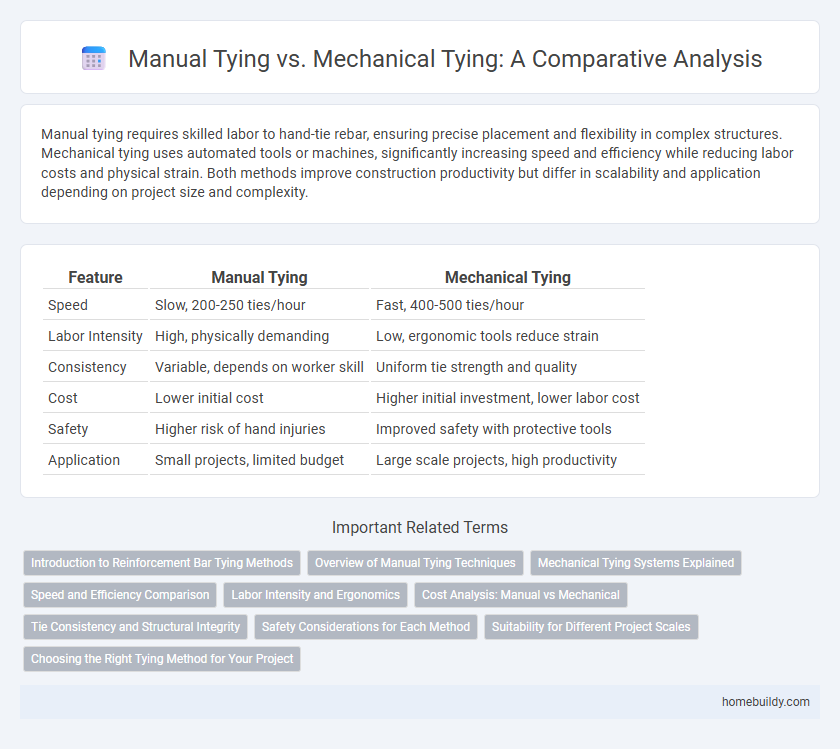
Manual tying requires skilled labor to hand-tie rebar, ensuring precise placement and flexibility in complex structures. Mechanical tying uses automated tools or machines, significantly increasing speed and efficiency while reducing labor costs and physical strain. Both methods improve construction productivity but differ in scalability and application depending on project size and complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Tying | Mechanical Tying |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow, 200-250 ties/hour | Fast, 400-500 ties/hour |
| Labor Intensity | High, physically demanding | Low, ergonomic tools reduce strain |
| Consistency | Variable, depends on worker skill | Uniform tie strength and quality |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment, lower labor cost |
| Safety | Higher risk of hand injuries | Improved safety with protective tools |
| Application | Small projects, limited budget | Large scale projects, high productivity |
Introduction to Reinforcement Bar Tying Methods
Manual tying of reinforcement bars involves using wire and pliers to secure bars together, offering flexibility and low initial cost but requiring significant labor. Mechanical tying utilizes automatic or semi-automatic tools that improve speed, consistency, and reduce worker fatigue, making it ideal for large-scale construction projects. Choosing the appropriate method depends on project size, labor availability, and desired efficiency in reinforcing concrete structures.
Overview of Manual Tying Techniques
Manual tying of reinforcement bars involves using steel wire and pliers to secure rebar intersections by hand, ensuring flexibility and tactile control in complex or tight spaces. Techniques include saddle ties, wrap-around ties, and figure-eight ties, each designed to maintain structural integrity by preventing bar displacement during concrete pouring. This method requires skilled labor and is time-consuming but allows precise placement and adjustment of rebar configurations on-site.
Mechanical Tying Systems Explained
Mechanical tying systems for reinforcement bars enhance construction efficiency by automating the process of fastening rebar intersections, significantly reducing labor time and minimizing repetitive strain injuries. These systems use powered tools or automated machines that deliver consistent tie strength and uniform spacing, improving structural integrity and compliance with building codes. Integration of mechanical tying improves productivity on construction sites while ensuring precise, reliable reinforcement bar placement.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Manual tying of reinforcement bars is significantly slower, requiring approximately 20-30 seconds per tie, which limits overall construction speed and labor efficiency. Mechanical tying tools can reduce tying time to as little as 5 seconds per tie, enhancing productivity by up to 4-6 times compared to manual methods. The increased speed and consistent tie quality of mechanical tying directly contribute to improved project timelines and labor cost savings on site.
Labor Intensity and Ergonomics
Manual tying of reinforcement bars demands high labor intensity with repetitive hand motions that can lead to worker fatigue and musculoskeletal strain. Mechanical tying significantly reduces physical effort by using powered tools that enhance productivity and improve ergonomic conditions, minimizing the risk of injuries. Optimizing labor efficiency and worker safety, mechanical tying is preferred in large-scale construction projects requiring consistent reinforcement quality.
Cost Analysis: Manual vs Mechanical
Manual tying of reinforcement bars incurs higher labor costs and longer project timelines due to the intensive manual effort required per tie. Mechanical tying machines significantly reduce labor expenses by increasing tying speed and consistency, leading to improved productivity and overall cost savings on large-scale construction projects. Despite the initial investment in mechanical equipment, the long-term operational cost benefits and reduced labor dependency make mechanical tying more economical for extensive reinforcement bar installations.
Tie Consistency and Structural Integrity
Manual tying of reinforcement bars often leads to variable tie consistency due to human error and fatigue, which can compromise the uniform distribution of load and affect structural integrity. Mechanical tying ensures consistent tension and placement accuracy, promoting uniform load transfer and enhancing the durability of reinforced concrete structures. Consistent tie strength achieved through mechanical methods reduces weak points, thereby improving overall structural performance and safety.
Safety Considerations for Each Method
Manual tying of reinforcement bars involves workers handling sharp wire ties and awkward postures, increasing the risk of cuts, puncture wounds, and musculoskeletal injuries. Mechanical tying reduces these hazards by using powered tools that minimize direct contact with wires and improve tie consistency, lowering fatigue and repetitive strain injuries. Safety protocols for both methods emphasize proper personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and eye protection to prevent common injuries on construction sites.
Suitability for Different Project Scales
Manual tying of reinforcement bars is highly suitable for small to medium-scale construction projects where flexibility and precision in tight spaces are required. Mechanical tying systems excel in large-scale projects, significantly increasing efficiency and consistency while reducing labor costs and time. Selecting the appropriate tying method depends on project size, complexity, and desired productivity outcomes.
Choosing the Right Tying Method for Your Project
Choosing the right tying method for reinforcement bars depends on project scale, labor availability, and budget constraints. Manual tying offers precision and flexibility for small or complex structures but demands skilled labor and more time. Mechanical tying speeds up large-scale projects with consistent tie strength and reduced physical strain, making it ideal for high-volume construction sites.
Manual tying vs Mechanical tying Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com