Sandblasted rebar offers enhanced surface roughness that significantly improves bonding strength with concrete, reducing slippage and increasing overall structural integrity. Non-sandblasted rebar has a smoother surface, which may result in weaker adhesion and potential corrosion issues over time due to less effective concrete encapsulation. Choosing sandblasted rebar improves durability and load-bearing capacity in reinforced concrete structures, making it the preferred option for high-performance construction projects.
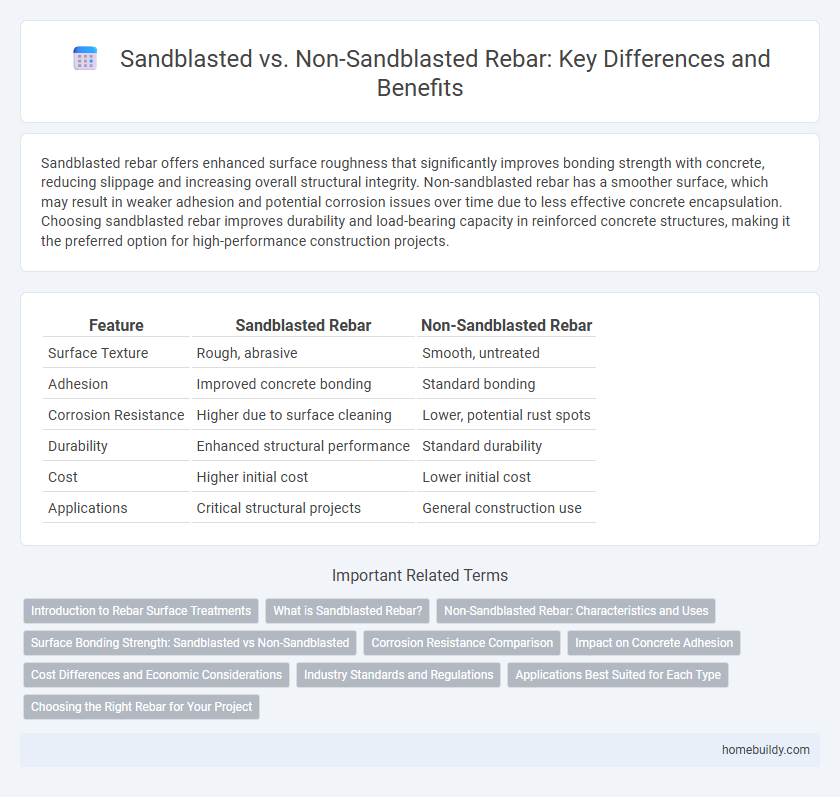
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sandblasted Rebar | Non-Sandblasted Rebar |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Texture | Rough, abrasive | Smooth, untreated |
| Adhesion | Improved concrete bonding | Standard bonding |
| Corrosion Resistance | Higher due to surface cleaning | Lower, potential rust spots |
| Durability | Enhanced structural performance | Standard durability |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Applications | Critical structural projects | General construction use |
Introduction to Rebar Surface Treatments
Rebar surface treatments, such as sandblasting, enhance the bond strength between steel reinforcement and concrete by increasing surface roughness and removing contaminants. Sandblasted rebar offers improved adhesion and corrosion resistance compared to non-sandblasted rebar, which may retain mill scale and oils that impair concrete bonding. Selecting the appropriate surface treatment directly impacts the structural integrity and longevity of reinforced concrete constructions.
What is Sandblasted Rebar?
Sandblasted rebar is steel reinforcement bar that has undergone a surface treatment process using high-pressure abrasive materials to remove rust, mill scale, and contaminants. This process enhances the adhesion between the rebar and concrete by providing a clean, roughened surface texture. In contrast, non-sandblasted rebar retains its mill scale and surface impurities, potentially reducing bonding efficiency within concrete structures.
Non-Sandblasted Rebar: Characteristics and Uses
Non-sandblasted rebar features a smooth, rust-free surface that retains its mill scale, providing natural corrosion resistance and increased adhesion with concrete. This type of rebar is commonly used in construction projects where environmental exposure is limited or where cost-efficiency is prioritized, such as interior concrete slabs and foundations. The absence of surface abrasion makes non-sandblasted rebar suitable for applications requiring minimal surface treatment while maintaining structural integrity.
Surface Bonding Strength: Sandblasted vs Non-Sandblasted
Sandblasted rebar exhibits superior surface bonding strength compared to non-sandblasted rebar due to its increased surface roughness, which enhances mechanical interlock with concrete. The sandblasting process removes mill scale and contaminants, promoting better adhesion and reducing slip at the rebar-concrete interface. Non-sandblasted rebar, with a smoother surface, typically demonstrates lower bond strength, potentially compromising structural integrity in reinforced concrete applications.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Sandblasted rebar offers superior corrosion resistance compared to non-sandblasted rebar due to the removal of surface contaminants and rust, which enhances the adhesion of protective coatings. The sandblasting process increases surface roughness, promoting better bonding with concrete and reducing the risk of corrosion-induced deterioration. Non-sandblasted rebar retains mill scale and impurities that can trap moisture, accelerating corrosion and compromising structural integrity over time.
Impact on Concrete Adhesion
Sandblasted rebar significantly improves concrete adhesion due to its roughened surface, which enhances mechanical interlock between the steel and concrete matrix. Non-sandblasted rebar has a smoother surface that may reduce bond strength, potentially compromising structural integrity in reinforced concrete applications. Studies show that sandblasted rebar can increase bond strength by up to 30%, optimizing load transfer and durability in construction projects.
Cost Differences and Economic Considerations
Sandblasted rebar incurs higher costs due to the added surface preparation process, which improves steel adhesion and corrosion resistance, thereby extending the lifespan of concrete structures. Non-sandblasted rebar is less expensive upfront but may lead to increased maintenance and repair expenses over time because of weaker bonding and higher susceptibility to rust. Economic considerations must weigh the initial investment against potential long-term savings in durability and reduced structural deterioration.
Industry Standards and Regulations
Sandblasted rebar complies with stringent industry standards such as ASTM A775/A775M, ensuring superior surface cleanliness that enhances concrete bonding and corrosion resistance. Non-sandblasted rebar may fall short of these regulations, leading to potential issues in structural integrity and durability. Regulatory bodies increasingly recommend sandblasted finishes to meet safety and performance criteria in construction projects.
Applications Best Suited for Each Type
Sandblasted rebar offers enhanced surface roughness, improving concrete bonding and making it ideal for high-strength structural applications like bridges and high-rise buildings. Non-sandblasted rebar, with its smoother surface, suits general construction projects where standard bonding and corrosion resistance are sufficient, such as residential foundations and retaining walls. Choosing the appropriate rebar type directly impacts durability and load-bearing capacity in specific construction scenarios.
Choosing the Right Rebar for Your Project
Sandblasted rebar offers superior adhesion with concrete due to its roughened surface, enhancing structural integrity in critical construction projects. Non-sandblasted rebar, while more cost-effective, may result in weaker bonding and is better suited for non-load-bearing applications or temporary structures. Selecting the right rebar depends on project requirements, budget constraints, and desired durability, with sandblasted rebar recommended for high-stress or longevity-focused builds.
Sandblasted Rebar vs Non-Sandblasted Rebar Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com