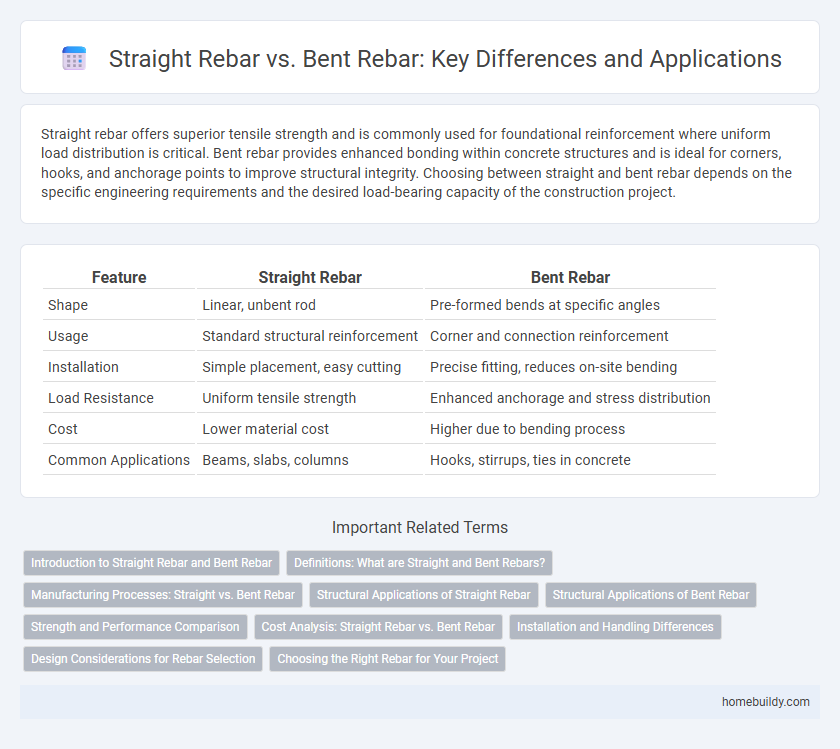
Straight rebar offers superior tensile strength and is commonly used for foundational reinforcement where uniform load distribution is critical. Bent rebar provides enhanced bonding within concrete structures and is ideal for corners, hooks, and anchorage points to improve structural integrity. Choosing between straight and bent rebar depends on the specific engineering requirements and the desired load-bearing capacity of the construction project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Straight Rebar | Bent Rebar |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Linear, unbent rod | Pre-formed bends at specific angles |
| Usage | Standard structural reinforcement | Corner and connection reinforcement |
| Installation | Simple placement, easy cutting | Precise fitting, reduces on-site bending |
| Load Resistance | Uniform tensile strength | Enhanced anchorage and stress distribution |
| Cost | Lower material cost | Higher due to bending process |
| Common Applications | Beams, slabs, columns | Hooks, stirrups, ties in concrete |
Introduction to Straight Rebar and Bent Rebar
Straight rebar consists of steel bars with a uniform, linear shape, commonly used to reinforce concrete in foundations, slabs, and columns, providing tensile strength and resistance to cracking. Bent rebar features pre-formed angles or hooks designed to fit specific structural requirements, helping to anchor reinforcement in beams, corners, and complex geometries. Both types are essential in concrete construction, with straight rebar offering straightforward reinforcement and bent rebar enhancing structural integrity at critical joints and stress points.
Definitions: What are Straight and Bent Rebars?
Straight rebar refers to steel reinforcement bars that maintain a uniform, linear shape without any bends or hooks, commonly used to provide tensile strength in concrete constructions. Bent rebar, on the other hand, includes steel bars that are intentionally shaped with hooks, bends, or angles to enhance anchorage and improve mechanical interlocking within concrete structures. The choice between straight and bent rebar depends on structural requirements and load distribution needs in construction projects.
Manufacturing Processes: Straight vs. Bent Rebar
Straight rebar is manufactured through a continuous rolling process that shapes steel billets into uniform, linear rods, ensuring consistent tensile strength and surface texture for concrete reinforcement. Bent rebar undergoes an additional fabrication step where straight bars are mechanically bent or cold-formed into specified angles or shapes, enhancing their adaptability for structural elements like beams, columns, and corners. The bending process may affect the steel's yield strength and requires precise control to prevent micro-cracks or weakening, distinguishing it from the uniform properties of straight rebar.
Structural Applications of Straight Rebar
Straight rebar is predominantly used in structural applications where linear tension and compression forces are present, providing uniform reinforcement within concrete beams, columns, and slabs. Its unbent form allows for efficient load transfer and enhanced tensile strength, critical in maintaining structural integrity under stress. Engineers often specify straight rebar for applications requiring predictable performance and straightforward installation in reinforced concrete frameworks.
Structural Applications of Bent Rebar
Bent rebar enhances structural integrity by effectively distributing stress around corners and curves in concrete forms, reducing the risk of cracks and weaknesses. Its use in beam-column joints, retaining walls, and foundation reinforcements ensures better load transfer and resistance to tensile forces compared to straight rebar. Structural applications benefit from bent rebar's ability to conform to complex shapes and improve concrete bonding, optimizing overall durability and safety.
Strength and Performance Comparison
Straight rebar provides uniform tensile strength and is ideal for structures requiring direct load support, ensuring consistent performance under stress. Bent rebar enhances anchorage and bonding within concrete, improving resistance to shear forces and preventing slippage in corners and hooks. The combination of straight and bent rebar optimizes structural integrity by balancing tensile strength with improved load distribution and stress management.
Cost Analysis: Straight Rebar vs. Bent Rebar
Straight rebar generally costs less than bent rebar due to simpler manufacturing and reduced labor for installation. Bent rebar requires additional shaping, increasing production time and labor expenses, which raises its overall cost. Project specifications, including complexity and structural requirements, heavily influence the choice between straight and bent rebar concerning budget considerations.
Installation and Handling Differences
Straight rebar offers easier handling and quicker installation due to its uniform shape, reducing labor time and mechanical fastening complexity at construction sites. Bent rebar requires more careful positioning and secured bending angles to ensure structural integrity, often necessitating specialized tools and skilled labor for precise alignment. The choice between straight and bent rebar directly impacts installation efficiency and handling safety protocols in reinforcing concrete frameworks.
Design Considerations for Rebar Selection
Design considerations for selecting straight rebar versus bent rebar primarily involve load distribution, structural integrity, and ease of installation. Straight rebar offers superior tensile strength and is typically used in uniform load scenarios, while bent rebar provides enhanced anchorage and resistance to shear forces in complex structural shapes. Engineers must evaluate factors such as bending radius, concrete cover, and reinforcement detailing to optimize rebar performance and comply with building codes like ACI 318 or Eurocode 2.
Choosing the Right Rebar for Your Project
Choosing the right rebar depends on the structural requirements and load distribution of your project. Straight rebar offers uniform tensile strength and is ideal for simple, linear reinforcement, while bent rebar provides flexibility in design and is essential for corners, bends, and complex shapes. Selecting the appropriate rebar type ensures optimal concrete reinforcement, improving durability and structural integrity.
Straight Rebar vs Bent Rebar Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com