Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes offer superior flexibility and resistance to temperature variations compared to polypropylene pipes, making them ideal for hot and cold water applications. Polypropylene pipes provide excellent chemical resistance and durability in harsh environments but are less flexible and more prone to cracking under extreme temperature changes. Choosing between PEX and polypropylene pipes depends on the specific plumbing requirements, such as temperature tolerance and chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
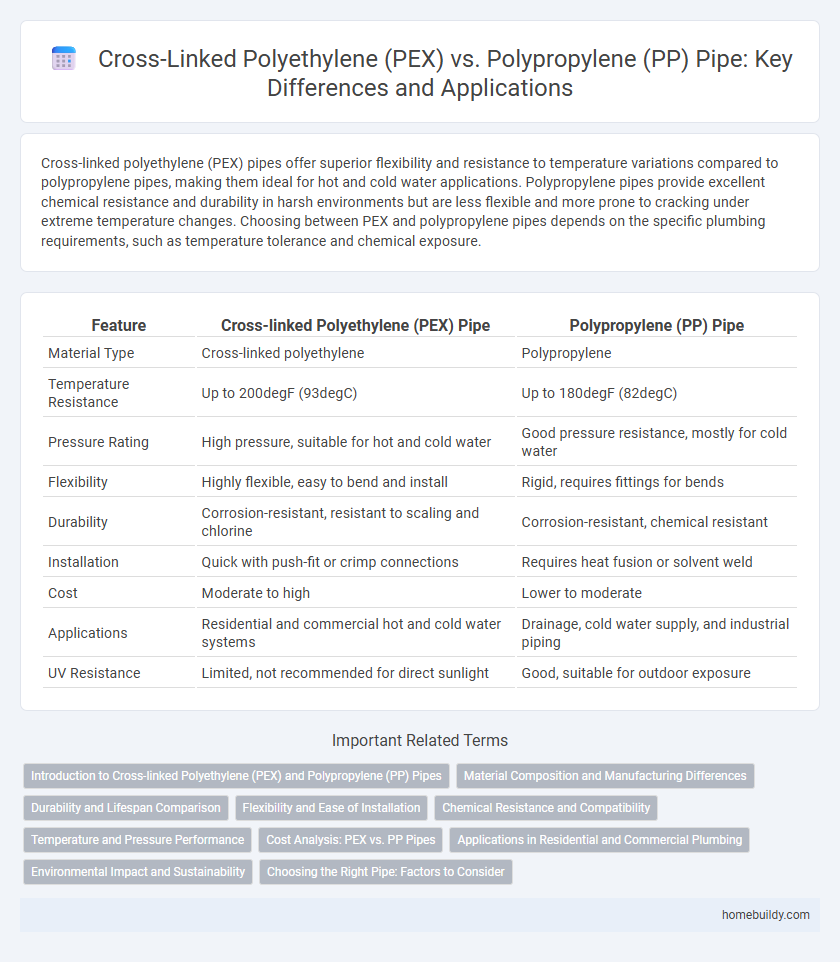
| Feature | Cross-linked Polyethylene (PEX) Pipe | Polypropylene (PP) Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Cross-linked polyethylene | Polypropylene |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 200degF (93degC) | Up to 180degF (82degC) |
| Pressure Rating | High pressure, suitable for hot and cold water | Good pressure resistance, mostly for cold water |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, easy to bend and install | Rigid, requires fittings for bends |
| Durability | Corrosion-resistant, resistant to scaling and chlorine | Corrosion-resistant, chemical resistant |
| Installation | Quick with push-fit or crimp connections | Requires heat fusion or solvent weld |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower to moderate |
| Applications | Residential and commercial hot and cold water systems | Drainage, cold water supply, and industrial piping |
| UV Resistance | Limited, not recommended for direct sunlight | Good, suitable for outdoor exposure |
Introduction to Cross-linked Polyethylene (PEX) and Polypropylene (PP) Pipes
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes offer superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance ideal for residential and commercial plumbing systems. Polypropylene (PP) pipes exhibit excellent chemical resistance, high impact strength, and are commonly used in drainage, wastewater, and industrial applications. Both materials provide durable, corrosion-resistant alternatives to traditional metal pipes, with PEX favored for hot water lines and PP preferred for cold water and chemical transport.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes consist of chemically cross-linked polyethylene molecules, enhancing flexibility, thermal resistance, and durability, while polypropylene (PP) pipes are made from polymerized propylene, offering excellent chemical resistance and a higher melting point. PEX pipes undergo a cross-linking process using methods such as peroxide, silane, or electron beam radiation, which transforms the polymer chains into a three-dimensional network structure, improving impact resistance and reducing creep. Polypropylene pipes are produced through extrusion without cross-linking, resulting in a rigid, lightweight material that withstands high pressure and resists alkaline environments effectively.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes exhibit superior flexibility and resistance to temperature extremes, contributing to a lifespan of up to 50 years in plumbing applications. Polypropylene (PP) pipes, known for their chemical resistance and rigidity, typically offer a similar durability range but can become brittle under prolonged UV exposure. Both materials resist corrosion and scaling, with PEX favored in residential settings for adaptability and PP in industrial uses for chemical resistance.
Flexibility and Ease of Installation
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes offer superior flexibility compared to polypropylene (PP) pipes, allowing them to bend around corners and obstacles without requiring multiple fittings, which simplifies installation. PEX pipes are lightweight and can be easily cut and joined using crimp or clamp systems, reducing labor time and costs on-site. Polypropylene pipes, while rigid and resistant to chemical corrosion, often require more fittings and specialized tools during installation, making them less convenient for complex plumbing layouts.
Chemical Resistance and Compatibility
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance to a wide range of acids, bases, and salts, making them ideal for plumbing systems exposed to aggressive substances. Polypropylene (PP) pipes offer excellent resistance to high concentrations of alkalis and organic solvents but may degrade when exposed to strong oxidizing agents. Selecting the appropriate pipe depends on the specific chemical environment and long-term compatibility with transported fluids.
Temperature and Pressure Performance
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes exhibit superior temperature resistance, operating effectively at temperatures up to 200degF (93degC) while maintaining high pressure tolerance, typically rated for 160 psi at 73degF and 100 psi at 180degF. Polypropylene (PP) pipes, however, have a lower temperature threshold, generally suitable for applications up to 180degF (82degC), with pressure ratings around 100 psi at 73degF and decreasing as temperature rises. The enhanced thermal stability and pressure endurance of PEX make it preferable for hot water plumbing systems compared to PP pipes.
Cost Analysis: PEX vs. PP Pipes
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes typically present a lower initial cost than polypropylene (PP) pipes due to simpler manufacturing processes and extensive market availability. PP pipes tend to have higher upfront expenses but offer enhanced chemical resistance and longer service life, which may reduce replacement frequency and maintenance costs over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership requires considering both the upfront material price and the long-term durability factors of PEX versus PP plumbing systems.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Plumbing
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes offer exceptional flexibility and resistance to high temperatures, making them ideal for residential water supply lines and radiant floor heating systems. Polypropylene (PP) pipes provide superior chemical resistance and stiffness, which benefits commercial plumbing setups involving aggressive fluids or where structural integrity is critical. Both materials support potable water delivery, but PEX is favored for ease of installation in tight spaces, while polypropylene excels in industrial and commercial applications requiring durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes have a lower carbon footprint during production compared to polypropylene (PP) pipes, but their recycling options are limited, impacting end-of-life sustainability. Polypropylene pipes are more easily recyclable and contribute to less environmental pollution due to their chemical stability and non-toxic composition. Both materials offer durability and resistance to corrosion, but polypropylene's higher recyclability makes it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable plumbing systems.
Choosing the Right Pipe: Factors to Consider
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes offer superior flexibility and resistance to high temperatures, making them ideal for residential water supply and radiant heating systems. Polypropylene (PP) pipes provide excellent chemical resistance and durability, suitable for industrial applications and wastewater systems. When choosing between PEX and PP pipes, consider factors such as temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, installation environment, and cost-effectiveness.
Cross-linked polyethylene vs Polypropylene pipe Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com