Stainless steel pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to galvanized pipes, making them ideal for long-term plumbing applications. Galvanized pipes, coated with a layer of zinc, are more prone to rust and scale buildup over time, which can reduce water flow and pipe integrity. Choosing stainless steel pipes ensures better hygiene and lower maintenance costs, especially in environments with high moisture or corrosive elements.
Table of Comparison
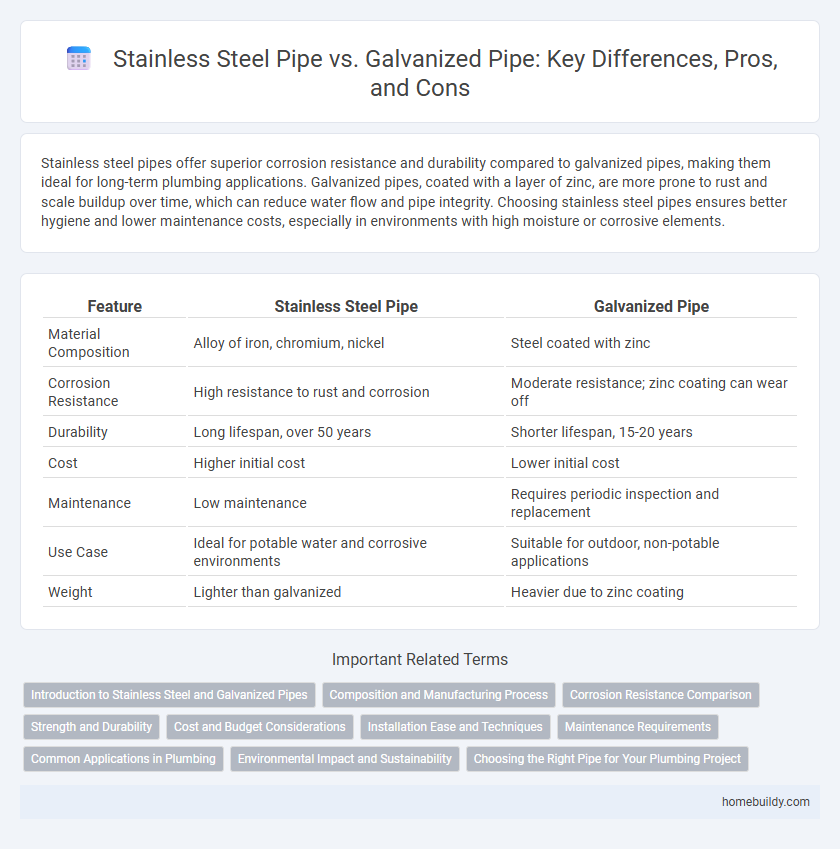
| Feature | Stainless Steel Pipe | Galvanized Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alloy of iron, chromium, nickel | Steel coated with zinc |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to rust and corrosion | Moderate resistance; zinc coating can wear off |
| Durability | Long lifespan, over 50 years | Shorter lifespan, 15-20 years |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires periodic inspection and replacement |
| Use Case | Ideal for potable water and corrosive environments | Suitable for outdoor, non-potable applications |
| Weight | Lighter than galvanized | Heavier due to zinc coating |
Introduction to Stainless Steel and Galvanized Pipes
Stainless steel pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and durability due to their chromium content, making them ideal for high-pressure and chemically aggressive environments. Galvanized pipes are steel pipes coated with a layer of zinc to protect against rust and corrosion, commonly used in water distribution and outdoor applications. While stainless steel pipes provide longer lifespan and low maintenance, galvanized pipes are more cost-effective but prone to rust over time.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Stainless steel pipes are composed primarily of iron alloyed with chromium, often including nickel and molybdenum, which enhances corrosion resistance and strength; they are manufactured through processes like hot rolling, cold rolling, and welding to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. Galvanized pipes consist of carbon steel coated with a layer of zinc applied through hot-dip galvanizing or electro-galvanizing, providing corrosion protection primarily for outdoor or water distribution applications. The stainless steel manufacturing process results in higher durability and longevity compared to galvanized pipes, which are prone to zinc coating degradation over time.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Stainless steel pipes offer superior corrosion resistance due to their chromium-rich alloy composition, which forms a passive oxide layer protecting against rust and chemical damage. Galvanized pipes, coated with a layer of zinc, provide moderate corrosion resistance but tend to degrade over time as the zinc layer wears away, exposing the underlying steel to rust. In environments with high moisture or aggressive chemicals, stainless steel pipes maintain integrity much longer than galvanized pipes, making them ideal for long-term plumbing reliability.
Strength and Durability
Stainless steel pipes exhibit superior strength and durability compared to galvanized pipes due to their corrosion-resistant alloy composition, making them ideal for high-pressure and long-term applications. Galvanized pipes, coated with zinc, offer good protection against rust but tend to degrade over time as the zinc layer wears off, leading to reduced structural integrity. Stainless steel pipes maintain their mechanical properties and resist pitting and corrosion under harsh conditions, ensuring a longer service life in plumbing systems.
Cost and Budget Considerations
Stainless steel pipes generally have a higher initial cost compared to galvanized pipes due to their corrosion resistance and durability, making them a long-term investment for plumbing systems. Galvanized pipes offer a more budget-friendly option upfront, but they are prone to rust and may require more frequent replacement and maintenance. Choosing between stainless steel and galvanized pipes depends on balancing immediate budget constraints with the potential long-term expenses of repairs and replacements.
Installation Ease and Techniques
Stainless steel pipes offer superior installation ease due to their corrosion resistance, which eliminates the need for additional protective coatings or treatments, simplifying handling and joint preparation. Galvanized pipes require careful surface cleaning and often specialized fittings to prevent rust and ensure secure connections during installation. Welding and threading techniques vary as stainless steel demands precision welding and can be more labor-intensive, while galvanized pipes are typically joined using threaded fittings that allow for quicker assembly.
Maintenance Requirements
Stainless steel pipes require minimal maintenance due to their corrosion resistance and durability, reducing the frequency of inspections and repairs. Galvanized pipes need regular maintenance to prevent rust buildup and corrosion, often requiring cleaning or recoating to extend their lifespan. The long-term cost efficiency of stainless steel pipes is higher because they avoid the recurring maintenance issues common with galvanized pipes.
Common Applications in Plumbing
Stainless steel pipes are commonly used in plumbing systems that require high corrosion resistance, such as potable water lines, chemical transport, and outdoor installations. Galvanized pipes find frequent application in water supply lines and outdoor water systems due to their zinc-coated surface providing moderate rust prevention. Both materials are suitable for residential and commercial plumbing, but stainless steel offers enhanced durability in harsh environments where long-term reliability is critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Stainless steel pipes offer superior environmental sustainability due to their high recyclability and longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and waste. Galvanized pipes, while initially cost-effective, tend to corrode faster, leading to more frequent replacements and increased environmental burden from metal extraction and disposal. The production of stainless steel, although energy-intensive, results in a more durable and recyclable product, supporting eco-friendly plumbing infrastructure over time.
Choosing the Right Pipe for Your Plumbing Project
Choosing the right pipe for your plumbing project requires understanding the differences between stainless steel and galvanized pipes. Stainless steel pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and longevity, making them ideal for high-pressure or corrosive environments, while galvanized pipes, coated with zinc, provide affordable protection against rust but may corrode over time, especially in acidic water conditions. Evaluate your project's water quality, budget, and durability needs to select the pipe material that ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Stainless steel pipe vs Galvanized pipe Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com