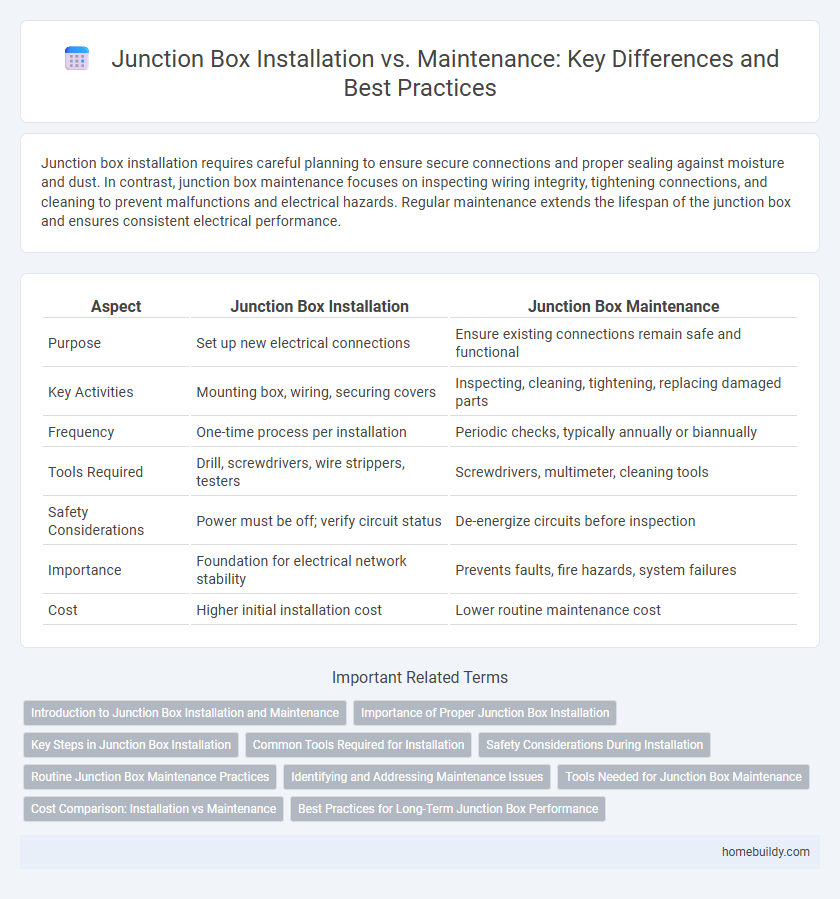
Junction box installation requires careful planning to ensure secure connections and proper sealing against moisture and dust. In contrast, junction box maintenance focuses on inspecting wiring integrity, tightening connections, and cleaning to prevent malfunctions and electrical hazards. Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of the junction box and ensures consistent electrical performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Junction Box Installation | Junction Box Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Set up new electrical connections | Ensure existing connections remain safe and functional |
| Key Activities | Mounting box, wiring, securing covers | Inspecting, cleaning, tightening, replacing damaged parts |
| Frequency | One-time process per installation | Periodic checks, typically annually or biannually |
| Tools Required | Drill, screwdrivers, wire strippers, testers | Screwdrivers, multimeter, cleaning tools |
| Safety Considerations | Power must be off; verify circuit status | De-energize circuits before inspection |
| Importance | Foundation for electrical network stability | Prevents faults, fire hazards, system failures |
| Cost | Higher initial installation cost | Lower routine maintenance cost |
Introduction to Junction Box Installation and Maintenance
Junction box installation involves securely mounting the enclosure, correctly connecting wiring, and ensuring compliance with electrical codes to protect electrical connections and prevent hazards. Maintenance of junction boxes includes regular inspection for corrosion, tightening loose connections, and replacing damaged components to maintain system safety and functionality. Proper installation combined with routine maintenance extends the lifespan of electrical systems and reduces the risk of electrical failures.
Importance of Proper Junction Box Installation
Proper junction box installation is crucial to ensure electrical safety, prevent wiring damage, and maintain system reliability. Incorrect installation can lead to short circuits, fire hazards, and increased maintenance costs due to frequent repairs. Prioritizing precise wiring connections, secure mounting, and appropriate box selection enhances the longevity and functionality of electrical systems.
Key Steps in Junction Box Installation
Key steps in junction box installation include selecting the appropriate box size and material to suit the electrical load and environmental conditions, securely mounting the box to a stable surface, and ensuring proper grounding and cable entry using clamps or bushings. Accurate wire stripping, correct terminal connections, and adherence to local electrical codes are essential to prevent faults and enhance system safety. Sealing the box with an appropriate cover protects the connections from moisture, dust, and physical damage, reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
Common Tools Required for Installation
Junction box installation commonly requires tools such as wire strippers, screwdrivers, voltage testers, pliers, and drills to ensure secure mounting and proper electrical connections. These tools facilitate accurate wire stripping, fastening of wiring terminals, and verifying electrical continuity, which are critical during the initial setup phase. In contrast, junction box maintenance focuses more on inspection tools like multimeters and cleaning equipment to ensure ongoing functionality and safety.
Safety Considerations During Installation
Junction box installation requires strict adherence to electrical codes and ensuring proper grounding to prevent electrical hazards. Safety considerations during installation include securely fastening the box, avoiding overfilling with wires, and using insulated tools to minimize the risk of electric shock. Regular maintenance can prevent potential faults, but correct installation is critical to creating a safe foundation for long-term electrical system reliability.
Routine Junction Box Maintenance Practices
Routine junction box maintenance practices include regularly inspecting seals and gaskets to prevent moisture ingress and corrosion, ensuring all electrical connections remain tight to avoid overheating or arcing, and cleaning dirt or debris from the enclosure to maintain optimal functionality. Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of junction boxes, reduces the risk of electrical failures, and enhances safety by preventing potential electrical hazards. Compared to installation, which focuses on initial setup and compliance with electrical codes, maintenance emphasizes ongoing inspections and repairs to sustain reliable operation.
Identifying and Addressing Maintenance Issues
Identifying and addressing maintenance issues in junction box systems is critical for ensuring electrical safety and preventing potential hazards. Regular inspections reveal signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections that require timely repair to avoid failures. Effective maintenance strategies reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of junction boxes by maintaining optimal functionality.
Tools Needed for Junction Box Maintenance
Junction box maintenance requires specific tools such as insulated screwdrivers, wire strippers, voltage testers, and multimeters to safely inspect and repair electrical connections. Proper maintenance tools ensure accurate diagnosis of faults, prevent electrical hazards, and extend the lifespan of the junction box. Regular tool use during maintenance is crucial to maintaining electrical safety standards and system reliability.
Cost Comparison: Installation vs Maintenance
Junction box installation typically incurs a higher initial cost due to materials, labor, and potential customization, often ranging from $100 to $500 depending on complexity and location. Maintenance costs, including inspections, repairs, and replacements, are generally lower per occurrence but can accumulate over time, averaging $50 to $150 annually. Evaluating long-term expenses reveals that investing in quality installation reduces frequent maintenance needs and overall lifecycle costs for junction boxes.
Best Practices for Long-Term Junction Box Performance
Optimal long-term junction box performance depends on meticulous installation practices such as securing proper waterproof seals, using corrosion-resistant materials, and ensuring correct wire connections according to electrical codes. Regular maintenance includes inspecting for moisture intrusion, tightening connections, and replacing damaged components to prevent electrical faults and prolong operational lifespan. Implementing both precise installation standards and consistent maintenance routines ensures reliability and safety in electrical systems.
Junction box installation vs Junction box maintenance Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com