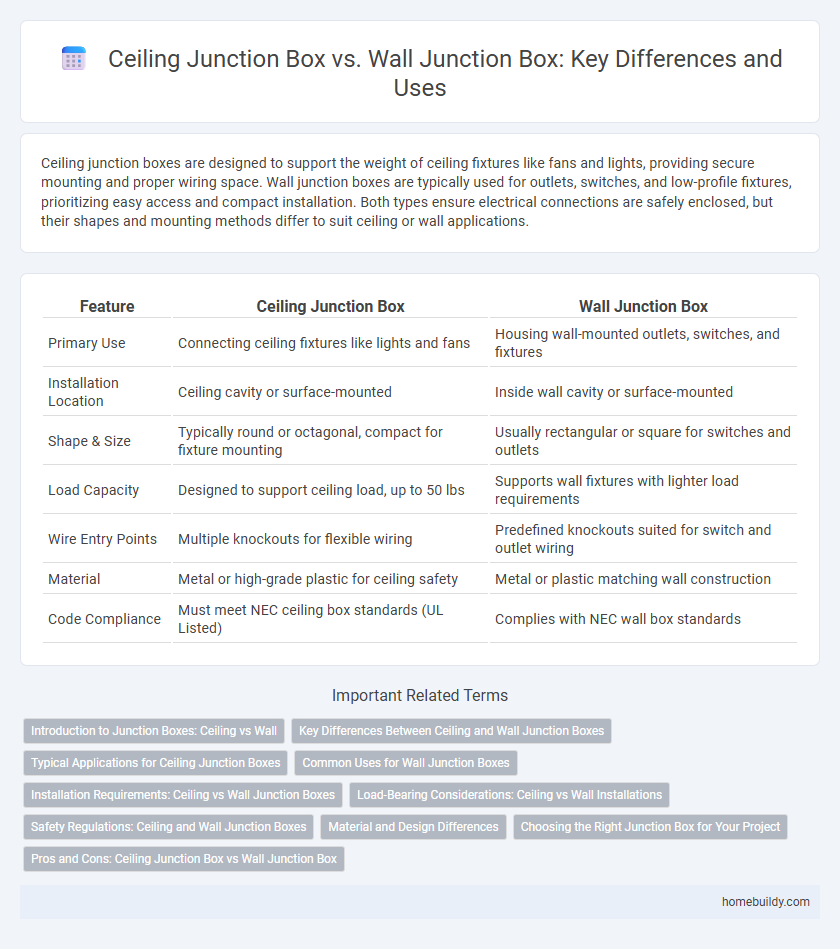
Ceiling junction boxes are designed to support the weight of ceiling fixtures like fans and lights, providing secure mounting and proper wiring space. Wall junction boxes are typically used for outlets, switches, and low-profile fixtures, prioritizing easy access and compact installation. Both types ensure electrical connections are safely enclosed, but their shapes and mounting methods differ to suit ceiling or wall applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceiling Junction Box | Wall Junction Box |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Connecting ceiling fixtures like lights and fans | Housing wall-mounted outlets, switches, and fixtures |
| Installation Location | Ceiling cavity or surface-mounted | Inside wall cavity or surface-mounted |
| Shape & Size | Typically round or octagonal, compact for fixture mounting | Usually rectangular or square for switches and outlets |
| Load Capacity | Designed to support ceiling load, up to 50 lbs | Supports wall fixtures with lighter load requirements |
| Wire Entry Points | Multiple knockouts for flexible wiring | Predefined knockouts suited for switch and outlet wiring |
| Material | Metal or high-grade plastic for ceiling safety | Metal or plastic matching wall construction |
| Code Compliance | Must meet NEC ceiling box standards (UL Listed) | Complies with NEC wall box standards |
Introduction to Junction Boxes: Ceiling vs Wall
Ceiling junction boxes are typically designed to support overhead fixtures like chandeliers and ceiling fans, offering reinforced mounting capabilities and secure wiring connections in overhead installations. Wall junction boxes are engineered for vertical surface mounting, accommodating switches, outlets, and wall-mounted fixtures while ensuring safe electrical connectivity within wall cavities. Both types adhere to electrical codes for safety and accessibility but are optimized for their respective installation orientations and load requirements.
Key Differences Between Ceiling and Wall Junction Boxes
Ceiling junction boxes differ from wall junction boxes primarily in their shape and mounting orientation; ceiling boxes are typically round or octagonal to support ceiling fixtures and are strictly designed for overhead installations, whereas wall junction boxes are usually rectangular or square to accommodate wall switches and outlets. Ceiling boxes require support strong enough to hold the weight of light fixtures or fans, often incorporating a mounting bracket or brace, while wall boxes focus on securing switches and receptacles with standard mounting tabs. Wiring configurations may also vary, with ceiling boxes accommodating fixture wiring plus power feeds, and wall boxes mainly handling switch loops and outlet connections.
Typical Applications for Ceiling Junction Boxes
Ceiling junction boxes are commonly used for installing light fixtures, ceiling fans, and smoke detectors, providing a secure and accessible point for electrical connections. These boxes support fixtures that require overhead mounting and are typically designed to accommodate heavier loads compared to wall junction boxes. Their placement in ceilings ensures proper wiring distribution for overhead lighting and electrical devices in residential and commercial spaces.
Common Uses for Wall Junction Boxes
Wall junction boxes are primarily used to house electrical connections for outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures mounted on walls. These boxes provide safe containment for wiring splices in residential and commercial applications. Common uses include installations behind light switches, power receptacles, and wall-mounted lighting controls.
Installation Requirements: Ceiling vs Wall Junction Boxes
Ceiling junction boxes require secure mounting to support the weight of light fixtures, often necessitating reinforcement with ceiling joists or metal brackets to prevent sagging or collapse. Wall junction boxes must be installed at specific heights and firmly anchored within wall studs to safely accommodate switches, outlets, or other wiring devices, ensuring compliance with electrical codes regarding box depth and accessibility. Both ceiling and wall boxes demand precise wiring space and appropriate box fill capacity to avoid overcrowding and overheating risks during installation.
Load-Bearing Considerations: Ceiling vs Wall Installations
Ceiling junction boxes typically require higher load-bearing capacity due to the need to support fixtures like lighting or fans, which can be heavy and exert downward force. Wall junction boxes generally experience less load stress since they primarily serve as connection points for switches or outlets without substantial weight. Selecting the appropriate junction box involves ensuring compliance with load rating specifications to prevent structural failures in ceiling versus wall installations.
Safety Regulations: Ceiling and Wall Junction Boxes
Ceiling junction boxes and wall junction boxes must comply with National Electrical Code (NEC) safety regulations to ensure secure wiring connections and prevent fire hazards. Ceiling junction boxes require secure mounting to support fixtures, meeting load-bearing standards, while wall junction boxes must be installed flush with the surface to maintain proper grounding and reduce electrical shock risk. Both types demand the use of approved box materials, proper wire connectors, and adherence to clearance requirements to maintain overall electrical safety.
Material and Design Differences
Ceiling junction boxes are typically made from lightweight metal or plastic designed to support the weight of light fixtures, featuring a flat or slightly curved surface to align with ceiling contours. Wall junction boxes often use more robust metals like galvanized steel to withstand external forces and provide secure mounting for switches and outlets, with deeper designs to accommodate wiring and device installations. The materials and design differences prioritize load-bearing capacity for ceiling boxes and structural durability for wall boxes.
Choosing the Right Junction Box for Your Project
Ceiling junction boxes are designed to support the weight and wiring of overhead fixtures like ceiling fans and lights, featuring reinforced mounting brackets and often a circular shape for easy fixture attachment. Wall junction boxes are typically rectangular and suit outlets, switches, or wall-mounted fixtures, prioritizing secure mounting within wall cavities. Selecting the right junction box depends on the fixture type, weight requirements, and installation location to ensure safety, code compliance, and long-term durability.
Pros and Cons: Ceiling Junction Box vs Wall Junction Box
Ceiling junction boxes provide versatile mounting options for lighting fixtures and ceiling fans, offering easy access for wiring but can be challenging to reach in high ceilings. Wall junction boxes are ideal for switches and outlets, simplifying installation and maintenance, yet they may limit fixture placement and wiring routes. Choosing between ceiling and wall junction boxes depends on the specific electrical layout, accessibility requirements, and the type of devices being installed.
Ceiling junction box vs Wall junction box Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com