A junction box serves as a central point for connecting and organizing electrical wires, providing protection and streamlined wiring management without housing circuit protection devices. In contrast, a fuse box contains fuses or circuit breakers that protect electrical circuits by interrupting power in case of overloads or faults. While a junction box focuses on wiring connections and distribution, a fuse box is specifically designed for circuit safety and control.
Table of Comparison
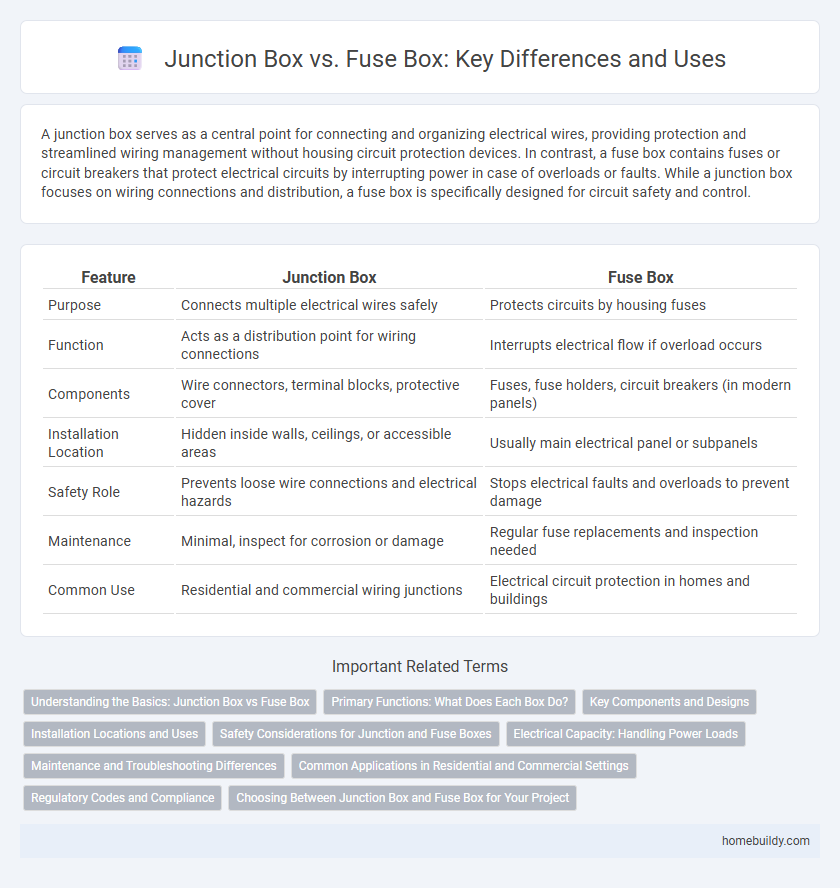
| Feature | Junction Box | Fuse Box |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Connects multiple electrical wires safely | Protects circuits by housing fuses |
| Function | Acts as a distribution point for wiring connections | Interrupts electrical flow if overload occurs |
| Components | Wire connectors, terminal blocks, protective cover | Fuses, fuse holders, circuit breakers (in modern panels) |
| Installation Location | Hidden inside walls, ceilings, or accessible areas | Usually main electrical panel or subpanels |
| Safety Role | Prevents loose wire connections and electrical hazards | Stops electrical faults and overloads to prevent damage |
| Maintenance | Minimal, inspect for corrosion or damage | Regular fuse replacements and inspection needed |
| Common Use | Residential and commercial wiring junctions | Electrical circuit protection in homes and buildings |
Understanding the Basics: Junction Box vs Fuse Box
A junction box serves as a central point where electrical wires are connected and branched off to different circuits, providing protection and organization for wire splices. A fuse box, by contrast, houses fuses that protect electrical circuits by breaking the circuit if an overload or short circuit occurs. Understanding the basics involves recognizing that a junction box is primarily for wire management and connection safety, while a fuse box is focused on circuit protection and electrical fault prevention.
Primary Functions: What Does Each Box Do?
A junction box primarily serves as a protective enclosure where multiple electrical wires connect and branch out, ensuring safe wire management and preventing short circuits. In contrast, a fuse box functions as a central distribution point for electrical circuits and includes fuses or circuit breakers that protect the circuits by interrupting power during overloads or short circuits. While a junction box focuses on safely housing and organizing wiring connections, a fuse box is essential for circuit protection and control.
Key Components and Designs
A junction box primarily serves as a protective housing for electrical connections, featuring terminal blocks or wire connectors, but lacks fuses or circuit breakers found in fuse boxes. Fuse boxes incorporate fuses or circuit breakers designed to interrupt power during electrical faults, ensuring safety by preventing overloads and short circuits. The design of junction boxes emphasizes secure wire management and insulation, while fuse boxes focus on integrating protective devices within accessible compartments.
Installation Locations and Uses
Junction boxes are typically installed where multiple electrical cables converge, providing a secure, organized enclosure to protect wire connections, often found within walls or ceilings. Fuse boxes, meanwhile, are usually located near the main electrical panel or service entrance, serving as the central point for circuit protection by housing fuses that control electrical circuits. Installation of junction boxes prioritizes accessibility for maintenance and expansion, whereas fuse boxes focus on safety and centralized circuit management.
Safety Considerations for Junction and Fuse Boxes
Junction boxes provide secure housing for wire connections, reducing the risk of electrical shorts and fire hazards by maintaining organized and insulated wiring. Fuse boxes offer overcurrent protection by containing fuses that disconnect power when current exceeds safe levels, preventing circuit damage and potential electrical fires. Proper installation and maintenance of both junction and fuse boxes are critical to ensure electrical safety and compliance with local electrical codes.
Electrical Capacity: Handling Power Loads
A junction box primarily serves as a connection point for electrical wiring, designed to safely handle power loads without interrupting the circuit. Fuse boxes, in contrast, are equipped with fuses or circuit breakers that manage electrical capacity by protecting the circuit from overloads and short circuits. Junction boxes focus on organizing and distributing electrical wiring, whereas fuse boxes control and safeguard the electrical system's power handling capacity.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Differences
Junction boxes require less frequent maintenance as they primarily serve as connection points for electrical wires, whereas fuse boxes demand regular inspection to ensure fuses are intact and functioning properly. Troubleshooting junction boxes involves checking wire continuity and securing connections, while fuse box issues typically focus on identifying and replacing blown fuses to restore circuit functionality. Understanding these differences helps optimize electrical system safety and reliability.
Common Applications in Residential and Commercial Settings
Junction boxes serve as central connection points for electrical wiring, commonly used in both residential and commercial buildings to organize and protect wire splices. Fuse boxes primarily house fuses that protect circuits from overload, typically found in older residential setups and some commercial installations requiring simple circuit protection. In modern settings, junction boxes are preferred for distributing power safely and facilitating maintenance, while fuse boxes offer straightforward overload protection but less flexibility for complex wiring needs.
Regulatory Codes and Compliance
Junction boxes and fuse boxes serve distinct roles in electrical systems, with regulatory codes explicitly defining their compliance requirements. Junction boxes must adhere to National Electrical Code (NEC) standards, ensuring secure wire connections and protection against fire hazards. Fuse boxes require compliance with additional safety regulations governing overcurrent protection and often must meet Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification standards for proper fuse installation and operation.
Choosing Between Junction Box and Fuse Box for Your Project
Choosing between a junction box and a fuse box depends on your project's electrical needs and safety requirements. A junction box serves as a centralized point for connecting and protecting electrical wires without containing circuit protection devices, while a fuse box distributes power and provides overcurrent protection through fuses or circuit breakers. For projects requiring circuit protection and overload prevention, a fuse box is essential, whereas a junction box is ideal for organizing and securing wiring connections.
Junction box vs Fuse box Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com