A junction box serves as a protective enclosure for electrical connections, primarily used to securely join wires together and organize circuits within a single point. In contrast, a distribution board functions as a central hub that distributes electrical power to multiple circuits, providing circuit protection through breakers or fuses. While both are essential in electrical installations, junction boxes focus on connection management, and distribution boards emphasize power distribution and circuit control.
Table of Comparison
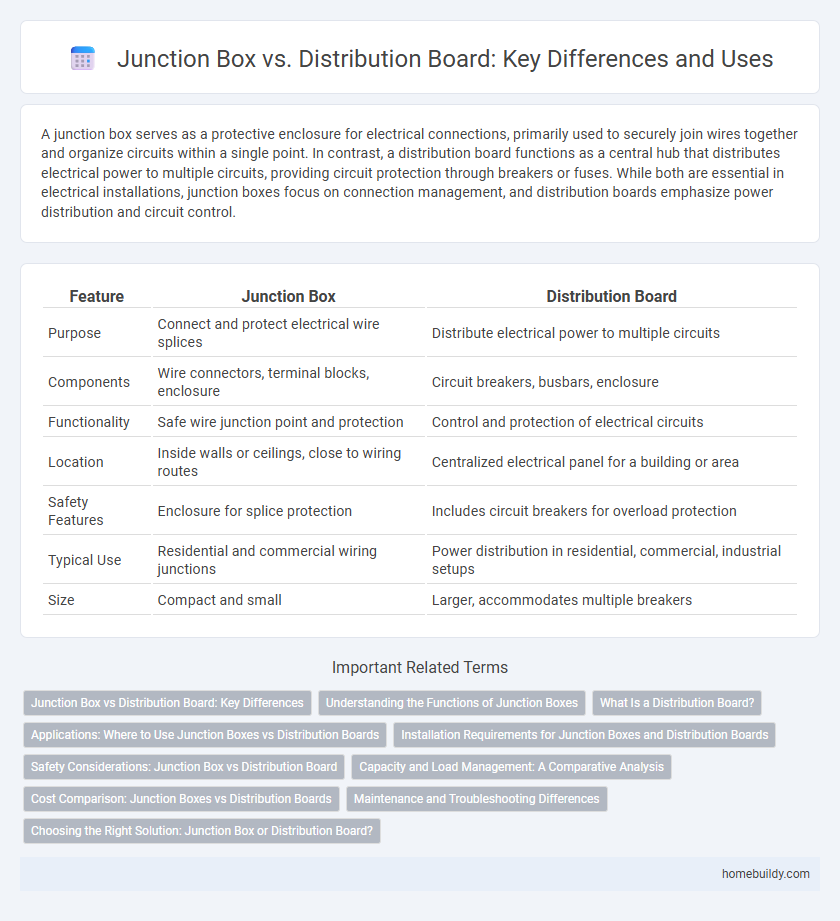
| Feature | Junction Box | Distribution Board |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Connect and protect electrical wire splices | Distribute electrical power to multiple circuits |
| Components | Wire connectors, terminal blocks, enclosure | Circuit breakers, busbars, enclosure |
| Functionality | Safe wire junction point and protection | Control and protection of electrical circuits |
| Location | Inside walls or ceilings, close to wiring routes | Centralized electrical panel for a building or area |
| Safety Features | Enclosure for splice protection | Includes circuit breakers for overload protection |
| Typical Use | Residential and commercial wiring junctions | Power distribution in residential, commercial, industrial setups |
| Size | Compact and small | Larger, accommodates multiple breakers |
Junction Box vs Distribution Board: Key Differences
A junction box is primarily used to protect and house electrical wire connections, while a distribution board manages and distributes power to various circuits in a building. Junction boxes serve as a safe enclosure for wiring splices without circuit control or protection features, whereas distribution boards contain circuit breakers or fuses to regulate and safeguard electrical flow. The main differences lie in their functions: junction boxes connect and organize wires, and distribution boards control circuit power.
Understanding the Functions of Junction Boxes
Junction boxes serve as secure enclosures that connect and protect electrical wiring, ensuring safe and organized cable splicing without overloading circuits. Unlike distribution boards, which distribute electrical power to various circuits and house protective devices like circuit breakers, junction boxes focus primarily on housing wire connections and facilitating maintenance access. Proper understanding of junction box functions is essential for safe electrical installations, preventing hazards by isolating and safeguarding critical wiring junctions.
What Is a Distribution Board?
A distribution board, also known as a panelboard or breaker panel, is an electrical device that divides an electrical power feed into subsidiary circuits, providing a protective fuse or circuit breaker for each circuit in a common enclosure. It serves as the central point for electrical distribution within a building, ensuring safe and efficient power management. Unlike a junction box, which primarily connects and protects wiring junctions without circuit protection, a distribution board actively controls and distributes electrical power while safeguarding circuits against overloads and short circuits.
Applications: Where to Use Junction Boxes vs Distribution Boards
Junction boxes are primarily used in residential and commercial wiring systems to safely connect and protect electrical cables at specific points without distributing power to multiple circuits. Distribution boards, on the other hand, are essential in larger electrical installations like industrial buildings and complex commercial setups, where they manage and distribute electricity across multiple circuits with circuit breakers for safety. Selecting the appropriate device depends on the application scale and the need for circuit control, with junction boxes ideal for simple cable connections and distribution boards suited for comprehensive power distribution and load management.
Installation Requirements for Junction Boxes and Distribution Boards
Junction boxes require secure mounting in accessible locations to facilitate cable connections, ensuring proper grounding and compliance with IP ratings for environmental protection. Distribution boards demand more space for circuit breakers and must be installed in easily reachable areas, adhering to clearances defined by electrical standards for safety and maintenance. Both installations require correct cable entry points and robust fastening to support structured wiring systems and enhance operational reliability.
Safety Considerations: Junction Box vs Distribution Board
Junction boxes and distribution boards play distinct roles in electrical safety, with junction boxes primarily designed to protect wire connections from damage and prevent accidental contacts, reducing the risk of electrical fires. Distribution boards offer comprehensive safety features by housing circuit breakers or fuses that control and isolate electrical circuits, ensuring overcurrent protection and facilitating safer maintenance. Proper installation and adherence to electrical codes for both devices are critical to maintaining overall system safety and preventing hazards.
Capacity and Load Management: A Comparative Analysis
Junction boxes primarily serve as connection points for electrical wiring and do not inherently manage load distribution, whereas distribution boards are designed with breakers and fuses to handle specific capacity loads and provide circuit protection. Distribution boards support higher electrical capacities with organized load management, enabling efficient circuit control and fault isolation. Junction boxes facilitate wire splicing in various circuits but lack the integrated componentry essential for managing electrical load and protecting against overload or short circuits.
Cost Comparison: Junction Boxes vs Distribution Boards
Junction boxes generally cost less than distribution boards due to their simpler design and limited functionality, primarily focusing on wire connections and protection. Distribution boards are more expensive because they incorporate circuit breakers, fuses, and other components for load management and safety. When budgeting for electrical installations, junction boxes offer a cost-effective solution for basic wiring needs, while distribution boards require higher investment for comprehensive circuit control and protection.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Differences
Junction boxes are simpler devices primarily used for connecting wiring, making maintenance straightforward due to fewer components and easier access to cables. Distribution boards are complex assemblies containing circuit breakers and switches, requiring specialized knowledge for troubleshooting and more detailed maintenance procedures to ensure electrical safety and system integrity. Understanding these differences is crucial for efficient electrical system management and reducing downtime during repairs.
Choosing the Right Solution: Junction Box or Distribution Board?
Choosing the right electrical enclosure depends on the project's complexity and circuit management needs. A junction box serves primarily as a connection point for wiring, offering protection and organization without circuit breaking capabilities, ideal for simple or smaller scale installations. Distribution boards provide comprehensive circuit control, incorporating breakers or fuses to manage and protect multiple circuits, making them suitable for larger, more complex electrical systems requiring centralized power distribution and enhanced safety.
Junction box vs Distribution board Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com