Z-flashing offers a streamlined installation process and superior water shedding due to its angled design, making it ideal for vertical siding applications. In contrast, galvanized flashing provides enhanced rust resistance and durability, benefiting projects exposed to harsh weather conditions. Choosing between Z-flashing and galvanized flashing depends on the specific needs for water protection and material longevity in your building project.
Table of Comparison
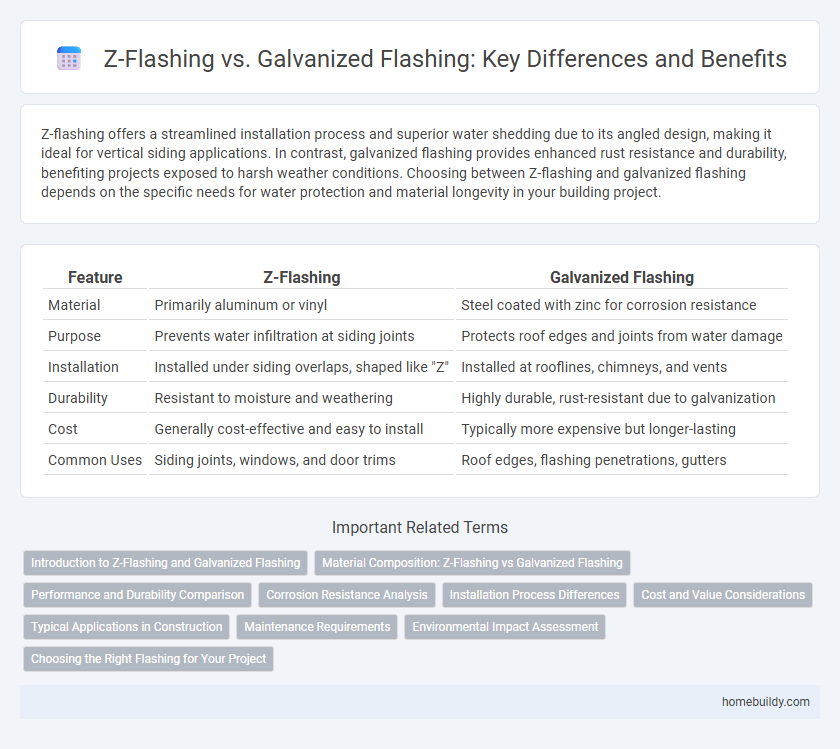
| Feature | Z-Flashing | Galvanized Flashing |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Primarily aluminum or vinyl | Steel coated with zinc for corrosion resistance |
| Purpose | Prevents water infiltration at siding joints | Protects roof edges and joints from water damage |
| Installation | Installed under siding overlaps, shaped like "Z" | Installed at rooflines, chimneys, and vents |
| Durability | Resistant to moisture and weathering | Highly durable, rust-resistant due to galvanization |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective and easy to install | Typically more expensive but longer-lasting |
| Common Uses | Siding joints, windows, and door trims | Roof edges, flashing penetrations, gutters |
Introduction to Z-Flashing and Galvanized Flashing
Z-flashing is a metal flashing shaped like the letter "Z" designed to divert water away from wall joints and protect against moisture infiltration, commonly used in siding and masonry applications. Galvanized flashing, made from steel coated with a layer of zinc, offers enhanced corrosion resistance and durability, making it suitable for long-term exposure to weather elements. Both types of flashing serve critical roles in building envelope protection, but the choice depends on specific project requirements such as material compatibility and environmental conditions.
Material Composition: Z-Flashing vs Galvanized Flashing
Z-flashing is commonly made from aluminum or vinyl, offering excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight properties ideal for siding applications. Galvanized flashing consists of steel coated with a layer of zinc to prevent rust, providing enhanced durability but with a heavier and less flexible structure. The material composition of Z-flashing promotes easier installation and long-term maintenance compared to the robust but potentially more rigid galvanized flashing.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Z-flashing offers superior water resistance due to its shape, effectively channeling water away from joints and preventing leaks better than standard galvanized flashing. Galvanized flashing provides strong corrosion resistance through its zinc coating but may be more prone to damage over time in harsh weather conditions. The durability of Z-flashing is enhanced by its design, which reduces water infiltration and extends the lifespan of roofing and siding installations.
Corrosion Resistance Analysis
Z-flashing, made from coated steel or aluminum, provides moderate corrosion resistance effectively protecting building joints from water intrusion. Galvanized flashing, coated with zinc, offers superior long-term corrosion resistance, especially in harsh weather conditions, by forming a protective barrier against rust and oxidation. Comparing corrosion resistance, galvanized flashing outperforms Z-flashing in durability and lifespan due to its enhanced zinc coating and sacrificial anode properties.
Installation Process Differences
Z-flashing installation involves securing the metal flashing into a channel or groove in the siding or trim, allowing water to run off efficiently while maintaining a tight seal against moisture penetration. Galvanized flashing typically requires fastening directly to the structure, often needing extra caulking or sealant to prevent water infiltration, as the material's corrosion resistance differs from coated options. The unique shape of Z-flashing provides a smoother integration with siding panels, streamlining the installation process compared to the more rigid and flat profiles of galvanized flashing.
Cost and Value Considerations
Z-flashing offers a cost-effective solution compared to galvanized flashing, often priced lower due to its simpler manufacturing process and material usage. Despite the lower initial cost, galvanized flashing provides superior durability and corrosion resistance, translating into longer-term value and reduced maintenance expenses. Evaluating project budgets against expected lifespan and environmental exposure helps determine the most economically efficient choice between the two flashing types.
Typical Applications in Construction
Z-flashing is commonly used in residential and commercial construction to prevent water intrusion at horizontal joints, especially above windows and doors where siding meets other materials. Galvanized flashing, often made from zinc-coated steel, is favored for roofing applications and areas exposed to harsh weather due to its superior corrosion resistance and durability. Both types serve crucial roles in waterproofing building envelopes, with Z-flashing typically installed behind cladding and galvanized flashing used in gutters, roof edges, and chimneys.
Maintenance Requirements
Z-flashing requires less frequent maintenance compared to galvanized flashing due to its corrosion-resistant aluminum composition, which withstands moisture and weathering more effectively. Galvanized flashing demands regular inspection and treatment to prevent rust and corrosion, especially in harsh climates where protective coatings can degrade. Choosing Z-flashing reduces long-term upkeep costs and extends the lifespan of exterior cladding systems by minimizing maintenance interventions.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Z-flashing typically has a lower environmental impact compared to galvanized flashing due to its simpler manufacturing process and reduced use of zinc coatings, which can leach heavy metals into the environment. Galvanized flashing involves zinc galvanization that contributes to resource depletion and potential soil and water contamination during disposal. Life cycle assessments indicate Z-flashing offers better sustainability metrics by minimizing toxic waste and facilitating easier recycling.
Choosing the Right Flashing for Your Project
Choosing the right flashing is crucial for effective moisture protection, with Z-flashing providing a cost-effective solution ideal for siding and trim where water runoff management is essential. Galvanized flashing offers superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for long-term durability in harsh weather conditions and critical flashing points such as roof-to-wall transitions. Assess project requirements including exposure to elements, material compatibility, and lifespan expectations to determine whether Z-flashing or galvanized flashing aligns best with your construction goals.
Z-flashing vs galvanized flashing Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com