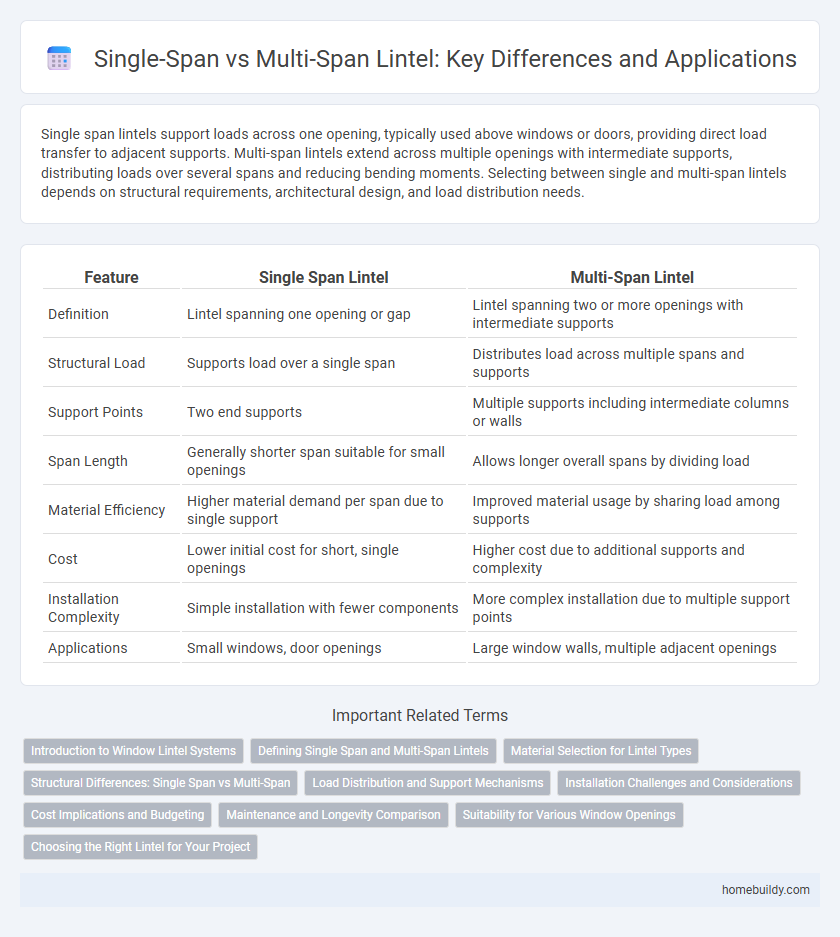
Single span lintels support loads across one opening, typically used above windows or doors, providing direct load transfer to adjacent supports. Multi-span lintels extend across multiple openings with intermediate supports, distributing loads over several spans and reducing bending moments. Selecting between single and multi-span lintels depends on structural requirements, architectural design, and load distribution needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single Span Lintel | Multi-Span Lintel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lintel spanning one opening or gap | Lintel spanning two or more openings with intermediate supports |
| Structural Load | Supports load over a single span | Distributes load across multiple spans and supports |
| Support Points | Two end supports | Multiple supports including intermediate columns or walls |
| Span Length | Generally shorter span suitable for small openings | Allows longer overall spans by dividing load |
| Material Efficiency | Higher material demand per span due to single support | Improved material usage by sharing load among supports |
| Cost | Lower initial cost for short, single openings | Higher cost due to additional supports and complexity |
| Installation Complexity | Simple installation with fewer components | More complex installation due to multiple support points |
| Applications | Small windows, door openings | Large window walls, multiple adjacent openings |
Introduction to Window Lintel Systems
Single span window lintels support loads directly above one opening, effectively transferring weight to the adjacent supports, making them ideal for smaller or isolated windows. Multi-span lintels, extending across multiple openings, distribute loads over several supports, enhancing structural stability in larger window arrangements. Choosing between single span and multi-span lintels depends on factors like span length, load requirements, and architectural design.
Defining Single Span and Multi-Span Lintels
A single span lintel is a horizontal structural element that extends across one opening, such as a door or window, supporting the load directly above it without intermediate supports. Multi-span lintels consist of multiple spans connected with intermediate supports or piers, distributing loads over a larger area and increasing structural efficiency in wider openings. The choice between single span and multi-span lintels depends on factors like load requirements, opening width, and architectural design.
Material Selection for Lintel Types
Material selection for single span lintels often favors reinforced concrete or steel due to their high tensile strength and ability to bear concentrated loads effectively over a short distance. Multi-span lintels require materials with enhanced flexibility and durability, such as prestressed concrete or composite steel sections, to accommodate the additional bending moments and shear forces induced by longer and continuous spans. Choosing the appropriate material ensures structural integrity, cost efficiency, and longevity tailored to the specific span configuration of the lintel.
Structural Differences: Single Span vs Multi-Span
Single span lintels bear loads directly between two supports, creating a straightforward bending moment distribution with maximum stress at mid-span. Multi-span lintels distribute loads over multiple supports, resulting in reduced bending moments and forces due to negative moments at intermediate supports. Structural efficiency in multi-span lintels often allows for smaller cross-sectional dimensions compared to single span lintels carrying equivalent loads.
Load Distribution and Support Mechanisms
Single span lintels transfer loads directly to two end supports, resulting in concentrated reactions that require strong bearing surfaces. Multi-span lintels distribute loads over multiple supports, reducing bending moments and deflection by sharing the load across intermediate supports. This load distribution in multi-span lintels enhances structural efficiency and allows for longer openings with smaller cross-sectional dimensions.
Installation Challenges and Considerations
Single span lintels simplify installation due to their shorter length and fewer supports, reducing the need for extensive shoring and precise alignment during placement. Multi-span lintels require careful consideration of intermediate supports and load distribution, often necessitating more complex formwork and temporary bracing to ensure structural integrity. Installation challenges for multi-span lintels include managing differential settlement at multiple supports and ensuring consistent bearing capacity across all spans.
Cost Implications and Budgeting
Single span lintels generally incur lower initial costs due to simpler design and reduced material requirements, making them budget-friendly for small openings. Multi-span lintels, while more expensive upfront, provide cost efficiency in larger structures by distributing loads over multiple supports, reducing the need for heavy-duty materials. Budget planning must factor in long-term savings from structural durability and load distribution benefits inherent in multi-span lintel systems.
Maintenance and Longevity Comparison
Single span lintels typically require less maintenance due to fewer joints and simpler load distribution, reducing the risk of cracking and water infiltration. Multi-span lintels, while capable of supporting longer openings, may experience increased stress at intermediate supports, necessitating more frequent inspections and repairs to prevent structural deterioration. Proper material selection and installation significantly influence the longevity and maintenance demands of both lintel types.
Suitability for Various Window Openings
Single span lintels are ideal for narrow window openings, providing direct support with minimal deflection and easier installation. Multi-span lintels suit wider window openings by distributing loads across multiple supports, reducing bending stress in large spans. Structural engineers select between these lintel types based on window width, load requirements, and architectural design constraints for optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Lintel for Your Project
Single span lintels efficiently support loads over short openings, providing straightforward installation and cost-effectiveness for residential projects. Multi-span lintels distribute weight across multiple supports, ideal for larger openings or commercial buildings requiring enhanced structural stability. Selecting the right lintel depends on load requirements, span length, and architectural design, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
single span lintel vs multi-span lintel Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com