A tie rod is a structural element designed to resist tension, commonly used to hold two components together or provide lateral support in frameworks. Stay rods also provide tension support but are typically adjustable and used to stabilize structures like poles or towers by anchoring them to a fixed point. Both serve to enhance stability, but tie rods are often fixed components within a structure, while stay rods allow for tension adjustments.
Table of Comparison
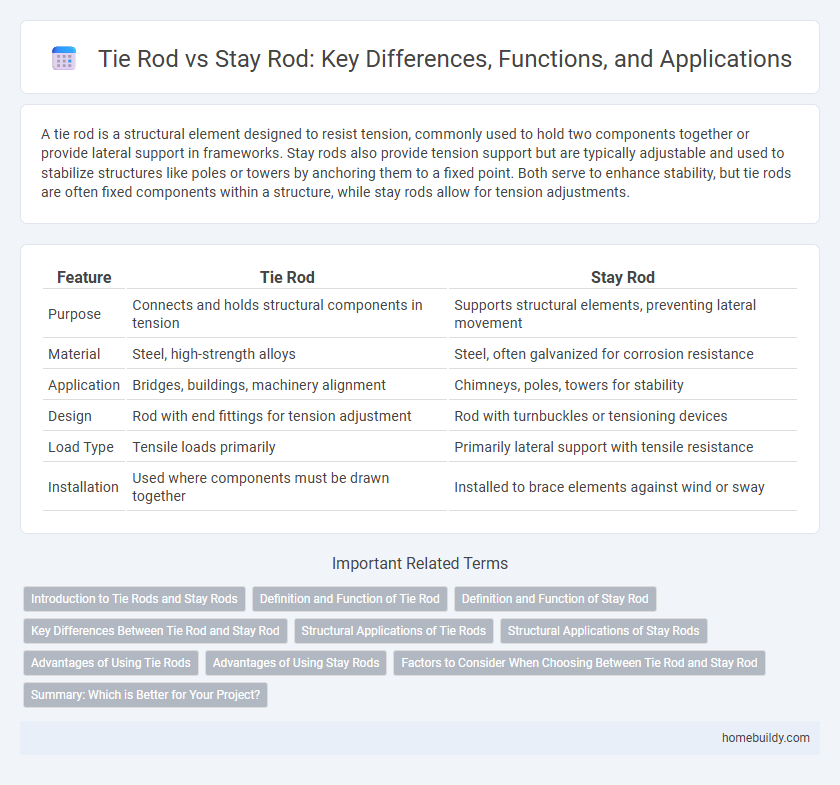
| Feature | Tie Rod | Stay Rod |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Connects and holds structural components in tension | Supports structural elements, preventing lateral movement |
| Material | Steel, high-strength alloys | Steel, often galvanized for corrosion resistance |
| Application | Bridges, buildings, machinery alignment | Chimneys, poles, towers for stability |
| Design | Rod with end fittings for tension adjustment | Rod with turnbuckles or tensioning devices |
| Load Type | Tensile loads primarily | Primarily lateral support with tensile resistance |
| Installation | Used where components must be drawn together | Installed to brace elements against wind or sway |
Introduction to Tie Rods and Stay Rods
Tie rods and stay rods are essential structural components used to stabilize frameworks, with tie rods primarily designed to resist tensile forces by connecting two opposing members. Stay rods serve to support structures by maintaining compression and preventing buckling or lateral movement, often found in bridge construction and staircases. Understanding their distinct mechanical roles is crucial for ensuring structural integrity in architectural and engineering applications.
Definition and Function of Tie Rod
A tie rod is a structural component designed to resist tensile forces, typically used to connect and stabilize two points in frameworks such as bridges, buildings, and machinery. Its primary function is to maintain alignment and prevent outward spreading by transferring tension loads, ensuring structural integrity under dynamic and static conditions. Unlike stay rods, which provide support to compressive elements, tie rods are specifically engineered to handle tension, optimizing the durability and safety of engineering constructions.
Definition and Function of Stay Rod
A stay rod is a structural component designed to provide lateral support and stability by resisting tension forces, commonly used in frameworks and machinery to prevent movement and maintain alignment. Unlike a tie rod, which primarily resists tensile loads to hold parts together, the stay rod maintains the position of elements to ensure overall structural integrity. The function of a stay rod is critical in applications such as scaffolding, automotive suspensions, and marine rigging, where it stabilizes components against bending or buckling.
Key Differences Between Tie Rod and Stay Rod
Tie rods are primarily designed to resist tensile forces and maintain structural integrity by preventing components from moving apart, often used in frameworks and machinery. Stay rods, on the other hand, provide lateral support and stabilization, counteracting compressive forces to keep structures upright and aligned. The key difference lies in their functional roles: tie rods handle tension while stay rods manage compression, making each essential for different structural applications.
Structural Applications of Tie Rods
Tie rods are crucial structural components designed to resist tension and maintain stability in framed structures, bridges, and buildings by transferring tensile forces efficiently. Unlike stay rods, which primarily stabilize temporary or flexible elements, tie rods provide permanent reinforcement and load distribution in trusses, roof supports, and retaining walls. Their high tensile strength and ability to withstand dynamic loads make tie rods essential for enhancing the integrity and durability of structural systems.
Structural Applications of Stay Rods
Stay rods are primarily used in structural applications to provide lateral support and stability to frameworks, preventing buckling under compressive loads. Unlike tie rods, which resist tensile forces by pulling structural elements together, stay rods function to maintain alignment and brace components against sideways movement. Their integration in bridges, towers, and roof trusses enhances rigidity and distributes stresses effectively throughout the structure.
Advantages of Using Tie Rods
Tie rods offer superior tensile strength and flexibility compared to stay rods, making them ideal for withstanding dynamic loads and structural shifts. Their adjustable design allows for precise tensioning, enhancing stability and alignment in construction and machinery applications. Tie rods also reduce installation time and maintenance costs due to their durability and ease of replacement.
Advantages of Using Stay Rods
Stay rods provide enhanced stability and load distribution compared to tie rods, reducing structural stress and potential deformation in frameworks. Their adaptability in length and tension adjustment allows precise alignment and improved resistance to dynamic forces, ideal for applications requiring long-term durability. Stay rods also offer easier maintenance and inspection access, contributing to safer and more efficient structural integrity management.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Tie Rod and Stay Rod
Selecting between a tie rod and a stay rod depends primarily on load type, environmental conditions, and structural requirements. Tie rods excel in tension applications where precise load distribution and minimal movement are critical, while stay rods offer enhanced flexibility and resistance in dynamic or corrosive environments. Material composition, installation complexity, and maintenance demands must also influence the decision to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Summary: Which is Better for Your Project?
Tie rods provide superior tensile strength and flexibility for structural support, making them ideal for dynamic load-bearing applications. Stay rods offer enhanced stability and resistance against lateral forces, often preferred in static or less flexible environments. Choosing between tie rod and stay rod depends on specific project requirements such as load type, environmental conditions, and desired durability.
tie rod vs stay rod Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com