A tie rod is a tension member used in construction and machinery to hold parts together and resist pulling forces, often adjustable to align components. A dowel is a cylindrical pin used primarily for alignment and to transfer shear loads between machine parts or wooden components without adjustment. While tie rods provide strength and tension control, dowels focus on positioning and load distribution in assemblies.
Table of Comparison
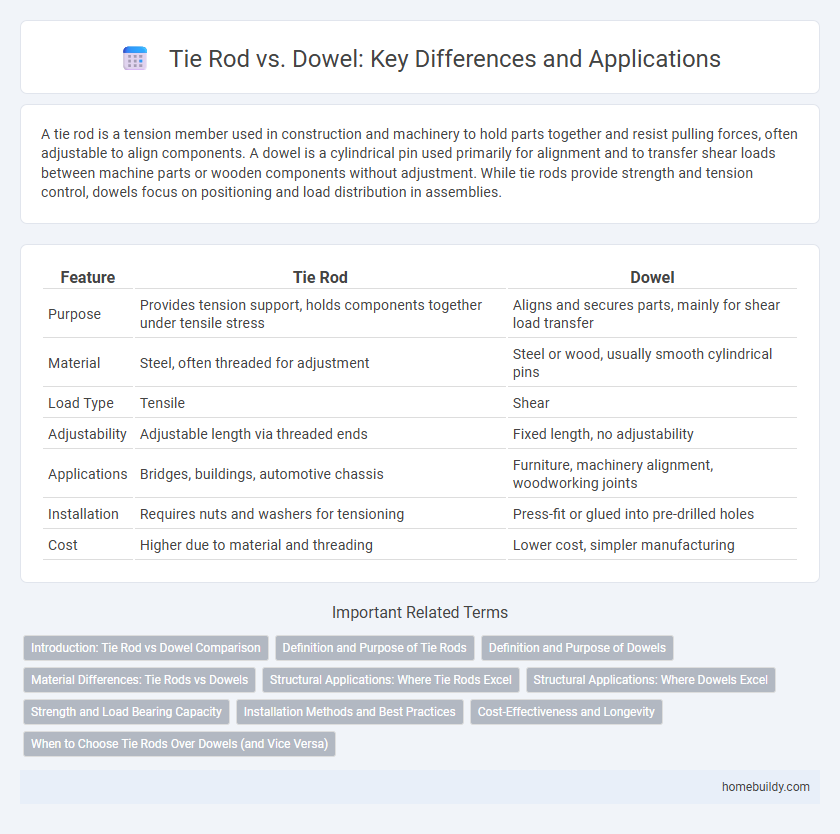
| Feature | Tie Rod | Dowel |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides tension support, holds components together under tensile stress | Aligns and secures parts, mainly for shear load transfer |
| Material | Steel, often threaded for adjustment | Steel or wood, usually smooth cylindrical pins |
| Load Type | Tensile | Shear |
| Adjustability | Adjustable length via threaded ends | Fixed length, no adjustability |
| Applications | Bridges, buildings, automotive chassis | Furniture, machinery alignment, woodworking joints |
| Installation | Requires nuts and washers for tensioning | Press-fit or glued into pre-drilled holes |
| Cost | Higher due to material and threading | Lower cost, simpler manufacturing |
Introduction: Tie Rod vs Dowel Comparison
Tie rods and dowels serve distinct purposes in construction and machinery; tie rods provide tensile strength by holding components together under tension, while dowels primarily function as alignment tools ensuring precise positioning. Tie rods are typically made from high-strength steel and can be adjusted or tensioned, whereas dowels are usually solid cylindrical pins that fit tightly into corresponding holes without tension adjustment. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate fastener based on load requirements and structural stability.
Definition and Purpose of Tie Rods
Tie rods are mechanical components designed to resist tensile forces and maintain structural integrity by holding parts together under tension, commonly used in construction and machinery frameworks. Unlike dowels, which primarily serve as alignment or locating pins to prevent lateral movement without bearing tensile load, tie rods actively ensure stability and load distribution. Their purpose centers on reinforcing structures against pulling forces to prevent deformation or separation of connected elements.
Definition and Purpose of Dowels
Dowels are cylindrical rods used primarily for precise alignment and reinforcement in woodworking and construction, ensuring structural stability by preventing lateral movement between joined parts. Unlike tie rods, which are designed to bear tension and hold structures together under load, dowels serve as locating pins to maintain exact positioning without bearing significant stress. The main purpose of dowels is to create tight, durable joints by fitting snugly into corresponding holes, enhancing alignment and strength within assemblies.
Material Differences: Tie Rods vs Dowels
Tie rods are typically made from high-strength steel alloys designed for tensile load resistance and flexibility, while dowels are usually crafted from hardened steel or stainless steel to provide rigid shear support. The choice of material impacts performance, with tie rods requiring materials that can withstand tension and bending without deformation, whereas dowels need materials optimized for compressive and shear forces. Understanding these material differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate component in structural and mechanical applications.
Structural Applications: Where Tie Rods Excel
Tie rods provide superior tensile strength and flexibility in structural applications compared to dowels, making them ideal for resisting dynamic loads and elongation. Their ability to be tensioned and adjusted on-site allows for precise alignment and reinforcement in long-span structures. Unlike dowels, tie rods accommodate movement and thermal expansion without compromising the structural integrity of bridges, buildings, and heavy machinery frameworks.
Structural Applications: Where Dowels Excel
Dowels provide superior shear strength and precise alignment in structural applications, making them ideal for heavy-load connections in timber framing and concrete formwork. Tie rods primarily handle tensile forces and are best suited for applications requiring adjustable tension and reinforcement, such as in bridge construction and suspension systems. Structural engineers often select dowels over tie rods when rigid, non-movable joints and exact component positioning are critical for stability and durability.
Strength and Load Bearing Capacity
Tie rods exhibit superior load-bearing capacity compared to dowels due to their tensile strength and ability to handle axial forces effectively. Unlike dowels, which primarily resist shear loads, tie rods are designed to withstand significant tension, enhancing structural integrity in applications such as bridge construction and machinery. This makes tie rods preferable for scenarios demanding high strength and durability under dynamic or heavy loads.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
Tie rods are installed by threading them into pre-drilled holes and securing with nuts, allowing for adjustable tension, whereas dowels are typically press-fitted or glued into place, offering fixed alignment without tension adjustment. Best practices for tie rod installation include ensuring threads are clean and properly lubricated, using correct torque specifications to prevent loosening, and verifying alignment for structural integrity. In contrast, dowel installation requires precise hole sizing and alignment to prevent movement or misalignment during curing or use.
Cost-Effectiveness and Longevity
Tie rods generally offer greater cost-effectiveness compared to dowels due to their easier installation and lower material expenses. Their adjustable design enhances longevity by accommodating structural movements and reducing stress concentrations, unlike dowels which are rigid and prone to cracking. This combination of affordability and durability makes tie rods a preferred choice in construction and mechanical applications requiring long-term stability.
When to Choose Tie Rods Over Dowels (and Vice Versa)
Tie rods provide superior tensile strength and are ideal for applications requiring adjustable tension and resistance to lateral forces, making them suitable for long spans and structural frameworks. Dowels offer precise alignment and shear strength in fixed joints, commonly used in woodworking and cabinetry to maintain exact positioning without movement. Choose tie rods when flexibility and load adjustment are critical; opt for dowels when joint accuracy and shear load distribution are the primary concerns.
tie rod vs dowel Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com