Tie bars connect concrete slabs on the same plane to maintain alignment and reduce horizontal movement, while dowel bars transfer load across joints between adjacent slabs to improve structural load-bearing capacity. Tie bars prevent joints from opening or separating, enhancing slab stability under thermal expansion or contraction. Dowel bars facilitate smooth weight transfer by allowing limited horizontal movement, minimizing joint stress and reducing pavement deterioration.
Table of Comparison
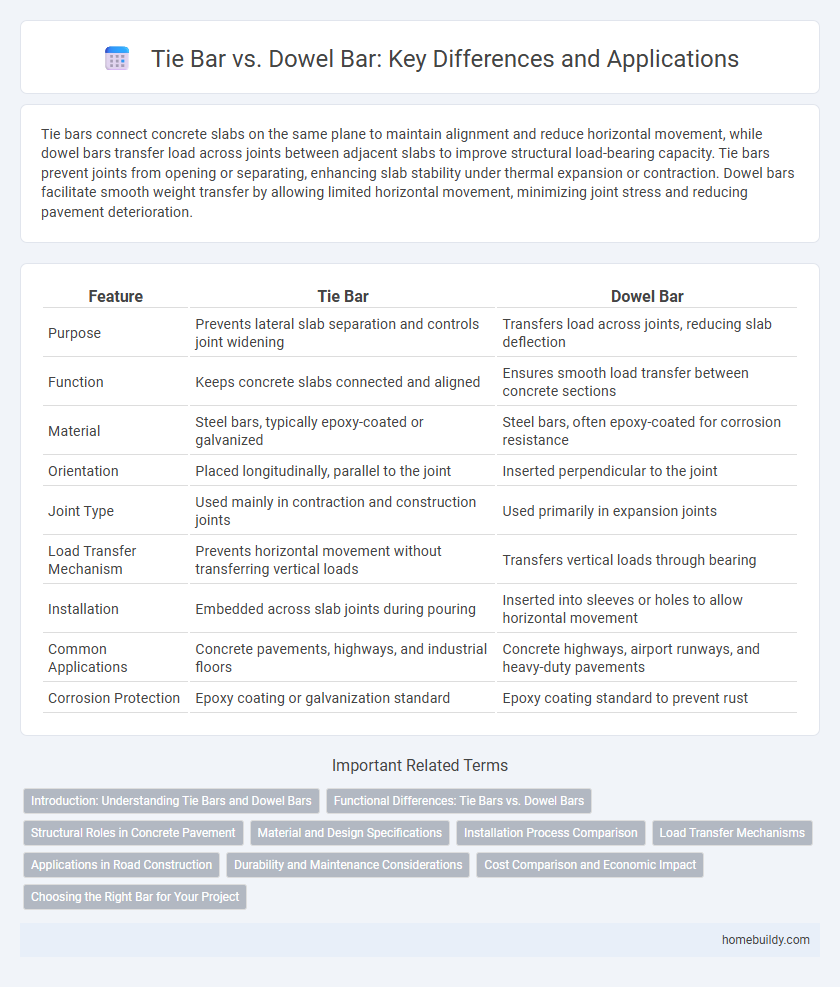
| Feature | Tie Bar | Dowel Bar |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents lateral slab separation and controls joint widening | Transfers load across joints, reducing slab deflection |
| Function | Keeps concrete slabs connected and aligned | Ensures smooth load transfer between concrete sections |
| Material | Steel bars, typically epoxy-coated or galvanized | Steel bars, often epoxy-coated for corrosion resistance |
| Orientation | Placed longitudinally, parallel to the joint | Inserted perpendicular to the joint |
| Joint Type | Used mainly in contraction and construction joints | Used primarily in expansion joints |
| Load Transfer Mechanism | Prevents horizontal movement without transferring vertical loads | Transfers vertical loads through bearing |
| Installation | Embedded across slab joints during pouring | Inserted into sleeves or holes to allow horizontal movement |
| Common Applications | Concrete pavements, highways, and industrial floors | Concrete highways, airport runways, and heavy-duty pavements |
| Corrosion Protection | Epoxy coating or galvanization standard | Epoxy coating standard to prevent rust |
Introduction: Understanding Tie Bars and Dowel Bars
Tie bars and dowel bars are essential components in concrete construction, specifically for slab reinforcement and joint stability. Tie bars primarily maintain alignment and prevent displacement between adjacent concrete sections, while dowel bars transfer load across joints to minimize stress and cracking. Understanding the distinct roles of tie bars and dowel bars enhances the design and durability of pavements and slabs in infrastructure projects.
Functional Differences: Tie Bars vs. Dowel Bars
Tie bars primarily serve to hold adjacent concrete slabs together, preventing faulting and maintaining alignment under load, while dowel bars enable horizontal load transfer by allowing controlled joint movement and reducing stress at the joint. Tie bars are typically deformed steel bars that resist separation and maintain slab continuity, whereas dowel bars are smooth steel bars designed to facilitate shear transfer across expansion joints. Understanding these functional differences is essential for optimizing pavement performance and durability in concrete road construction.
Structural Roles in Concrete Pavement
Tie bars primarily provide longitudinal load transfer and prevent slab separation in concrete pavement joints by tying adjacent slabs together, enhancing structural stability. Dowel bars serve to transfer vertical loads across joints, reducing slab deflection and distributing stress more evenly for increased pavement durability. Both elements are essential for maintaining pavement integrity but address different structural functions within concrete pavement systems.
Material and Design Specifications
Tie bars are typically made from high-strength steel with deformed surfaces to enhance bonding within concrete joints, offering flexibility to accommodate slab movements. Dowel bars are usually smooth, coated steel bars designed to transfer loads across joints while allowing horizontal movement without restraining expansion or contraction. Material choice and design specifications for tie bars emphasize tensile strength and deformation pattern, whereas dowel bars focus on corrosion resistance and precise diameter to ensure effective load transfer and reduced joint deterioration.
Installation Process Comparison
Tie bars are installed by placing them transversely across concrete slabs to restrict joint opening, requiring precise alignment and anchoring within the slab edges. Dowel bars are inserted into preformed sleeves or drilled holes on one slab side, allowing horizontal load transfer while permitting joint movement and requiring grouting after placement. The tie bar installation emphasizes joint restraint and concrete edge bonding, whereas dowel bars focus on load transfer efficiency with more complex insertion and grouting steps.
Load Transfer Mechanisms
Tie bars primarily provide load transfer by connecting adjacent concrete slabs, allowing movement while maintaining alignment and reducing joint faulting. Dowel bars facilitate load transfer through direct shear force transfer across joints by embedding into adjacent slabs, enabling concrete slab deflection under traffic loads. The choice between tie bars and dowel bars affects pavement performance, with dowel bars offering superior load transfer efficiency and tie bars ensuring slab stability.
Applications in Road Construction
Tie bars are primarily used to connect adjacent concrete pavement slabs, providing load transfer and preventing faulting in jointed concrete pavements. In contrast, dowel bars facilitate load transfer across expansion joints, allowing for horizontal slab movement while maintaining alignment. Tie bars are more effective in contraction joints where slab continuity is required, whereas dowel bars are preferred in expansion joints to accommodate thermal expansion in road construction.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Tie bars offer enhanced durability compared to dowel bars due to their continuous anchorage within concrete slabs, minimizing movement and reducing joint wear. Maintenance requirements are lower for tie bars as they effectively prevent slab separation and reduce the frequency of joint repairs. Dowel bars, while allowing transverse joint movement, can experience corrosion and require more frequent inspections and replacements to maintain pavement integrity.
Cost Comparison and Economic Impact
Tie bars typically cost less than dowel bars due to simpler manufacturing and installation processes, resulting in lower overall project expenses. The reduced labor and material costs associated with tie bars can significantly impact budget allocation in concrete pavement joint reinforcement. Choosing tie bars over dowel bars often leads to enhanced economic efficiency without sacrificing structural performance in many applications.
Choosing the Right Bar for Your Project
Choosing the right bar for your project depends on load transfer requirements and joint performance, with tie bars providing superior restraint against joint opening in concrete slabs. Dowel bars primarily facilitate load transfer across joints by allowing horizontal movements while minimizing stress, making them ideal for slabs subject to expansion and contraction. Evaluating factors such as traffic load, slab design, and environmental conditions will determine whether tie bars or dowel bars offer optimal durability and structural integrity.
Tie bar vs Dowel bar Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com