A tie bar provides structural stability by firmly connecting two components, typically in tension, to reduce movement or separation under load. A splice plate is a flat metal plate used to join two sections of material, often reinforcing a joint to restore strength where continuity is interrupted. Both serve to enhance structural integrity, but tie bars focus on tension resistance while splice plates emphasize joint reinforcement.
Table of Comparison
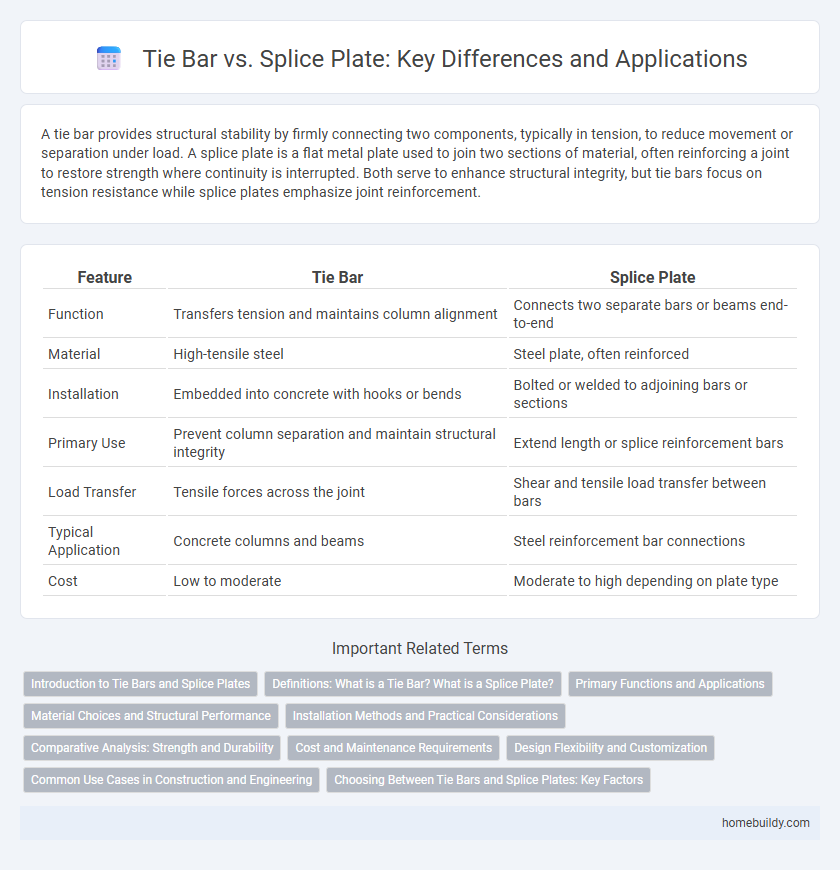
| Feature | Tie Bar | Splice Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Transfers tension and maintains column alignment | Connects two separate bars or beams end-to-end |
| Material | High-tensile steel | Steel plate, often reinforced |
| Installation | Embedded into concrete with hooks or bends | Bolted or welded to adjoining bars or sections |
| Primary Use | Prevent column separation and maintain structural integrity | Extend length or splice reinforcement bars |
| Load Transfer | Tensile forces across the joint | Shear and tensile load transfer between bars |
| Typical Application | Concrete columns and beams | Steel reinforcement bar connections |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high depending on plate type |
Introduction to Tie Bars and Splice Plates
Tie bars are steel reinforcements used primarily to connect and stabilize concrete slabs, improving load distribution and reducing crack formation in construction joints. Splice plates serve as metal connectors that join two steel sections, ensuring structural continuity and strength in steel frameworks. Both components are critical in construction, with tie bars enhancing concrete integrity while splice plates maintain steel structural alignment.
Definitions: What is a Tie Bar? What is a Splice Plate?
A tie bar is a steel reinforcement component used in concrete slabs to maintain alignment and resist joint separation by transferring tensile stresses across joints. A splice plate is a metal connector that joins two structural elements, such as beams or columns, ensuring continuity and strength at the connection point. Tie bars primarily control movement in concrete pavements, while splice plates focus on structural element connections in steel frameworks.
Primary Functions and Applications
Tie bars provide structural reinforcement by connecting concrete elements to control cracking and maintain alignment under stress, commonly used in slab construction and expansion joints. Splice plates primarily serve to join steel components, such as beams and columns, ensuring load transfer and continuity in steel frameworks. While tie bars excel in tension control for concrete, splice plates are essential for structural steel connections in building frames and bridges.
Material Choices and Structural Performance
Tie bars, commonly made from high-strength steel or reinforced concrete, offer superior tensile strength and ductility compared to splice plates, which are often fabricated from carbon steel or alloy steel. The continuous nature of tie bars ensures uniform load distribution and enhanced structural integrity, while splice plates rely on bolted or welded connections that may introduce stress concentrations and reduced fatigue resistance. Material choices influence durability and maintenance requirements, with tie bars generally providing better long-term performance in dynamic or seismic applications.
Installation Methods and Practical Considerations
Tie bars require precise positioning within concrete slabs, installed by embedding them perpendicular to saw cuts to control joint movement and reduce slab cracking. Splice plates are typically surface-mounted with bolts or welds to connect steel elements, allowing for easier adjustments during installation but requiring additional on-site labor and alignment checks. The choice between tie bars and splice plates depends on project specifications, structural demands, and installation environment constraints.
Comparative Analysis: Strength and Durability
Tie bars offer superior strength and durability compared to splice plates due to their continuous steel construction, which minimizes stress concentration points and distributes loads evenly across the joint. Splice plates, while easier to install, create localized stress areas at bolt holes, potentially reducing the overall structural integrity under dynamic or high-load conditions. The continuous nature of tie bars ensures longer-lasting performance in concrete slab reinforcements, making them the preferred choice for heavy-duty applications.
Cost and Maintenance Requirements
Tie bars offer a cost-effective alternative to splice plates by minimizing material and installation expenses, as they require fewer components and simpler labor processes. Maintenance demands for tie bars are generally lower due to their integrated design, reducing inspection frequency and potential for joint failure compared to splice plates, which involve multiple fasteners prone to corrosion and loosening. Choosing tie bars can lead to long-term savings through decreased upkeep and enhanced structural integrity.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Tie bars offer greater design flexibility and customization compared to splice plates by allowing tailored length, thickness, and material specifications to fit unique structural requirements. Unlike splice plates, tie bars can be easily adjusted or fabricated onsite to accommodate complex geometries and load conditions. This adaptability makes tie bars a preferred choice in projects demanding precise alignment and enhanced structural integrity.
Common Use Cases in Construction and Engineering
Tie bars are commonly used in concrete construction to reinforce joints and control cracking, providing tensile strength across expansion joints and slabs. Splice plates are preferred in steel construction for joining structural members, such as beams and columns, offering rigid and strong connections in frameworks. Both components enhance structural integrity but serve distinct purposes: tie bars are ideal for maintaining alignment in concrete, while splice plates facilitate the extension or repair of steel elements.
Choosing Between Tie Bars and Splice Plates: Key Factors
Choosing between tie bars and splice plates depends on factors such as load requirements, installation complexity, and structural design. Tie bars provide superior tension capacity and are ideal for controlling crack widths in concrete slabs. Splice plates offer ease of installation and cost-effectiveness in connecting steel members but may not provide the same load distribution as tie bars.
Tie bar vs Splice plate Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com