A tie bar is a structural element designed to resist tension forces, providing lateral stability by connecting two points and preventing them from moving apart. In contrast, a truss is a framework composed of triangular units that efficiently distribute both tension and compression forces throughout the structure. Understanding the differences between a tie bar and a truss is essential for optimizing design in construction and engineering projects.
Table of Comparison
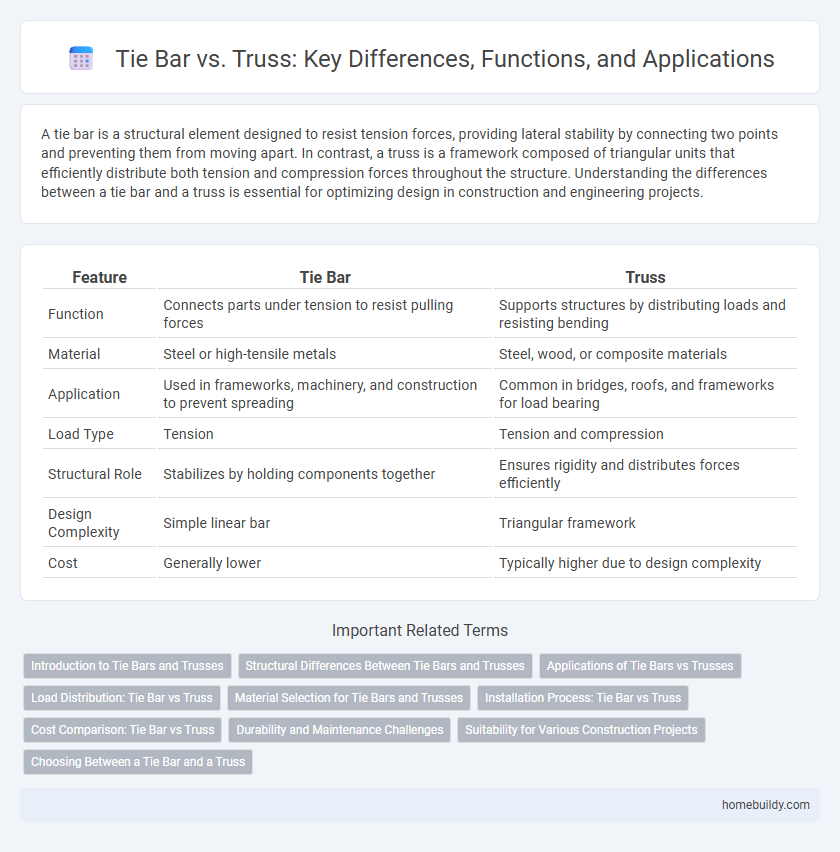
| Feature | Tie Bar | Truss |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Connects parts under tension to resist pulling forces | Supports structures by distributing loads and resisting bending |
| Material | Steel or high-tensile metals | Steel, wood, or composite materials |
| Application | Used in frameworks, machinery, and construction to prevent spreading | Common in bridges, roofs, and frameworks for load bearing |
| Load Type | Tension | Tension and compression |
| Structural Role | Stabilizes by holding components together | Ensures rigidity and distributes forces efficiently |
| Design Complexity | Simple linear bar | Triangular framework |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher due to design complexity |
Introduction to Tie Bars and Trusses
Tie bars and trusses are structural elements used to resist tension and compression forces in construction frameworks. Tie bars are typically slender rods or bars designed to handle tensile loads by connecting two components, while trusses are composed of interconnected triangles distributing both tensile and compressive forces for enhanced stability. Selecting between tie bars and trusses depends on load requirements, span length, and the nature of the structural application.
Structural Differences Between Tie Bars and Trusses
Tie bars are slender, tension-only members designed to resist pulling forces, whereas trusses consist of interconnected triangles that handle both tension and compression. Tie bars primarily provide lateral support to prevent structural elements from spreading, while trusses distribute loads efficiently through their triangular framework for enhanced stability. The fundamental difference lies in tie bars being simple tensile connectors, while trusses function as complex load-bearing assemblies offering multi-directional strength.
Applications of Tie Bars vs Trusses
Tie bars are primarily used in applications requiring tension support, such as reinforcing concrete slabs and maintaining structural alignment under tensile forces. Trusses are ideal for distributing loads in bridges, roofs, and towers, providing stability through triangulated frameworks that handle both compression and tension. The choice between tie bars and trusses depends on load type and structural requirements, with tie bars focusing on tensile reinforcement and trusses optimizing weight distribution and overall strength.
Load Distribution: Tie Bar vs Truss
Tie bars primarily handle tensile loads, efficiently distributing tension forces across structural elements without bearing compressive stresses. Trusses distribute both compressive and tensile loads through interconnected triangular units, providing enhanced stiffness and load-bearing capacity in multiple directions. The load distribution in trusses results in better resistance to bending moments, whereas tie bars offer focused tension support within frameworks.
Material Selection for Tie Bars and Trusses
Tie bars frequently utilize high-strength steel alloys for their superior tensile properties and durability under dynamic loads, whereas trusses often incorporate a combination of steel and lightweight aluminum to optimize weight and structural efficiency. Material selection for tie bars prioritizes fatigue resistance and flexibility, essential for maintaining tension, while truss materials are chosen for compressive strength and stiffness to support distributed loads. Engineering decisions balance corrosion resistance, cost, and mechanical performance to meet specific application requirements in both tie bars and trusses.
Installation Process: Tie Bar vs Truss
The installation process of tie bars is generally simpler and faster compared to trusses due to their straightforward design and fewer connection points. Tie bars require precise alignment and anchoring to prevent post-tensioning failures, while trusses often involve complex assembly with multiple diagonal and vertical components demanding more time and specialized labor. In construction projects where rapid deployment and minimal installation complexity are critical, tie bars provide an efficient alternative to the more intricate truss systems.
Cost Comparison: Tie Bar vs Truss
Tie bars generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to trusses due to simpler fabrication and installation processes. Trusses, while often more expensive initially, provide enhanced load distribution and structural stability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses. The choice between tie bars and trusses should consider both initial budget constraints and lifecycle costs to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Durability and Maintenance Challenges
Tie bars offer superior durability compared to trusses due to their fewer connection points and simpler load distribution, resulting in reduced wear and tear over time. Maintenance challenges for tie bars are generally lower, as their straightforward design allows easier inspection and quicker repairs. Trusses, with multiple joints and complex geometry, often require more frequent monitoring and specialized maintenance to address potential fatigue and corrosion issues.
Suitability for Various Construction Projects
Tie bars provide essential tensile strength in concrete structures, making them ideal for projects requiring resistance to tensile forces such as retaining walls and slab reinforcements. Trusses offer superior load distribution and are suitable for long-span applications like bridges and large roof structures due to their triangular framework. Choosing between tie bars and trusses depends on the specific load requirements, structural design, and project scale within construction planning.
Choosing Between a Tie Bar and a Truss
Choosing between a tie bar and a truss depends primarily on the application's structural requirements and space constraints. Tie bars provide direct tensile support to prevent frame distortion under load, making them ideal for reinforcing narrow or open-frame designs, while trusses offer enhanced rigidity and distribute loads through a triangulated structure, suitable for larger spans and heavy-duty applications. Evaluating load conditions, installation space, and desired stiffness guides the optimal selection for frame reinforcement.
Tie bar vs Truss Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com