Stud shoes provide a protective barrier around concrete studs to prevent wear and corrosion, enhancing durability in construction applications. Stud anchors, by contrast, are fasteners embedded in concrete to secure structural elements and transfer loads effectively. Understanding the distinction between stud shoes and stud anchors is crucial for selecting the appropriate component in building and infrastructure projects.
Table of Comparison
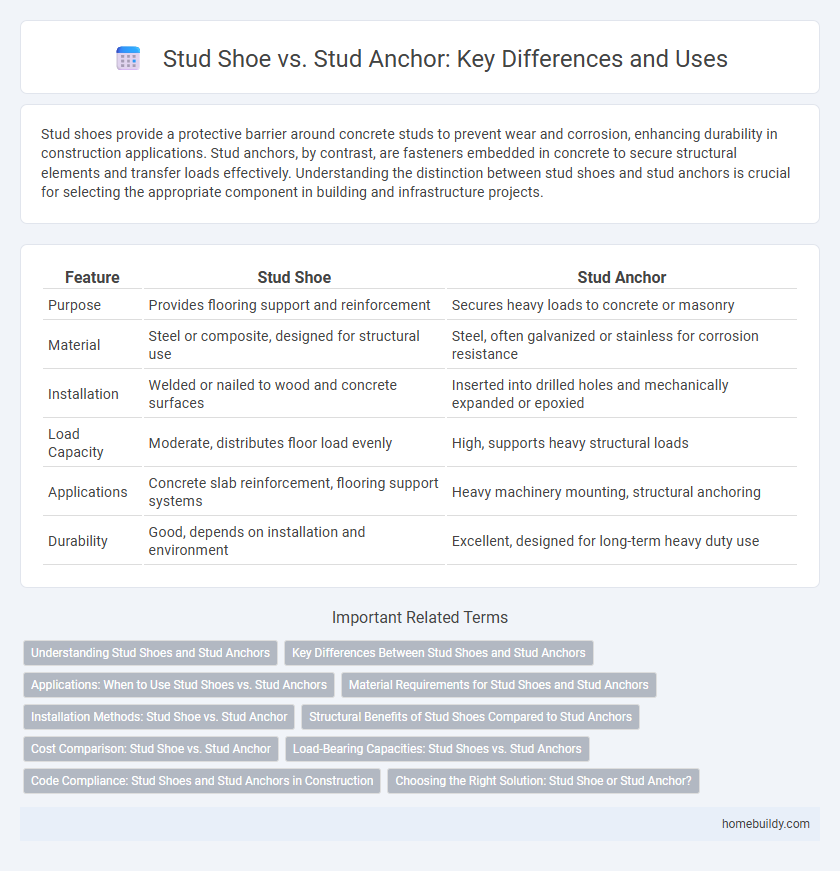
| Feature | Stud Shoe | Stud Anchor |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides flooring support and reinforcement | Secures heavy loads to concrete or masonry |
| Material | Steel or composite, designed for structural use | Steel, often galvanized or stainless for corrosion resistance |
| Installation | Welded or nailed to wood and concrete surfaces | Inserted into drilled holes and mechanically expanded or epoxied |
| Load Capacity | Moderate, distributes floor load evenly | High, supports heavy structural loads |
| Applications | Concrete slab reinforcement, flooring support systems | Heavy machinery mounting, structural anchoring |
| Durability | Good, depends on installation and environment | Excellent, designed for long-term heavy duty use |
Understanding Stud Shoes and Stud Anchors
Stud shoes provide a secure base for fastening bolts in construction, primarily designed to anchor structural elements to concrete or masonry. Stud anchors, on the other hand, are mechanical fasteners that expand within a drilled hole to create a strong hold in solid materials. Both components are critical in heavy-duty applications, but stud shoes offer a specialized interface for attaching studs, whereas stud anchors focus on embedding bolts firmly into substrates.
Key Differences Between Stud Shoes and Stud Anchors
Stud shoes are metal fittings welded to steel structures, providing a secure anchor point for concrete slabs by enhancing shear strength. Stud anchors, by contrast, are mechanical fasteners embedded into concrete to affix steel components, relying on friction and bearing resistance for stability. The key difference lies in their installation method and function: stud shoes are integral to structural connection within steel frameworks, while stud anchors serve as attachment points between steel and concrete elements.
Applications: When to Use Stud Shoes vs. Stud Anchors
Stud shoes are ideal for use in structural steel connections where a continuous load transfer is required, such as in beam-to-column joints and shear connections in steel frameworks. Stud anchors are typically used to secure fixtures to concrete or masonry surfaces, providing strong anchorage for equipment, railings, or heavy machinery bases. Choosing stud shoes over stud anchors depends on whether the application demands integration within a steel framework or attachment to a solid substrate like concrete.
Material Requirements for Stud Shoes and Stud Anchors
Stud shoes and stud anchors require high-strength steel with excellent tensile properties to ensure structural integrity and load transfer. Stud shoes often demand precise dimensional tolerances and corrosion-resistant coatings to accommodate concrete embedding and environmental exposure. Stud anchors typically use heat-treated alloy steel with high hardness to resist shear forces and provide durable fastening in construction applications.
Installation Methods: Stud Shoe vs. Stud Anchor
Stud shoes install by welding directly to steel structures, creating a strong, continuous bond ideal for composite decking and concrete slabs. Stud anchors require drilling holes into concrete or masonry, then inserting the anchor and securing it with mechanical expansion or chemical adhesive for load transfer. Welding offers faster installation but needs skilled labor, while stud anchors provide versatility for retrofit projects without welding equipment.
Structural Benefits of Stud Shoes Compared to Stud Anchors
Stud shoes provide superior load transfer and increased structural stability by fully encasing and supporting rebar ends, reducing stress concentrations commonly seen with stud anchors. Their design enhances concrete bond strength and improves anchorage capacity, leading to better performance under shear and tensile forces in reinforced concrete structures. This results in longer-lasting connections and increased safety margins compared to traditional stud anchors.
Cost Comparison: Stud Shoe vs. Stud Anchor
Stud shoes generally offer a lower initial cost compared to stud anchors due to simpler manufacturing and installation processes. Stud anchors, while typically more expensive upfront, provide enhanced load-bearing capacity and durability, often reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Cost comparison should consider project scale and structural requirements to determine the most economical choice between stud shoes and stud anchors.
Load-Bearing Capacities: Stud Shoes vs. Stud Anchors
Stud shoes provide enhanced load-bearing capacities by securely embedding structural steel beams into concrete foundations, distributing weight evenly and reducing stress concentrations. Stud anchors, while effective for fastening, typically offer lower load-bearing capacity due to limited surface contact and embedment depth. Choosing stud shoes over stud anchors ensures superior support for heavy-duty structural applications, improving stability and safety in construction projects.
Code Compliance: Stud Shoes and Stud Anchors in Construction
Stud shoes and stud anchors both serve to secure structural elements but differ in code compliance requirements specified by the International Building Code (IBC). Stud shoes are typically non-load bearing components used for bracing and must comply with ASTM standards for mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Stud anchors, designed for anchoring studs into concrete or masonry, require evaluation under ACI 318 for load capacities and must meet testing criteria to ensure proper embedment and shear resistance in construction applications.
Choosing the Right Solution: Stud Shoe or Stud Anchor?
Choosing between a stud shoe and a stud anchor depends on the specific load requirements and installation environment of the project. Stud shoes provide a larger bearing surface and better load distribution for heavy-duty structural connections, while stud anchors offer ease of installation and suitability for lighter loads or retrofit applications. Evaluating factors like concrete strength, load type, and precision alignment is essential to determine the optimal solution for secure and durable fastening.
Stud shoe vs stud anchor Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com