Stud shoes provide enhanced traction and stability by incorporating raised metal studs that grip surfaces firmly, making them ideal for construction and heavy-duty applications. Tie plates, on the other hand, serve as flat metal connectors that maintain the alignment of rails or structural components without offering traction. Comparing stud shoes to tie plates highlights the key difference: stud shoes prioritize grip and durability, while tie plates focus on secure and stable connections.
Table of Comparison
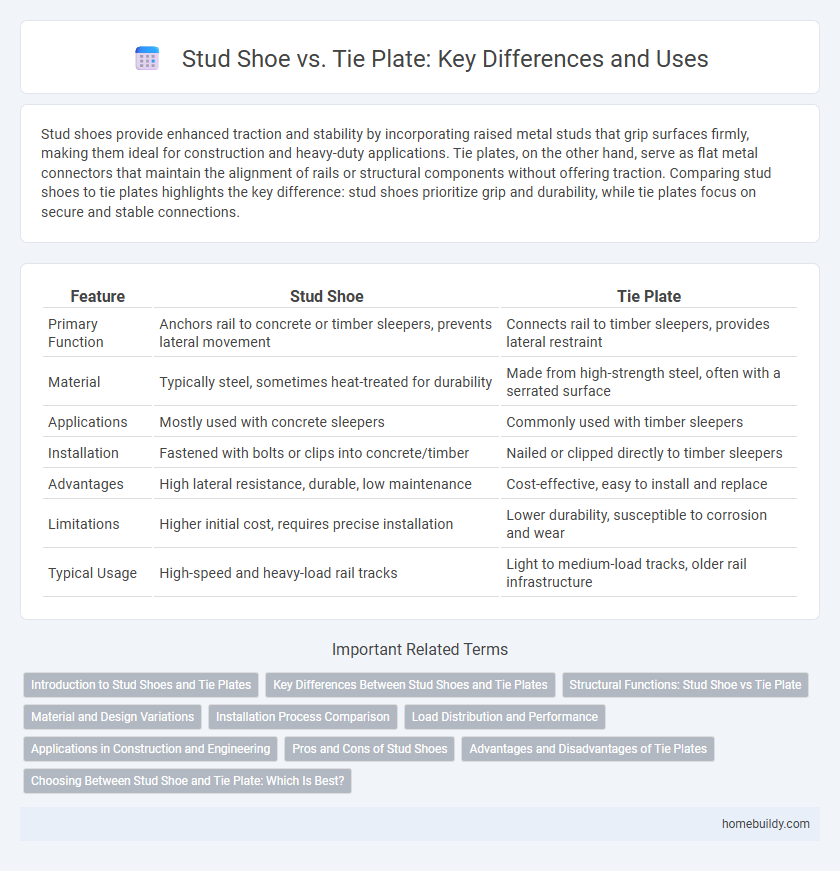
| Feature | Stud Shoe | Tie Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Anchors rail to concrete or timber sleepers, prevents lateral movement | Connects rail to timber sleepers, provides lateral restraint |
| Material | Typically steel, sometimes heat-treated for durability | Made from high-strength steel, often with a serrated surface |
| Applications | Mostly used with concrete sleepers | Commonly used with timber sleepers |
| Installation | Fastened with bolts or clips into concrete/timber | Nailed or clipped directly to timber sleepers |
| Advantages | High lateral resistance, durable, low maintenance | Cost-effective, easy to install and replace |
| Limitations | Higher initial cost, requires precise installation | Lower durability, susceptible to corrosion and wear |
| Typical Usage | High-speed and heavy-load rail tracks | Light to medium-load tracks, older rail infrastructure |
Introduction to Stud Shoes and Tie Plates
Stud shoes and tie plates serve distinct purposes in steel construction connections, with stud shoes designed to transfer loads between structural members through welded attachment, enhancing stability and load distribution. Tie plates, on the other hand, are fastening elements that connect steel components by providing shear transfer and reinforcement, commonly used in beam-to-column or beam-to-beam joints. Understanding the functional differences between stud shoes and tie plates is crucial for selecting appropriate connectors to optimize structural performance and safety.
Key Differences Between Stud Shoes and Tie Plates
Stud shoes and tie plates are both essential components in railway track construction, but they serve distinct functions with different designs. Stud shoes are designed to secure rails to the sleepers by providing enhanced grip through raised studs, preventing longitudinal rail movement under dynamic loads. Tie plates, on the other hand, are flat metal plates placed between the rail and the sleeper, distributing the load over a larger area and minimizing rail wear, but they do not provide the same anti-movement features as stud shoes.
Structural Functions: Stud Shoe vs Tie Plate
Stud shoes and tie plates serve distinct structural functions in steel construction, with stud shoes primarily designed to connect steel beams to concrete slabs, providing shear transfer and load distribution. Tie plates, in contrast, function mainly as connectors between steel members, enhancing moment resistance and ensuring alignment in beam-to-column joints. The choice between stud shoes and tie plates depends on specific load transfer requirements and the desired structural performance of the composite system.
Material and Design Variations
Stud shoes are typically made from heavy-duty steel or alloy, offering robust durability and impact resistance, while tie plates are generally constructed from softer metals like galvanized steel to balance strength with flexibility. The design of stud shoes features raised studs or spikes that enhance traction and grip on railway tracks, contrasting with tie plates' flat, plate-like structure designed to evenly distribute rail loads and maintain track gauge. Material choices and structural variations in both components directly influence their performance in track stability and longevity.
Installation Process Comparison
Stud shoes feature an integrated stud for straightforward installation, allowing the shoe to be directly nailed into the form, speeding up labor time and reducing the need for additional materials. Tie plates require precise alignment and additional fastening steps, including the use of nails or screws to secure both the plate and the studs separately, often extending the installation duration. The simplified attachment in stud shoes minimizes installation errors and is more efficient for high-volume construction projects compared to the complexity of tie plates.
Load Distribution and Performance
Stud shoes provide superior load distribution by evenly dispersing forces across a wider surface area, reducing stress concentrations compared to tie plates. This enhanced load distribution improves structural performance and longevity in applications such as railway tracks and concrete reinforcement. Tie plates, while effective for securing rails, concentrate loads in smaller regions, potentially increasing wear and maintenance requirements over time.
Applications in Construction and Engineering
Stud shoes provide superior load distribution and shear resistance in concrete connections, making them ideal for steel beam-to-concrete slab applications in construction and engineering. Tie plates offer enhanced alignment and stability for fastening structural steel elements but are less effective in transferring shear loads compared to stud shoes. In projects requiring high structural integrity under dynamic loads, such as bridges and high-rise buildings, stud shoes are preferred for their robust performance.
Pros and Cons of Stud Shoes
Stud shoes provide enhanced stability and grip on steel tracks by offering a more secure connection through the embedded studs, reducing lateral movement and improving safety in railway operations. They are easier to inspect and maintain compared to tie plates, but their installation can be more labor-intensive and costly due to the precise placement required. While stud shoes offer superior load distribution and durability in high-stress areas, tie plates remain more versatile and cost-effective for general track fastening needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tie Plates
Tie plates offer stronger fastening for rails and reduce rail movement better than stud shoes, enhancing track stability and safety. They distribute loads evenly across sleepers, minimizing wear and extending track lifespan, but their installation can be more complex and time-consuming compared to stud shoes. Tie plates may require more maintenance and are less adaptable to irregular or curved track sections, limiting their use in some railway environments.
Choosing Between Stud Shoe and Tie Plate: Which Is Best?
Stud shoes provide superior load distribution and enhanced stability by integrating directly with structural steel beams, making them ideal for high-stress applications. Tie plates offer cost-effective reinforcement by connecting beams without welding, suitable for lighter loads and simpler constructions. Selecting between stud shoes and tie plates depends on project-specific factors such as load requirements, structural complexity, and budget constraints.
stud shoe vs tie plate Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com