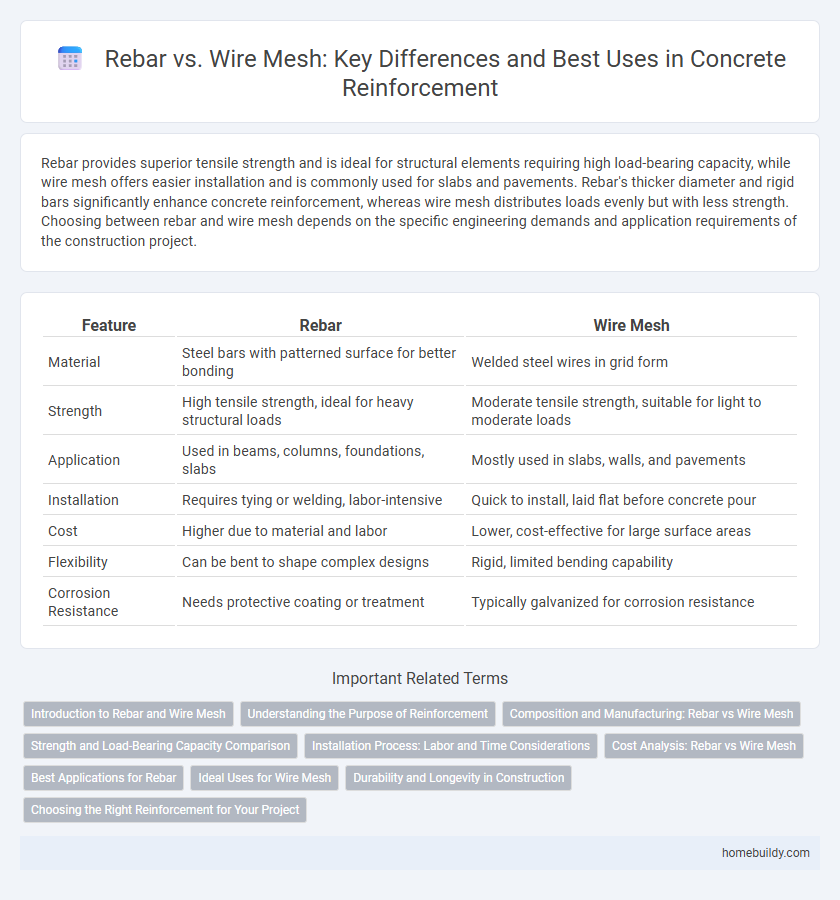
Rebar provides superior tensile strength and is ideal for structural elements requiring high load-bearing capacity, while wire mesh offers easier installation and is commonly used for slabs and pavements. Rebar's thicker diameter and rigid bars significantly enhance concrete reinforcement, whereas wire mesh distributes loads evenly but with less strength. Choosing between rebar and wire mesh depends on the specific engineering demands and application requirements of the construction project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rebar | Wire Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel bars with patterned surface for better bonding | Welded steel wires in grid form |
| Strength | High tensile strength, ideal for heavy structural loads | Moderate tensile strength, suitable for light to moderate loads |
| Application | Used in beams, columns, foundations, slabs | Mostly used in slabs, walls, and pavements |
| Installation | Requires tying or welding, labor-intensive | Quick to install, laid flat before concrete pour |
| Cost | Higher due to material and labor | Lower, cost-effective for large surface areas |
| Flexibility | Can be bent to shape complex designs | Rigid, limited bending capability |
| Corrosion Resistance | Needs protective coating or treatment | Typically galvanized for corrosion resistance |
Introduction to Rebar and Wire Mesh
Rebar, made of steel with ribbed surfaces, provides tensile strength and reinforcement in concrete structures, preventing cracks and structural failure. Wire mesh consists of welded steel wires arranged in a grid pattern, offering uniform distribution of stress and enhancing concrete durability. Both materials serve critical roles in construction, with rebar preferred for heavy load-bearing applications and wire mesh for surface reinforcement.
Understanding the Purpose of Reinforcement
Rebar provides tensile strength and structural support by embedding steel bars within concrete, which helps resist bending and cracking under heavy loads. Wire mesh offers uniform load distribution and prevents surface cracking but lacks the deep tensile reinforcement that rebar delivers. Selecting between rebar and wire mesh depends on the specific structural requirements, with rebar favored for heavy-duty reinforcement and wire mesh for controlling surface stress.
Composition and Manufacturing: Rebar vs Wire Mesh
Rebar consists of steel bars or rods, typically made from carbon steel, featuring deformations or ridges for improved bonding with concrete, manufactured through hot rolling and threading processes. Wire mesh is composed of interconnected steel wires welded or woven into a grid pattern, produced through wire drawing and welding techniques. The distinct compositions and manufacturing methods of rebar and wire mesh influence their tensile strength, flexibility, and suitability for different structural reinforcement applications.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity Comparison
Rebar offers superior tensile strength and load-bearing capacity compared to wire mesh, making it ideal for structural elements subjected to heavy stress such as beams and columns. Wire mesh provides adequate reinforcement for slabs and light load applications but lacks the rigidity and strength needed for high-load-bearing structures. Engineering assessments consistently favor rebar for critical load-bearing components due to its higher yield strength and durability under tension and compression.
Installation Process: Labor and Time Considerations
Rebar installation requires skilled labor to accurately place and tie each bar, often extending project timelines due to the precision needed in positioning and overlap. Wire mesh, being prefabricated in sheets, offers faster installation with less labor intensity since it can be quickly laid out and tied together, reducing overall construction time. Choosing between rebar and wire mesh depends on balancing labor availability, project complexity, and schedule constraints.
Cost Analysis: Rebar vs Wire Mesh
Rebar generally incurs higher upfront material and labor costs compared to wire mesh, but offers superior tensile strength and flexibility for heavy load-bearing structures. Wire mesh, while more cost-effective for smaller-scale projects and simpler slab reinforcement, may require supplemental support in high-stress applications, potentially increasing overall expenses. Evaluating project scale, structural demands, and installation complexity is essential for accurate cost analysis between rebar and wire mesh reinforcement options.
Best Applications for Rebar
Rebar offers superior tensile strength and is ideal for structural applications requiring heavy load-bearing capacity, such as foundations, beams, and columns in commercial and residential construction. It provides excellent bonding with concrete, enhancing durability in high-stress environments like bridges, highways, and industrial buildings. Wire mesh suits surface reinforcement but is less effective than rebar in structural frameworks demanding greater flexibility and resistance to dynamic forces.
Ideal Uses for Wire Mesh
Wire mesh is ideal for slab reinforcement, particularly in thin concrete sections such as driveways, sidewalks, and floor slabs where uniform load distribution is essential. Its lightweight, flexible nature allows easier handling and faster installation compared to rebar, making it suitable for large surface areas requiring crack control. Wire mesh also excels in applications with moderate structural demands, providing effective tensile strength and crack resistance in concrete.
Durability and Longevity in Construction
Rebar exhibits superior durability and longevity in construction compared to wire mesh due to its higher tensile strength and resistance to cracking under stress. Embedded in concrete, rebar enhances structural integrity by effectively distributing loads and minimizing corrosion risks when properly coated. Wire mesh, while useful for reducing surface cracking, generally lacks the robustness required for heavy-duty reinforcement and long-term durability in critical structural applications.
Choosing the Right Reinforcement for Your Project
Rebar offers superior tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for heavy structural loads and complex shapes, while wire mesh provides even distribution of load and is easier to install for slabs and flat surfaces. Choosing the right reinforcement depends on project requirements such as load capacity, structural complexity, and installation efficiency, with rebar preferred for beams and columns and wire mesh commonly used in floor slabs and pavements. Evaluating project-specific factors like cost, labor, and design specifications ensures optimal performance and durability.
Rebar vs Wire Mesh Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com