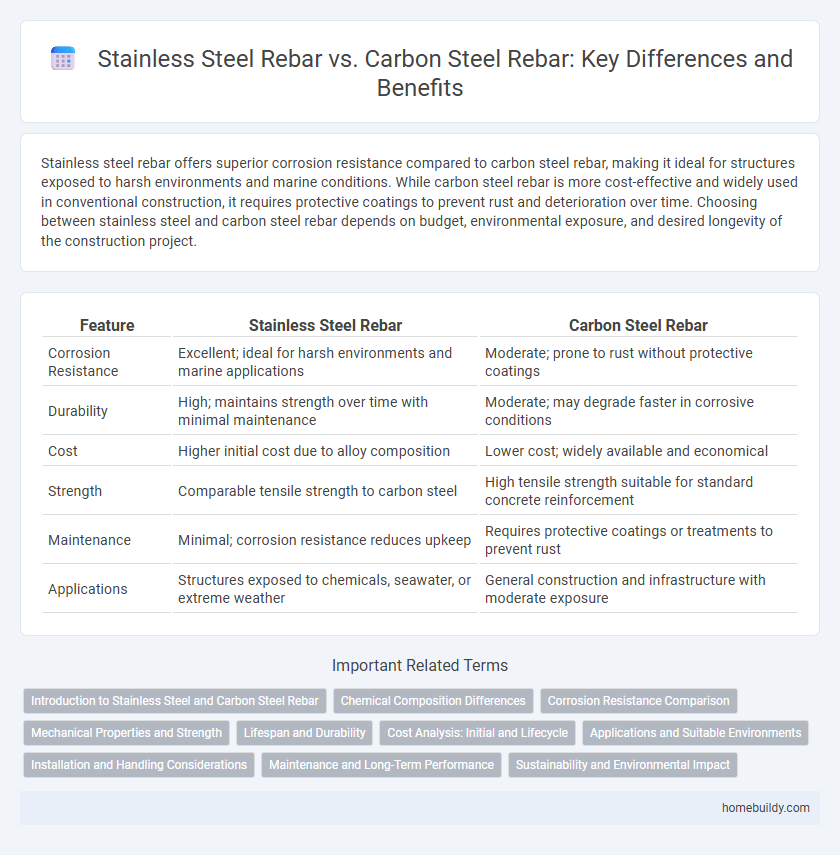
Stainless steel rebar offers superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel rebar, making it ideal for structures exposed to harsh environments and marine conditions. While carbon steel rebar is more cost-effective and widely used in conventional construction, it requires protective coatings to prevent rust and deterioration over time. Choosing between stainless steel and carbon steel rebar depends on budget, environmental exposure, and desired longevity of the construction project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stainless Steel Rebar | Carbon Steel Rebar |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent; ideal for harsh environments and marine applications | Moderate; prone to rust without protective coatings |
| Durability | High; maintains strength over time with minimal maintenance | Moderate; may degrade faster in corrosive conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to alloy composition | Lower cost; widely available and economical |
| Strength | Comparable tensile strength to carbon steel | High tensile strength suitable for standard concrete reinforcement |
| Maintenance | Minimal; corrosion resistance reduces upkeep | Requires protective coatings or treatments to prevent rust |
| Applications | Structures exposed to chemicals, seawater, or extreme weather | General construction and infrastructure with moderate exposure |
Introduction to Stainless Steel and Carbon Steel Rebar
Stainless steel rebar is composed primarily of iron, chromium, and nickel, offering superior corrosion resistance and durability in harsh environments compared to carbon steel rebar, which consists mainly of iron and carbon and is prone to rust and deterioration over time. The chromium content in stainless steel rebar forms a passive layer that protects against oxidation, making it ideal for marine, chemical, and high-moisture applications. Carbon steel rebar remains widely used due to its lower cost and adequate performance in standard construction projects with less aggressive exposure conditions.
Chemical Composition Differences
Stainless steel rebar contains higher levels of chromium (typically 10.5% to 30%), which forms a passive oxide layer providing corrosion resistance, while carbon steel rebar primarily consists of iron with a carbon content ranging from 0.1% to 0.3%, making it more susceptible to rust. The presence of nickel and molybdenum in stainless steel enhances its strength and durability in harsh acidic or saline environments. Carbon steel rebar's simpler chemical composition makes it cost-effective but requires protective coatings to prevent corrosion.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Stainless steel rebar offers superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel rebar due to its high chromium content, which forms a passive oxide layer that prevents rust formation. Carbon steel rebar, while cost-effective, is prone to corrosion in moist or chloride-rich environments, leading to structural degradation over time. Choosing stainless steel rebar significantly enhances the longevity and durability of reinforced concrete, especially in marine or chemically aggressive settings.
Mechanical Properties and Strength
Stainless steel rebar exhibits higher tensile strength and superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel rebar, making it ideal for structures exposed to harsh environments. Carbon steel rebar offers adequate mechanical properties with cost-effectiveness but is prone to rust that can weaken structural integrity over time. The enhanced durability and strength of stainless steel rebar result in longer lifespan and reduced maintenance in construction projects.
Lifespan and Durability
Stainless steel rebar offers superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel rebar, significantly extending its lifespan in harsh environments such as coastal or chemically aggressive areas. Carbon steel rebar typically has a shorter durability span due to its susceptibility to rust and corrosion, leading to structural weakening over time. The higher initial cost of stainless steel rebar is offset by reduced maintenance and replacement expenses, making it a more cost-effective choice for long-term infrastructure projects.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Lifecycle
Stainless steel rebar has a higher initial cost, often ranging from 3 to 8 times more than carbon steel rebar due to its corrosion-resistant alloy composition. However, stainless steel offers greater lifecycle value by significantly reducing maintenance, repair, and replacement expenses over time, especially in corrosive environments. Carbon steel rebar, while cheaper upfront, may lead to higher total costs from corrosion-induced damage, making stainless steel more cost-effective for long-term infrastructure projects.
Applications and Suitable Environments
Stainless steel rebar is highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for marine structures, bridges, and industrial facilities exposed to harsh chemicals and moisture. Carbon steel rebar, while more cost-effective, suits typical construction projects where exposure to corrosive elements is minimal or controlled. Choosing the appropriate rebar depends on environmental conditions such as chloride presence, humidity, and potential chemical exposure to ensure structural longevity.
Installation and Handling Considerations
Stainless steel rebar offers superior corrosion resistance, reducing the need for protective coatings during installation, while carbon steel rebar requires careful handling to prevent rust and may need epoxy coating or galvanization. The increased weight and flexibility of stainless steel rebar demand specialized cutting and bending tools, whereas carbon steel rebar is easier to manipulate but less durable in harsh environments. Proper storage and transportation are critical for both types to maintain material integrity and ensure structural longevity.
Maintenance and Long-Term Performance
Stainless steel rebar offers superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel rebar, significantly reducing maintenance needs and extending structural lifespan in harsh environments. Carbon steel rebar requires protective coatings and regular inspections to prevent rust and deterioration, increasing long-term maintenance costs. Investing in stainless steel rebar ensures enhanced durability and lower lifecycle expenses, particularly in marine, chemical, and high-moisture construction projects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Stainless steel rebar offers superior corrosion resistance, significantly reducing maintenance needs and extending the lifespan of concrete structures, which enhances sustainability by lowering resource consumption over time. Carbon steel rebar, although more cost-effective initially, is prone to rust, leading to concrete spalling and frequent repairs that increase environmental impact through additional material use and waste. Incorporating stainless steel rebar in infrastructure projects promotes durable construction with a smaller ecological footprint, aligning with green building standards and reducing long-term carbon emissions.
Stainless Steel Rebar vs Carbon Steel Rebar Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com