Steel radiators provide durability and excellent heat retention, making them ideal for maintaining consistent room warmth over time. Aluminum radiators heat up quickly and offer superior energy efficiency due to their lightweight and high thermal conductivity. Choosing between steel and aluminum radiators depends on priorities such as response time, heat retention, and budget.
Table of Comparison
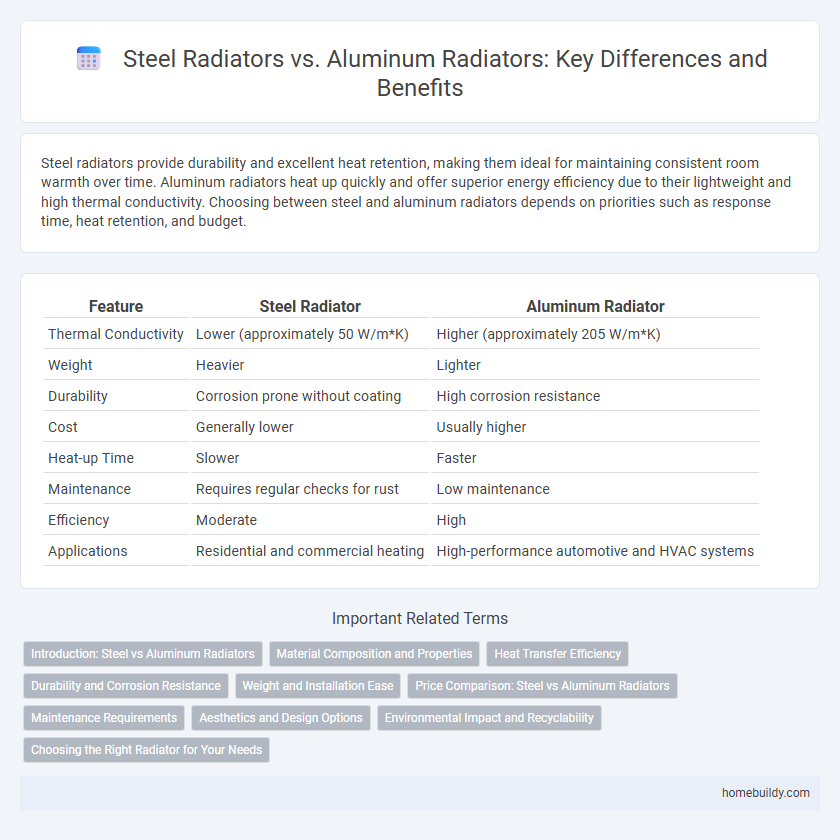
| Feature | Steel Radiator | Aluminum Radiator |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower (approximately 50 W/m*K) | Higher (approximately 205 W/m*K) |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Durability | Corrosion prone without coating | High corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower | Usually higher |
| Heat-up Time | Slower | Faster |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks for rust | Low maintenance |
| Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Residential and commercial heating | High-performance automotive and HVAC systems |
Introduction: Steel vs Aluminum Radiators
Steel radiators offer robust durability and high heat retention, making them ideal for sustained warmth in larger spaces. Aluminum radiators excel in rapid heat conduction and lightweight design, enabling faster room heating and easy installation. Choosing between steel and aluminum depends on specific heating needs, with steel favoring long-term heat retention and aluminum prioritizing efficient heat transfer.
Material Composition and Properties
Steel radiators offer high durability and excellent heat retention due to their dense material composition, making them ideal for long-lasting and consistent heating. Aluminum radiators feature superior thermal conductivity and lightweight properties, allowing for quicker heat response and easier installation. The choice depends on whether priority is given to efficiency and rapid heating or structural strength and heat retention.
Heat Transfer Efficiency
Steel radiators offer robust durability but have lower heat transfer efficiency compared to aluminum radiators due to steel's slower thermal conductivity. Aluminum radiators excel in quickly distributing heat throughout a space, leveraging aluminum's high thermal conductivity, which enhances energy efficiency and faster warming. The choice between steel and aluminum radiators significantly impacts heating performance and energy consumption in residential or commercial environments.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Steel radiators offer exceptional durability due to their robust construction and thicker material composition, making them highly resistant to dents and physical damage. Aluminum radiators excel in corrosion resistance thanks to their natural oxide layer, which prevents rust and extends lifespan in moist environments. While steel radiators may require protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, aluminum radiators provide superior longevity with minimal maintenance in corrosive conditions.
Weight and Installation Ease
Steel radiators generally weigh more than aluminum radiators, making them less ideal for installations where weight is a concern. Aluminum radiators offer superior ease of installation due to their lightweight properties, allowing for quicker mounting and reduced labor effort. The lighter weight of aluminum also makes these radiators more suitable for modern construction projects with structural limitations.
Price Comparison: Steel vs Aluminum Radiators
Steel radiators generally cost less upfront compared to aluminum radiators, making them a budget-friendly option for many homeowners. Aluminum radiators, while pricier, offer higher thermal conductivity and faster heat-up times, potentially reducing energy bills over time. The price difference reflects not only the material cost but also the manufacturing process and longevity, with steel being more affordable but aluminum providing better efficiency.
Maintenance Requirements
Steel radiators require regular inspection for rust and corrosion, as steel is prone to oxidation, demanding periodic repainting and flushing to maintain efficiency. Aluminum radiators offer lower maintenance needs due to their natural corrosion resistance and lightweight properties, often requiring only occasional cleaning and system checks. Choosing aluminum reduces the risk of leaks and prolongs radiator lifespan, making it a cost-effective option for long-term upkeep.
Aesthetics and Design Options
Steel radiators offer a sleek, minimalist design that easily fits into modern and industrial-style interiors, with customizable finishes and panel shapes enhancing visual appeal. Aluminum radiators stand out for their lightweight construction and contemporary aesthetic, often featuring slim profiles and vibrant color options that complement modern decor. Both materials provide diverse design flexibility, but aluminum typically allows for more intricate and innovative shapes due to its pliability and manufacturing process.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Steel radiators offer higher durability and a longer lifespan, reducing frequent replacements and overall environmental impact. Aluminum radiators excel in energy efficiency due to faster heat conduction and are highly recyclable, enabling a lower carbon footprint during production and disposal. Choosing aluminum supports circular economy principles, while steel provides robustness with moderate recyclability benefits.
Choosing the Right Radiator for Your Needs
Steel radiators offer excellent durability and heat retention, making them ideal for traditional home heating systems where consistent warmth is essential. Aluminum radiators heat up quickly and are lightweight, providing efficient heat transfer and energy savings suitable for contemporary, eco-friendly spaces. Selecting the right radiator depends on factors like heating speed, energy efficiency, installation requirements, and the aesthetic compatibility with your interior design.
Steel Radiator vs Aluminum Radiator Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com