PEX pipe offers superior flexibility and ease of installation compared to rigid CPVC pipe, reducing the need for fittings and allowing for quicker, more cost-effective plumbing projects. CPVC pipe, known for its high-temperature resistance and durability, performs well in hot water applications but can become brittle over time and is more prone to cracking. Both materials resist corrosion and chemical damage, but PEX pipe's ability to expand slightly makes it more resilient to freezing conditions, enhancing its longevity in colder climates.
Table of Comparison
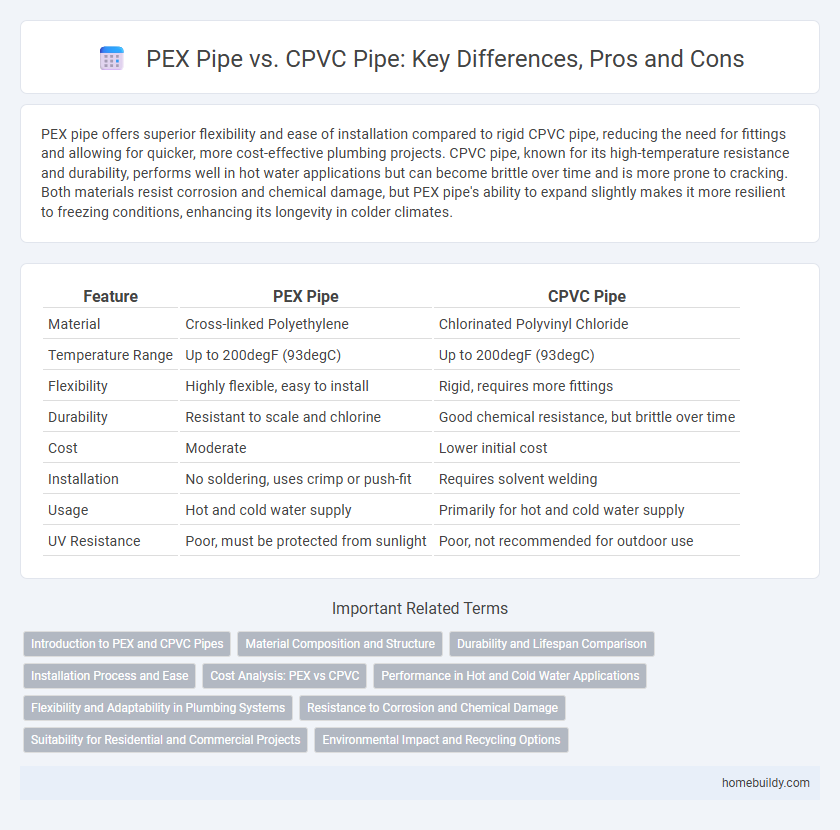
| Feature | PEX Pipe | CPVC Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Cross-linked Polyethylene | Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride |
| Temperature Range | Up to 200degF (93degC) | Up to 200degF (93degC) |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, easy to install | Rigid, requires more fittings |
| Durability | Resistant to scale and chlorine | Good chemical resistance, but brittle over time |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower initial cost |
| Installation | No soldering, uses crimp or push-fit | Requires solvent welding |
| Usage | Hot and cold water supply | Primarily for hot and cold water supply |
| UV Resistance | Poor, must be protected from sunlight | Poor, not recommended for outdoor use |
Introduction to PEX and CPVC Pipes
PEX pipe is a flexible, cross-linked polyethylene tubing known for its durability, resistance to scale and chlorine, and ease of installation in residential and commercial plumbing systems. CPVC pipe, or chlorinated polyvinyl chloride, offers high-temperature resistance and rigid structure, making it suitable for hot and cold water distribution in building plumbing. Both materials provide corrosion resistance and long service life but differ significantly in flexibility, installation methods, and temperature tolerances.
Material Composition and Structure
PEX pipe is made from cross-linked polyethylene, offering flexibility and resistance to corrosion, chemical damage, and temperature fluctuations. CPVC pipe consists of chlorinated polyvinyl chloride, providing a rigid structure with high heat tolerance and resistance to chlorine and chemical exposure. The molecular arrangement in PEX allows for bending without joints, while CPVC's thermoplastic structure requires fittings for connections but enhances structural rigidity.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
PEX pipes offer superior flexibility and resistance to corrosion, significantly extending their lifespan beyond 40 years in typical residential plumbing applications. CPVC pipes, while durable and resistant to high temperatures, generally have a lifespan of around 25 to 30 years and are more prone to cracking under extreme cold conditions. The durability of PEX makes it a preferred choice for long-term plumbing solutions, especially in environments prone to freezing temperatures.
Installation Process and Ease
PEX pipes offer a flexible design that simplifies installation by requiring fewer fittings and enabling quick connections with crimp or push-fit methods, reducing labor time and costs. CPVC pipes, being rigid, demand precise measuring, cutting, and solvent welding for joint assembly, which increases installation complexity and time. The ease of PEX installation is favored in remodeling or tight spaces, while CPVC is more common in new construction with straightforward layouts.
Cost Analysis: PEX vs CPVC
PEX pipe typically costs between $0.40 and $0.60 per foot, making it a more budget-friendly option compared to CPVC, which ranges from $0.50 to $1.00 per foot. Installation expenses for PEX are generally lower due to its flexibility and fewer fittings, reducing labor time and material costs. CPVC pipes require solvent welding, increasing labor costs and installation time, making PEX the more cost-effective choice overall for plumbing projects.
Performance in Hot and Cold Water Applications
PEX pipe offers superior flexibility and resistance to scale and chlorine, making it highly durable for both hot and cold water applications in residential plumbing. CPVC pipe withstands higher temperatures and maintains rigidity, providing reliable pressure resistance and chemical tolerance for hot water systems. Both materials perform well in cold water, but PEX's flexibility reduces the risk of bursting in freezing conditions.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Plumbing Systems
PEX pipe offers superior flexibility compared to CPVC pipe, allowing it to bend around corners and obstacles without the need for additional fittings, reducing installation time and potential leak points. Its adaptability enables use in a variety of plumbing systems, including hot and cold water distribution as well as radiant floor heating. CPVC pipe, while rigid and less flexible, maintains strength and resistance to higher temperatures, but requires joints and fittings for changes in direction, making PEX the preferred choice for dynamic plumbing layouts.
Resistance to Corrosion and Chemical Damage
PEX pipe demonstrates superior resistance to corrosion and chemical damage compared to CPVC pipe, as its cross-linked polyethylene composition withstands a wide range of chemicals and corrosive elements commonly found in plumbing systems. CPVC pipe, while resistant to many chemicals, can degrade over time when exposed to highly acidic or alkaline substances, leading to potential brittleness and cracking. This durability advantage makes PEX pipe a preferred choice for plumbing applications involving aggressive water chemistry or fluctuating temperatures.
Suitability for Residential and Commercial Projects
PEX pipe offers superior flexibility, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation, making it highly suitable for both residential and commercial plumbing projects, especially where complex layouts are involved. CPVC pipe provides excellent heat resistance and durability, ideal for hot water distribution in residential buildings but may require more labor-intensive installation in commercial settings. Choosing between PEX and CPVC depends on project size, budget constraints, and specific plumbing system requirements.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Options
PEX pipes have a lower environmental impact than CPVC pipes due to their energy-efficient manufacturing process and longer lifespan, which reduces replacement frequency. Unlike CPVC, which involves chlorine-based chemicals during production, PEX uses fewer harmful substances, making it less toxic for the environment. However, both PEX and CPVC present recycling challenges since they are thermoplastic materials that require specialized facilities, limiting widespread recycling options.
PEX pipe vs CPVC pipe Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com