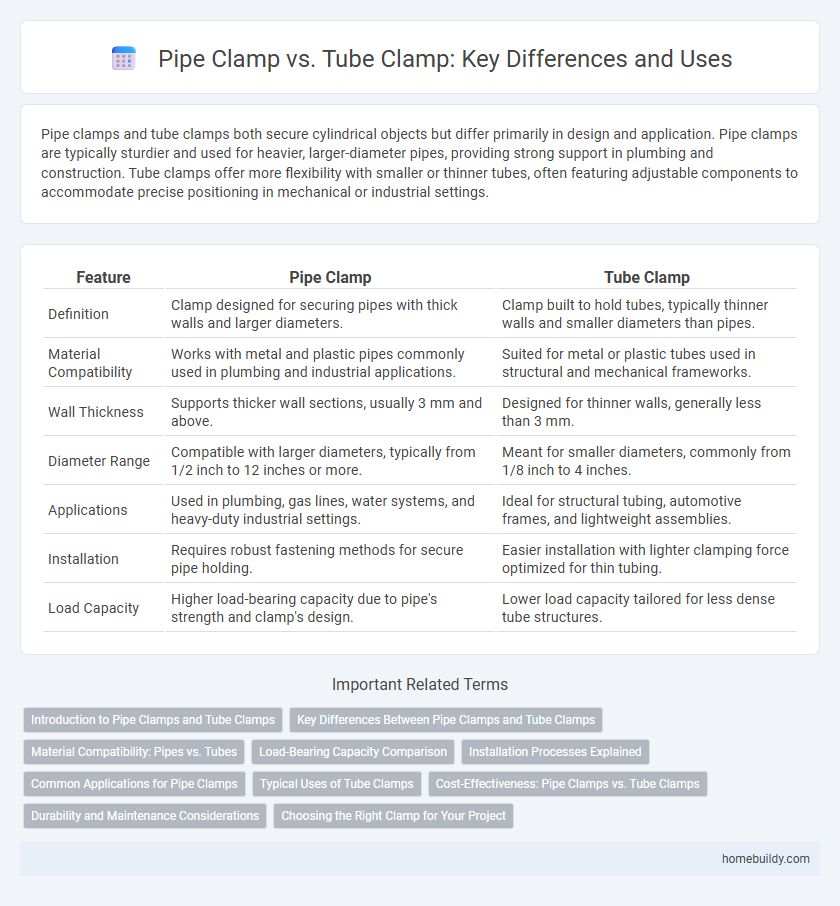
Pipe clamps and tube clamps both secure cylindrical objects but differ primarily in design and application. Pipe clamps are typically sturdier and used for heavier, larger-diameter pipes, providing strong support in plumbing and construction. Tube clamps offer more flexibility with smaller or thinner tubes, often featuring adjustable components to accommodate precise positioning in mechanical or industrial settings.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pipe Clamp | Tube Clamp |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clamp designed for securing pipes with thick walls and larger diameters. | Clamp built to hold tubes, typically thinner walls and smaller diameters than pipes. |
| Material Compatibility | Works with metal and plastic pipes commonly used in plumbing and industrial applications. | Suited for metal or plastic tubes used in structural and mechanical frameworks. |
| Wall Thickness | Supports thicker wall sections, usually 3 mm and above. | Designed for thinner walls, generally less than 3 mm. |
| Diameter Range | Compatible with larger diameters, typically from 1/2 inch to 12 inches or more. | Meant for smaller diameters, commonly from 1/8 inch to 4 inches. |
| Applications | Used in plumbing, gas lines, water systems, and heavy-duty industrial settings. | Ideal for structural tubing, automotive frames, and lightweight assemblies. |
| Installation | Requires robust fastening methods for secure pipe holding. | Easier installation with lighter clamping force optimized for thin tubing. |
| Load Capacity | Higher load-bearing capacity due to pipe's strength and clamp's design. | Lower load capacity tailored for less dense tube structures. |
Introduction to Pipe Clamps and Tube Clamps
Pipe clamps are designed to secure cylindrical pipes in plumbing, construction, and industrial applications, offering robust support for various pipe sizes and materials such as steel, copper, and PVC. Tube clamps, while similar in function, are typically used for smaller diameter tubes and provide precise alignment and stabilization in applications like automotive systems and laboratory setups. Both clamps enhance system integrity by preventing movement and vibration, but pipe clamps emphasize heavy-duty strength whereas tube clamps focus on lightweight and precision handling.
Key Differences Between Pipe Clamps and Tube Clamps
Pipe clamps are designed specifically for round pipes with standard diameters, providing a secure grip suitable for plumbing and industrial applications. Tube clamps accommodate various tube shapes and sizes, emphasizing versatility by offering customizable fittings for non-cylindrical tubing. The key differences lie in their shape compatibility, load capacity, and application scope, with pipe clamps favoring fixed pipe dimensions and tube clamps supporting diverse tubing materials and profiles.
Material Compatibility: Pipes vs. Tubes
Pipe clamps are typically designed to accommodate the thicker walls and larger diameters of pipes made from metals like steel, copper, and iron, ensuring secure support and durability. Tube clamps cater to thinner-walled tubes often fabricated from stainless steel, aluminum, or plastic, providing gentle yet firm grip to prevent deformation. Understanding the material compatibility and structural differences of pipes versus tubes is crucial in selecting the appropriate clamp for effective installation and longevity.
Load-Bearing Capacity Comparison
Pipe clamps generally offer higher load-bearing capacity compared to tube clamps due to their reinforced design and thicker materials, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Tube clamps, while versatile and easier to install, are typically better suited for lighter loads and less demanding environments. Selecting the appropriate clamp depends on the specific load requirements and structural demands of the piping or tubing system.
Installation Processes Explained
Pipe clamps install by securing pipes with a robust saddle design that distributes pressure evenly, minimizing damage to the pipe surface. Tube clamps, often featuring a narrower and lighter frame, are designed for quicker installation on thinner, more delicate tubing, enabling easier adjustments and repositioning. Both clamps use bolts or screws, but pipe clamps typically require heavier tools and more precise alignment due to the thicker pipe walls.
Common Applications for Pipe Clamps
Pipe clamps are primarily used in plumbing, construction, and industrial piping systems to secure pipes and prevent movement or vibration. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications involving large-diameter pipes carrying water, gas, or steam. Unlike tube clamps that accommodate smaller, lightweight tubing, pipe clamps offer robust support for metal or plastic pipes in infrastructure and mechanical installations.
Typical Uses of Tube Clamps
Tube clamps are primarily designed for lightweight structural applications such as temporary scaffolding, handrails, and display racks, where ease of assembly and adjustment are essential. Unlike pipe clamps, which secure round pipes for fluid transport, tube clamps accommodate a variety of tube shapes and sizes, making them ideal for modular frameworks and industrial furniture. Their versatility in construction and non-permanent installations highlights their typical use in both commercial and DIY projects.
Cost-Effectiveness: Pipe Clamps vs. Tube Clamps
Pipe clamps generally offer greater cost-effectiveness compared to tube clamps due to their simpler design and widespread availability, resulting in lower manufacturing and procurement costs. Pipe clamps are typically made from durable materials like galvanized steel, making them suitable for heavier loads at a lower price point than many tube clamps, which often require specialized materials or designs. Choosing pipe clamps can lead to significant savings in large-scale projects where budget constraints are critical without sacrificing essential support and stability.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Pipe clamps often feature robust materials such as stainless steel or heavy-duty carbon steel, offering superior durability in high-pressure and industrial environments compared to tube clamps, which are generally lighter and designed for lower-stress applications. Maintenance for pipe clamps typically involves routine inspections for corrosion and tightening due to their exposure to harsh conditions, whereas tube clamps require less frequent maintenance due to their use in less demanding settings. Choosing a pipe clamp ensures longer service life and reliability where durability and minimal maintenance are critical factors.
Choosing the Right Clamp for Your Project
Pipe clamps and tube clamps differ primarily in design and application, with pipe clamps being suited for nominal pipe sizes and heavier-duty tasks, while tube clamps are designed for precise tube dimensions and lighter structures. Selecting the right clamp depends on the material type, diameter, and the load requirements of the project, ensuring secure fastening and stability. For industrial or plumbing projects involving standard pipes, pipe clamps offer robust support, whereas tube clamps are ideal for furniture or lightweight framing using metal tubing.
Pipe clamp vs Tube clamp Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com