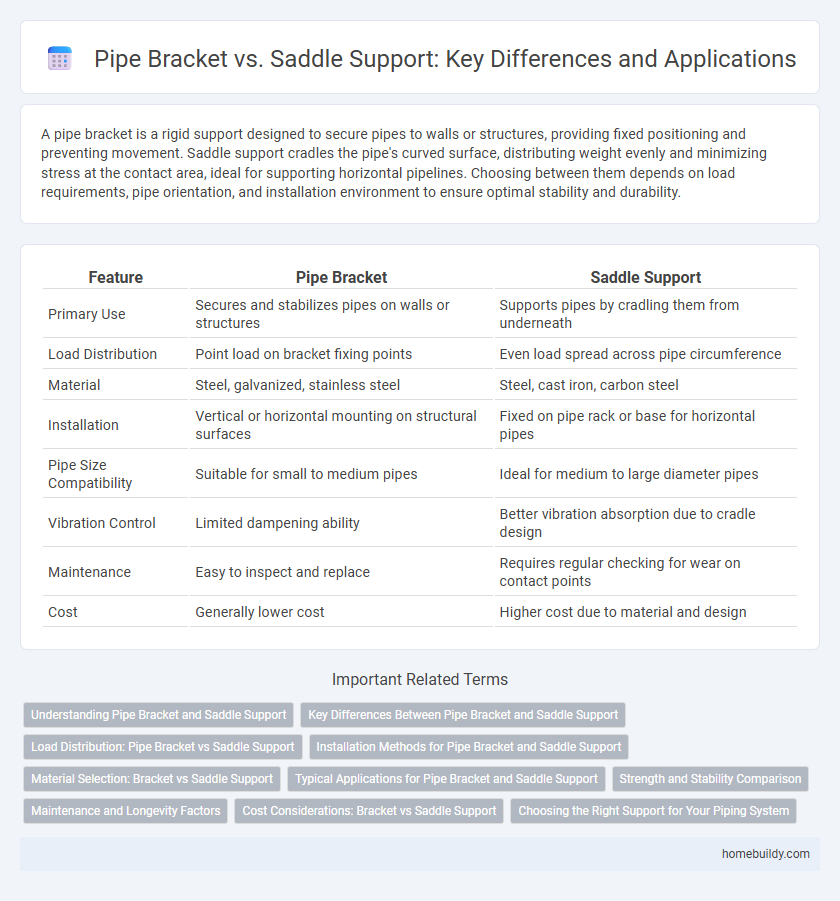
A pipe bracket is a rigid support designed to secure pipes to walls or structures, providing fixed positioning and preventing movement. Saddle support cradles the pipe's curved surface, distributing weight evenly and minimizing stress at the contact area, ideal for supporting horizontal pipelines. Choosing between them depends on load requirements, pipe orientation, and installation environment to ensure optimal stability and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pipe Bracket | Saddle Support |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Secures and stabilizes pipes on walls or structures | Supports pipes by cradling them from underneath |
| Load Distribution | Point load on bracket fixing points | Even load spread across pipe circumference |
| Material | Steel, galvanized, stainless steel | Steel, cast iron, carbon steel |
| Installation | Vertical or horizontal mounting on structural surfaces | Fixed on pipe rack or base for horizontal pipes |
| Pipe Size Compatibility | Suitable for small to medium pipes | Ideal for medium to large diameter pipes |
| Vibration Control | Limited dampening ability | Better vibration absorption due to cradle design |
| Maintenance | Easy to inspect and replace | Requires regular checking for wear on contact points |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to material and design |
Understanding Pipe Bracket and Saddle Support
Pipe brackets are rigid fixtures designed to hold pipes firmly in place, preventing axial and lateral movement, while saddle supports typically cradle pipes to distribute load evenly over a larger area, minimizing stress concentrations. Pipe brackets are ideal for applications requiring precise pipe positioning and stability, whereas saddle supports are favored for supporting heavy pipes over longer spans or elevated structures. Understanding the distinction between pipe brackets and saddle supports is crucial for selecting the appropriate support system based on load capacity, pipe size, and installation environment.
Key Differences Between Pipe Bracket and Saddle Support
Pipe brackets provide rigid support by clamping around the pipe, ensuring stability and reducing vibration, while saddle supports distribute the weight of the pipe evenly over a larger surface area, minimizing stress concentrations. Unlike pipe brackets, saddle supports are designed for horizontal or vertical pipes and are often used where thermal expansion occurs, accommodating movement without causing damage. Pipe brackets are typically easier to install and adjust, whereas saddle supports offer enhanced load distribution and protection for the pipe's exterior.
Load Distribution: Pipe Bracket vs Saddle Support
Pipe brackets provide localized support by clamping directly onto the pipe, resulting in concentrated load distribution at the contact points. Saddle supports, designed to cradle the pipe's curvature, distribute the load more evenly along a larger surface area, reducing stress concentrations. This difference in load distribution impacts pipe stability and material fatigue, with saddle supports generally offering superior performance for heavier or larger diameter pipes.
Installation Methods for Pipe Bracket and Saddle Support
Pipe brackets are typically installed by fastening directly to walls or structural beams using bolts or welds, providing rigid support with precise alignment for various pipe sizes. Saddle supports involve securing a curved base to a structure, cradling the pipe and distributing weight evenly, often requiring welding or bolted clamps for enhanced stability and load distribution. Installation of pipe brackets generally demands less surface contact, making them ideal for smaller pipes, while saddle supports are preferred for larger diameter pipes due to their superior load-bearing capacity and vibration dampening.
Material Selection: Bracket vs Saddle Support
Pipe brackets are typically made from carbon steel, stainless steel, or galvanized steel to provide robust support and resistance to environmental factors. Saddle supports often use similar materials but may incorporate cast iron or fabricated steel to allow better load distribution over the pipe's surface, minimizing stress concentration. Material selection depends on factors such as pipe size, weight, operating conditions, and required corrosion resistance for each support type.
Typical Applications for Pipe Bracket and Saddle Support
Pipe brackets are commonly used in vertical and horizontal pipe installations for securing and supporting piping systems in industrial, commercial, and residential settings. Saddle supports are typically applied in high-temperature and heavy-load pipelines, providing stable load distribution by cradling the pipe from below to prevent deformation. While pipe brackets excel in adjustable and easily accessible mounting solutions, saddle supports are preferred for maintaining pipe integrity in thermal expansion and contraction scenarios.
Strength and Stability Comparison
Pipe brackets provide superior strength and stability by firmly clamping pipes to structures, minimizing movement and vibration. Saddle supports cradle the pipe, distributing weight evenly and reducing stress concentrations, which enhances stability but offers less rigid restraint than pipe brackets. For applications requiring firm pipe alignment and load bearing, pipe brackets outperform saddle supports in maintaining structural integrity under dynamic conditions.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Pipe brackets require less frequent maintenance due to their simple design, which minimizes wear and tear on the pipe and support structure. Saddle supports distribute pipe load evenly, reducing stress points and extending the overall lifespan but may require periodic inspections to prevent corrosion or deformation. Choosing between pipe brackets and saddle supports depends on the maintenance capabilities and longevity needs of the piping system, with saddle supports often preferred for high-load or high-temperature applications.
Cost Considerations: Bracket vs Saddle Support
Pipe brackets generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to saddle supports due to their simpler design and reduced material requirements. Saddle supports involve greater fabrication complexity and higher installation costs, impacting the overall project budget. Selecting pipe brackets can optimize expenses for standard load conditions, while saddle supports, despite higher costs, provide superior stability for heavier or critical piping systems.
Choosing the Right Support for Your Piping System
Pipe brackets provide rigid support ideal for vertical or horizontal pipe runs subjected to moderate loads, ensuring secure attachment to structures and minimizing movement. Saddle supports distribute the load over a larger surface area, making them preferable for heavy or insulated pipes where stress concentration must be avoided. Selecting the right support depends on pipe size, load conditions, insulation requirements, and thermal expansion considerations to maintain system integrity and prevent mechanical failure.
Pipe bracket vs Saddle support Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com