Pipe brackets are designed to securely support pipes, providing stability and preventing movement in plumbing or piping systems. Conduit brackets specifically hold electrical conduits in place, ensuring proper alignment and safety for wiring installations. Choosing the right bracket depends on the application, as pipe brackets handle fluid-carrying pipes while conduit brackets organize and protect electrical cables.
Table of Comparison
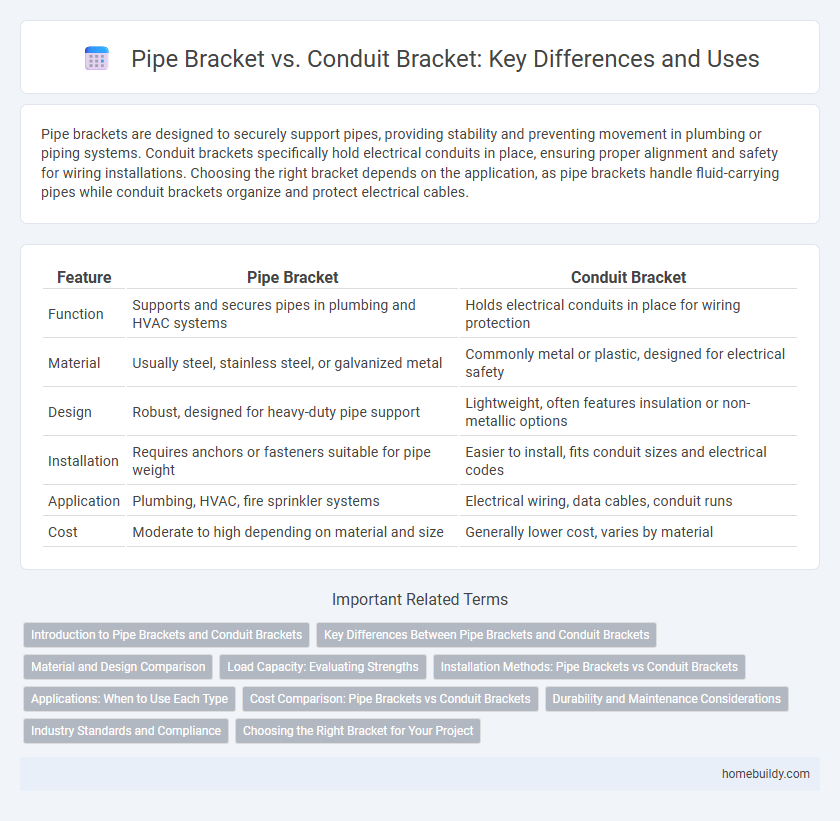
| Feature | Pipe Bracket | Conduit Bracket |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Supports and secures pipes in plumbing and HVAC systems | Holds electrical conduits in place for wiring protection |
| Material | Usually steel, stainless steel, or galvanized metal | Commonly metal or plastic, designed for electrical safety |
| Design | Robust, designed for heavy-duty pipe support | Lightweight, often features insulation or non-metallic options |
| Installation | Requires anchors or fasteners suitable for pipe weight | Easier to install, fits conduit sizes and electrical codes |
| Application | Plumbing, HVAC, fire sprinkler systems | Electrical wiring, data cables, conduit runs |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on material and size | Generally lower cost, varies by material |
Introduction to Pipe Brackets and Conduit Brackets
Pipe brackets are specialized supports designed to secure piping systems in place, ensuring stability and reducing stress on the pipes. Conduit brackets, while similar in function, are specifically engineered to hold electrical conduits, providing protection and organized routing for electrical wiring. Understanding the distinct applications and structural requirements of pipe brackets versus conduit brackets is essential for selecting the appropriate hardware in plumbing and electrical installations.
Key Differences Between Pipe Brackets and Conduit Brackets
Pipe brackets are designed primarily to support heavier, larger-diameter pipes in plumbing, HVAC, and industrial applications, while conduit brackets are tailored for securing electrical conduit with emphasis on protection and grounding. Pipe brackets typically feature robust materials like steel or cast iron to handle high loads and resist corrosion, whereas conduit brackets often include features for easy grounding and are made from lighter metals or plastic. The key differences lie in their load capacity, material composition, and specific use cases, making each bracket type optimized for its respective installation environment.
Material and Design Comparison
Pipe brackets are typically made from heavy-duty materials like stainless steel or galvanized steel to support high-pressure pipes, while conduit brackets often use lighter materials such as aluminum or plastic for electrical conduit protection. The design of pipe brackets emphasizes robust load-bearing capabilities with features like reinforced clamps and adjustable fittings, whereas conduit brackets focus on ease of installation and securing cables with clips or saddles. Material strength and structural design differences are critical in choosing between pipe brackets and conduit brackets based on their distinct functional requirements.
Load Capacity: Evaluating Strengths
Pipe brackets typically offer higher load capacity compared to conduit brackets, making them more suitable for supporting heavy pipes in industrial applications. The material composition and design of pipe brackets are engineered to withstand greater stress and weight, ensuring structural integrity in demanding environments. In contrast, conduit brackets are optimized for lighter loads, mainly supporting electrical conduits and not designed for heavy mechanical stress.
Installation Methods: Pipe Brackets vs Conduit Brackets
Pipe brackets are typically installed using clamps or U-bolts that secure the pipe directly to walls or ceilings, offering strong support for heavy-duty plumbing systems. Conduit brackets, designed for electrical conduits, often feature snap-on or strap mechanisms for quick attachment without the need for additional tools, facilitating faster and more flexible installations. The choice between pipe brackets and conduit brackets depends on load requirements and ease of installation, with pipe brackets favored for durability and conduit brackets optimized for speed and convenience.
Applications: When to Use Each Type
Pipe brackets are ideal for supporting heavy-duty industrial piping systems, ensuring stability in high-pressure environments like oil refineries and chemical plants. Conduit brackets are better suited for electrical conduit installations, offering protection and organization for wiring in commercial and residential buildings. Use pipe brackets when mechanical strength and load-bearing capacity are critical, while conduit brackets are preferred for electrical infrastructure requiring secure conduit routing and minimal vibration.
Cost Comparison: Pipe Brackets vs Conduit Brackets
Pipe brackets generally cost less than conduit brackets due to simpler design and common material usage like steel or aluminum. Conduit brackets often require specialized coatings or materials to comply with electrical safety standards, increasing their price. Choosing pipe brackets can reduce installation expenses, especially in non-electrical applications where durability is the priority.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Pipe brackets typically offer greater durability due to their robust metal construction, which resists corrosion and heavy loads better than most conduit brackets made from lighter materials like plastic or aluminum. Maintenance requirements for pipe brackets are generally lower, as their sturdier design prevents frequent replacements and reduces vulnerability to environmental wear. In contrast, conduit brackets may require more regular inspections and maintenance to address potential material fatigue and damage in harsher conditions.
Industry Standards and Compliance
Pipe brackets and conduit brackets must adhere to distinct industry standards to ensure optimal performance and safety; pipe brackets typically comply with ANSI B31.1 and ASME B36.10 for pressure piping systems, while conduit brackets follow NEC (National Electrical Code) guidelines for electrical installations. Material specifications and load rating requirements differ significantly as pipe brackets are designed to support heavier mechanical loads under varying environmental conditions, whereas conduit brackets are engineered for electrical conduit support with emphasis on grounding and insulation compliance. Selecting the correct bracket type based on these compliance factors is crucial in industrial applications to meet regulatory standards and maintain system integrity.
Choosing the Right Bracket for Your Project
Pipe brackets provide robust support for plumbing systems by securely holding pipes in place, while conduit brackets are specifically designed to protect electrical conduits from damage and maintain secure wiring routes. Choosing the right bracket involves considering factors such as the material type, load capacity, and environmental conditions to ensure durability and safety in your project. Correct selection enhances structural integrity and prevents future maintenance issues, making it essential to match the bracket to the specific application requirements.
pipe bracket vs conduit bracket Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com