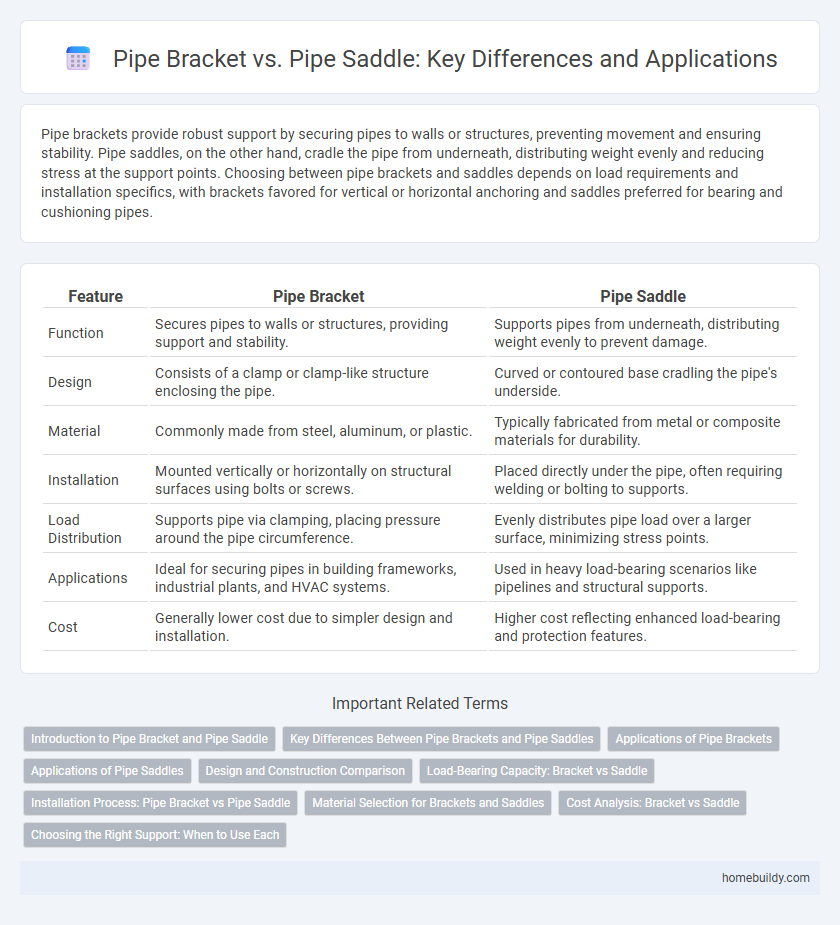
Pipe brackets provide robust support by securing pipes to walls or structures, preventing movement and ensuring stability. Pipe saddles, on the other hand, cradle the pipe from underneath, distributing weight evenly and reducing stress at the support points. Choosing between pipe brackets and saddles depends on load requirements and installation specifics, with brackets favored for vertical or horizontal anchoring and saddles preferred for bearing and cushioning pipes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pipe Bracket | Pipe Saddle |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Secures pipes to walls or structures, providing support and stability. | Supports pipes from underneath, distributing weight evenly to prevent damage. |
| Design | Consists of a clamp or clamp-like structure enclosing the pipe. | Curved or contoured base cradling the pipe's underside. |
| Material | Commonly made from steel, aluminum, or plastic. | Typically fabricated from metal or composite materials for durability. |
| Installation | Mounted vertically or horizontally on structural surfaces using bolts or screws. | Placed directly under the pipe, often requiring welding or bolting to supports. |
| Load Distribution | Supports pipe via clamping, placing pressure around the pipe circumference. | Evenly distributes pipe load over a larger surface, minimizing stress points. |
| Applications | Ideal for securing pipes in building frameworks, industrial plants, and HVAC systems. | Used in heavy load-bearing scenarios like pipelines and structural supports. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to simpler design and installation. | Higher cost reflecting enhanced load-bearing and protection features. |
Introduction to Pipe Bracket and Pipe Saddle
Pipe brackets and pipe saddles serve critical roles in piping systems by providing support and stability. Pipe brackets are metal supports designed to secure pipes to walls or structures, ensuring alignment and preventing movement. In contrast, pipe saddles cradle the pipe's circumference, distributing weight evenly and reducing stress points, which is essential for maintaining pipe integrity in load-bearing applications.
Key Differences Between Pipe Brackets and Pipe Saddles
Pipe brackets provide rigid support by securing pipes to walls or structures, offering vertical and lateral stability, whereas pipe saddles distribute the pipe's load over a larger surface area to prevent deformation or damage. Pipe brackets typically use clamps or straps for attachment, ideal for alignment and fixed positioning, while pipe saddles use contoured surfaces or padding to cradle the pipe, reducing stress at support points. Material choices for brackets often emphasize strength and durability, such as steel or galvanized metal, while saddles may incorporate cushioning materials like rubber to protect piping from mechanical wear.
Applications of Pipe Brackets
Pipe brackets are primarily used to support pipes, securing them to walls, ceilings, or structural frameworks in various industrial and residential applications. They provide easy access for inspection and maintenance, making them ideal for plumbing, HVAC, and fire protection systems. Unlike pipe saddles, pipe brackets allow for adjustable positioning and flexibility in alignment, accommodating different pipe sizes and load requirements.
Applications of Pipe Saddles
Pipe saddles provide structural support for pipelines under heavy loads or thermal expansion, commonly used in industrial settings like oil refineries and chemical plants. They are ideal for distributing stress evenly around the pipe circumference, preventing deformation and reducing wear. Compared to pipe brackets, pipe saddles excel in applications requiring enhanced load-bearing capacity and protection against mechanical damage.
Design and Construction Comparison
Pipe brackets feature a rigid, typically metal design that secures pipes to walls or ceilings, offering strong lateral support and ease of installation. Pipe saddles conform closely to the pipe's curve, distributing load evenly and reducing stress points, making them ideal for heavy or large-diameter pipes. Construction materials for pipe brackets often include steel or aluminum, while pipe saddles may incorporate cushioning materials to prevent pipe damage and vibration.
Load-Bearing Capacity: Bracket vs Saddle
Pipe brackets provide superior load-bearing capacity compared to pipe saddles due to their robust design that distributes weight evenly along the pipe's length, minimizing stress points. Unlike pipe saddles that primarily support pipes at discrete points, brackets offer continuous support, enhancing stability in heavy-duty applications. This makes pipe brackets ideal for high-load scenarios requiring maximum structural integrity and durability.
Installation Process: Pipe Bracket vs Pipe Saddle
The installation process for pipe brackets typically involves securing the bracket directly to a wall or structure using bolts or screws, allowing for adjustable positioning and easy access for maintenance. In contrast, pipe saddles require a clamping mechanism that cradles the pipe, often necessitating precise alignment and possible welding or bolting to ensure stability and load distribution. Pipe brackets offer simpler and faster installation, while pipe saddles provide enhanced pipe support, especially for heavier or larger diameter pipelines.
Material Selection for Brackets and Saddles
Pipe brackets are commonly made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or galvanized steel, chosen for their strength and corrosion resistance to securely support piping systems. Pipe saddles, often fabricated from similar metals or composite materials, require careful selection based on load distribution and thermal expansion properties to prevent damage to the pipe surface. Material choice for both brackets and saddles must consider environmental conditions, mechanical stress, and compatibility with the pipe material to ensure longevity and structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Bracket vs Saddle
Pipe brackets generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to pipe saddles, especially for long-span applications where fewer supports are needed, reducing material and installation expenses. Pipe saddles typically involve higher manufacturing costs due to their contoured design that provides enhanced load distribution and pipe protection. Selecting pipe brackets versus saddles depends on the project budget, load requirements, and long-term maintenance considerations, with brackets favored for budget-conscious installations and saddles preferred for high-stress or critical pipeline supports.
Choosing the Right Support: When to Use Each
Pipe brackets provide rigid support and secure pipes in place, ideal for maintaining alignment in vertical or horizontal runs with minimal movement. Pipe saddles distribute the pipe's weight over a larger area, reducing stress and preventing deformation in larger or heavier pipes, especially in horizontal applications. Selecting between a pipe bracket and pipe saddle depends on pipe size, load requirements, and the need for flexibility versus stability in the support system.
pipe bracket vs pipe saddle Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com